Spring源码分析七:JdbcTemplate连接数据库原理
文章目录
- (一)Spring连接数据库程序
-
- 1、创建数据库表
- 2、创建实体PO
- 3、创建mapper映射
- 4、创建业务接口
- 5、创建业务接口实现类
- 6、Spring配置文件
- 7、测试类
- (二)JdbcTemplate核心原理
-
- 1、update方法(执行DML语句)
- 2、execute底层方法(底层核心,DDL)
-
- (1)获取数据库连接
- (2)用户查询参数设置
- (3)执行回调方法
- (4)告警处理
- (5)资源释放
- 3、query方法(执行DQL语句)
- (三)总结
(一)Spring连接数据库程序
1、创建数据库表
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`number` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '学号',
`name` varchar(5) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
`major` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '专业',
PRIMARY KEY (`number`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=20180104 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='学生信息表'
2、创建实体PO
public class Student {
private Integer number;
private String name;
private String major;
//省略set和get方法以及构造函数
}
3、创建mapper映射
public class StudentMapper implements RowMapper {
@Override
public Object mapRow(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
return new Student(resultSet.getInt("number"),
resultSet.getString("name"),
resultSet.getString("major"));
}
}
4、创建业务接口
public interface StudentService {
void save(Student student);
List<Student> getStudents();
}
5、创建业务接口实现类
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource){
this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
@Override
public void save(Student student) {
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into student (name,major) values(?,?)",new Object[]{
student.getName(),student.getMajor()
});
}
@Override
public List<Student> getStudents() {
return jdbcTemplate.query("select * from student", new StudentMapper());
}
}
6、Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" default-autowire="byName">
<!-- 配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
<property name="maxIdle" value="30" />
<property name="defaultAutoCommit" value="true" />
<property name="removeAbandonedTimeout" value="60" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置业务bean-->
<bean id="studentService" class="com.spring.service.StudentServiceImpl">
<!--注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
</beans>
7、测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("config/applicationContext.xml");
StudentService studentService = applicationContext.getBean("studentService", StudentServiceImpl.class);
Student student = new Student("李四","物联网工程");
studentService.save(student);//保存方法
List<Student> students = studentService.getStudents();//查询方法
System.out.println(students);
}
输出结果如下:
[Student{number=20180101, name='杜子腾', major='软件学院'},
Student{number=20180102, name='范统', major='计算机科学与工程'},
Student{number=20180103, name='史珍香', major='计算机科学与工程'},
Student{number=20180104, name='张三', major='计算机科学与技术'},
Student{number=20180105, name='李四', major='物联网工程'}]
(二)JdbcTemplate核心原理
基于上述的Spring连接数据库操作中save->update,getStudents->query方法作为分析切入点,关于jdbcTemplate的赋值,示例中使用setDataSource方法初始化值,结合配置文件中bean的定义进行注入,本次分析的重点为update/query方法。
归类:
- update(XXX)类型的方法主要是执行DML语句(数据操作语言)即增、删、查、改(CRUD);
- query(XXX)类型的方法主要是执行DQL语句(数据查询语言)即SELECT语句;
- 底层execute方法是被update(XXX)和query(XXX所依赖,所以同样支持DML和DQL语句,但它本身主要是用于执行DDL语句(数据定义语言)即CREATE、DROP、ALTER等语句。
1、update方法(执行DML语句)
JdbcTemplate类中执行内部方法update,封装暴露给外部调用的接口主要是为了封装参数,为进一步执行SQL做足准备工作,使用ArgumentPreparedStatementSetter或newArgTypePreparedStatementSetter进行内部封装,然后再一步使用SimplePreparedStatementCreator封装,最后统一委托给内部update,底层执行是由execute执行SQL并将结果返回到updateCount方法并验证结果返回。
update整体流程如下:
- 暴露外部接口update,封装newArgPreparedStatementSetter或newArgTypePreparedStatementSetter;
- 二次使用update重载方法进行封装SimplePreparedStatementCreator;
- JdbcTemplate委托给内部update,交由execute通用方法执行SQL;
- 底层execute包含获取数据库连接、SQL预编译、查询条件限制、参数替换、回调方法执行SQL、处理告警等(下面介绍底层execute方法)。
//重载外部暴露update方法1封装newArgPreparedStatementSetter
public int update(String sql, @Nullable Object... args) throws DataAccessException {
return update(sql, newArgPreparedStatementSetter(args));
}
//重载外部暴露update方法2封装newArgTypePreparedStatementSetter
public int update(String sql, Object[] args, int[] argTypes) throws DataAccessException {
return update(sql, newArgTypePreparedStatementSetter(args, argTypes));
}
//JdbcTemplate封装SimplePreparedStatementCreator对象,也可暴露
public int update(String sql, @Nullable PreparedStatementSetter pss) throws DataAccessException {
return update(new SimplePreparedStatementCreator(sql), pss);//调用内部update方法
}
//JdbcTemplate内部执行方法,execute执行SQL、updateCount结果验证
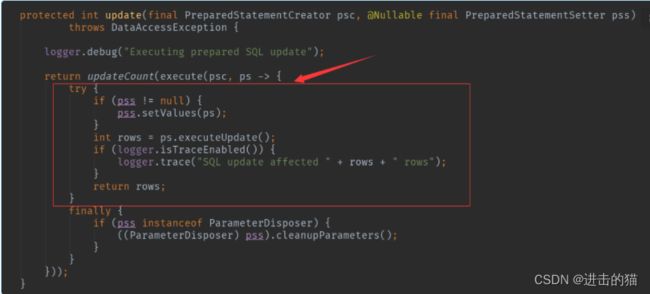
protected int update(final PreparedStatementCreator psc, @Nullable final PreparedStatementSetter pss)
throws DataAccessException {
/**
* execute处理SQL、查询结果、告警等
* updateCount负责校验结果
*/
return updateCount(execute(psc, ps -> {
try {
if (pss != null) {
pss.setValues(ps);//设置参数值包含参数?替换、value值设置等
}
int rows = ps.executeUpdate();//执行SQL语句
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("SQL update affected " + rows + " rows");
}
return rows;
}
finally {
if (pss instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
((ParameterDisposer) pss).cleanupParameters();
}
}
}));
}
2、execute底层方法(底层核心,DDL)
JdbcTemplate中的update、query等方法都是内部调用底层execute通用方法来执行SQL,可以执行DDL语句、DDM语句和DQL语句,直接使用则通常用于DDL语句,。
execute底层方法核心步骤:
- 获取数据库连接;
- 设置查询性能条件如一次查询多少数据、查询超时时间等;
- 执行内部update、query中的lamda回调方法;
- 处理告警;
- 释放资源。
public <T> T execute(PreparedStatementCreator psc, PreparedStatementCallback<T> action)
throws DataAccessException {
//验证psc和action回调方法不为空
Assert.notNull(psc, "PreparedStatementCreator must not be null");
Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");
//是否开启debugger级别的日志输出
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String sql = getSql(psc);
logger.debug("Executing prepared SQL statement" + (sql != null ? " [" + sql + "]" : ""));
}
//获取数据库连接(1)
Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(obtainDataSource());
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//创建预编译PreparedStatement类型的SQL对象
ps = psc.createPreparedStatement(con);
//设置查询性能条件如一次查询多少数据、查询超时时间等(2)
applyStatementSettings(ps);
//执行内部update、query中的lamda回调方法(3)
T result = action.doInPreparedStatement(ps);
//处理告警(4)
handleWarnings(ps);
return result;
}catch (SQLException ex) {
// 释放连接,避免数据库连接死锁
// 异常时清楚参数
if (psc instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
((ParameterDisposer) psc).cleanupParameters();
}
//关闭连接流
String sql = getSql(psc);
psc = null;
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(ps);
ps = null;
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
con = null;
throw translateException("PreparedStatementCallback", sql, ex);
}finally {
//执行结束时释放内存中的流(5)
if (psc instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
((ParameterDisposer) psc).cleanupParameters();
}
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(ps);
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
}
}
(1)获取数据库连接
获取连接核心步骤:
- (1)事务同步器中是否已存在数据库连接;存在则直接返回且连接数共用referenceCount自增;
- (2)fetchConnection方法从数据源中获取新的数据库连接;
- (3)是否开启事务同步支持,事务中要使用同一连接且引用referenceCount自增;
- (4)事务注册到事务同步器中;
- (5)异常时主动连接引用referenceCount自减。
public static Connection getConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws CannotGetJdbcConnectionException {
try {
//spring常规风格,干活的永远是doXXXX
return doGetConnection(dataSource);
}catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new CannotGetJdbcConnectionException("Failed to obtain JDBC Connection", ex);
}catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new CannotGetJdbcConnectionException("Failed to obtain JDBC Connection: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 获取连接整体思路
* (1)事务同步器中是否已存在数据库连接;存在则直接返回且连接数共用referenceCount自增;
* (2)fetchConnection方法从数据源中获取新的数据库连接;
* (3)是否开启事务同步支持,事务中要使用同一连接且引用referenceCount自增;
* (4)事务注册到事务同步器中;
* (5)异常时主动连接引用referenceCount自减;
*/
public static Connection doGetConnection(DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified");//数据源不为空验证
//获取线程是否已拥有数据库连接
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
if (conHolder != null && (conHolder.hasConnection() || conHolder.isSynchronizedWithTransaction())) {
conHolder.requested();//连接数+1,采用共用连接数,避免大量的销毁和创建连接
if (!conHolder.hasConnection()) {
conHolder.setConnection(fetchConnection(dataSource));
}
return conHolder.getConnection();//返回连接
}
// 当前线程无数据库连接时开始着手创建连接
Connection con = fetchConnection(dataSource);
// 当前线程是否支持事务同步
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
try {
// 在事务中使用同一个数据库连接
ConnectionHolder holderToUse = conHolder;
//conHolder连接为空,则说明TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource)不存在数据库连接
if (holderToUse == null) {
//使用fetchConnection获取的数据库连接作为事务中的同一连接
holderToUse = new ConnectionHolder(con);
}else {
holderToUse.setConnection(con);
}
//同一数据库连接+1
holderToUse.requested();
//将事务注册到synchronizations变量(ThreadLocal>)中
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(
new ConnectionSynchronization(holderToUse, dataSource));
holderToUse.setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);//开启事务同步
if (holderToUse != conHolder) {
//绑定事务
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(dataSource, holderToUse);
}
}catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// 程序异常时需要主动释放
releaseConnection(con, dataSource);
throw ex;
}
}
return con;
}
(2)用户查询参数设置
SQL执行的额外参数:
- (1)设置ResultSet返回数量;
- (2)设置ResultSet最大数量;
- (3)设置SQL执行的超时时间。
protected void applyStatementSettings(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
//获取用户设置的一次向数据库执行时的ResultSet数量,减少迭代ResultSet时多次访问数据库而设计,与分页查询数量无关
int fetchSize = getFetchSize();
if (fetchSize != -1) {
stmt.setFetchSize(fetchSize);
}
// 获取ResultSet数量的最大值
int maxRows = getMaxRows();
if (maxRows != -1) {
stmt.setMaxRows(maxRows);
}
//设置SQL执行的超时时间
DataSourceUtils.applyTimeout(stmt, getDataSource(), getQueryTimeout());
}
(3)执行回调方法
底层execute通用方法中的回调方法doInPreparedStatement,主要是依赖上层调用者中设置的lamda表达式,如update、query中的所示:
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
if (this.args != null) {
//参数遍历
for (int i = 0; i < this.args.length; i++) {
Object arg = this.args[i];
doSetValue(ps, i + 1, arg);//单个参数类型匹配和参数值设置
}
}
}
//参数类型匹配
protected void doSetValue(PreparedStatement ps, int parameterPosition, Object argValue) throws SQLException {
if (argValue instanceof SqlParameterValue) {
SqlParameterValue paramValue = (SqlParameterValue) argValue;
StatementCreatorUtils.setParameterValue(ps, parameterPosition, paramValue, paramValue.getValue());
} else {
StatementCreatorUtils.setParameterValue(ps, parameterPosition, SqlTypeValue.TYPE_UNKNOWN, argValue);
}
}
//参数设置值
public static void setParameterValue(PreparedStatement ps, int paramIndex, SqlParameter param,
@Nullable Object inValue) throws SQLException {
setParameterValueInternal(ps, paramIndex, param.getSqlType(), param.getTypeName(), param.getScale(), inValue);
}
//实际参数值的替换的方法
private static void setParameterValueInternal(PreparedStatement ps, int paramIndex, int sqlType,
@Nullable String typeName, @Nullable Integer scale, @Nullable Object inValue) throws SQLException {
String typeNameToUse = typeName;
int sqlTypeToUse = sqlType;
Object inValueToUse = inValue;
// 对SqlParameterValue类型的进行单独处理,获取SqlType、TypeName和value
if (inValue instanceof SqlParameterValue) {
SqlParameterValue parameterValue = (SqlParameterValue) inValue;
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding type info with runtime info from SqlParameterValue: column index " + paramIndex +
", SQL type " + parameterValue.getSqlType() + ", type name " + parameterValue.getTypeName());
}
if (parameterValue.getSqlType() != SqlTypeValue.TYPE_UNKNOWN) {
sqlTypeToUse = parameterValue.getSqlType();
}
if (parameterValue.getTypeName() != null) {
typeNameToUse = parameterValue.getTypeName();
}
inValueToUse = parameterValue.getValue();
}
//日志跟踪
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Setting SQL statement parameter value: column index " + paramIndex +
", parameter value [" + inValueToUse +
"], value class [" + (inValueToUse != null ? inValueToUse.getClass().getName() : "null") +
"], SQL type " + (sqlTypeToUse == SqlTypeValue.TYPE_UNKNOWN ? "unknown" : Integer.toString(sqlTypeToUse)));
}
//设置值
if (inValueToUse == null) {
setNull(ps, paramIndex, sqlTypeToUse, typeNameToUse);
} else {
setValue(ps, paramIndex, sqlTypeToUse, typeNameToUse, scale, inValueToUse);
}
}
(4)告警处理
SQLWarning主要是用于访问数据库时出现的警告异常,这些告警的信息可以从Connection、Statement和ResultSet对象中获取,如在关闭的连接上或结果集中获取警告将会抛出异常,用户主要是可以设置处理告警的两种方式:一种是默认忽略警告,只打印警告;另一种则是直接抛出异常也就是代码中的else分支代码逻辑。
protected void handleWarnings(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
//是否忽略告警信息
if (isIgnoreWarnings()) {
//是否开启日志打印
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
SQLWarning warningToLog = stmt.getWarnings();//常见的异常时DataTruncation
while (warningToLog != null) {
logger.debug("SQLWarning ignored: SQL state '" + warningToLog.getSQLState() + "', error code '" +
warningToLog.getErrorCode() + "', message [" + warningToLog.getMessage() + "]");
warningToLog = warningToLog.getNextWarning();
}
}
}else {
//抛出异常
handleWarnings(stmt.getWarnings());
}
}
(5)资源释放
释放资源步骤:
- (1)releaseConnection概念性封装,用于給上层统一调用;
- (2)doReleaseConnection用于对事务同步器中的共用连接自减,并不是真正意义上的释放;
- (3)doCloseConnection用于关闭连接。
//releaseConnection概念性封装,用于給上层统一调用
public static void releaseConnection(@Nullable Connection con, @Nullable DataSource dataSource) {
try {
doReleaseConnection(con, dataSource);
} catch (SQLException ex) {
logger.debug("Could not close JDBC Connection", ex);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.debug("Unexpected exception on closing JDBC Connection", ex);
}
}
public static void doReleaseConnection(@Nullable Connection con, @Nullable DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
if (con == null) {
return;
}
if (dataSource != null) {
ConnectionHolder conHolder = (ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(dataSource);
//当前线程存在事务时说明存在共用数据库连接直接使用ConnectionHolder中的released方法进行连接数自减,而不是真正释放连接
if (conHolder != null && connectionEquals(conHolder, con)) {
// 事务中的连接引用自减
conHolder.released();
return;
}
}
doCloseConnection(con, dataSource);
}
//关闭连接
public static void doCloseConnection(Connection con, @Nullable DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
if (!(dataSource instanceof SmartDataSource) || ((SmartDataSource) dataSource).shouldClose(con)) {
con.close();
}
}
3、query方法(执行DQL语句)
query方法与update类似,原理大体相同,不再进行详细分析。
public <T> List<T> query(String sql, RowMapper<T> rowMapper) throws DataAccessException {
// 查询器的封装RowMapperResultSetExtractor
return result(query(sql, new RowMapperResultSetExtractor<>(rowMapper)));
}
public <T> T query(final String sql, final ResultSetExtractor<T> rse) throws DataAccessException {
//SQL和rse不为空验证
Assert.notNull(sql, "SQL must not be null");
Assert.notNull(rse, "ResultSetExtractor must not be null");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Executing SQL query [" + sql + "]");
}
/**
* 回调doInStatement方法与update中的回调类似
*/
class QueryStatementCallback implements StatementCallback<T>, SqlProvider {
@Override
@Nullable
public T doInStatement(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);//执行SQL查询
return rse.extractData(rs);
} finally {
JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(rs);
}
}
@Override
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
}
// 传入通用底层execute方法进行操作数据库
return execute(new QueryStatementCallback());
}
(三)总结
JdbcTmeplate原理总结:
- update、query、queryForObject、batchUpdate等方法都是依赖于execute底层核心方法;
- execute底层核心步骤分为:
- (1)获取数据库连接;
- (2)设置查询性能条件如一次查询多少数据、查询超时时间等;
- (3)执行内部update、query中的lamda回调方法;
- (4)处理告警;
- (5)释放资源。