- C++11堆操作深度解析:std::is_heap与std::is_heap_until原理解析与实践
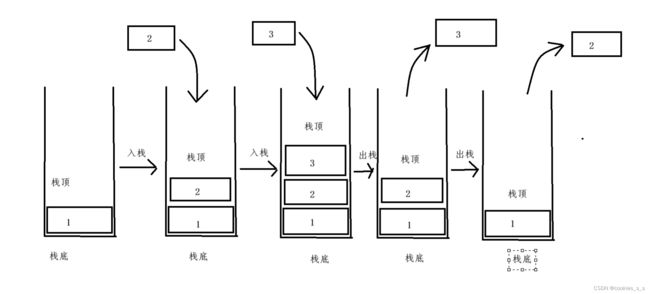
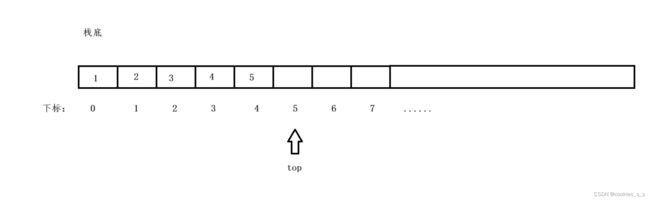
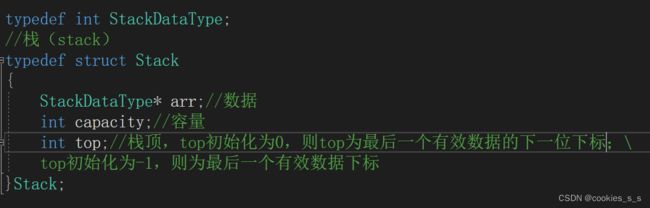
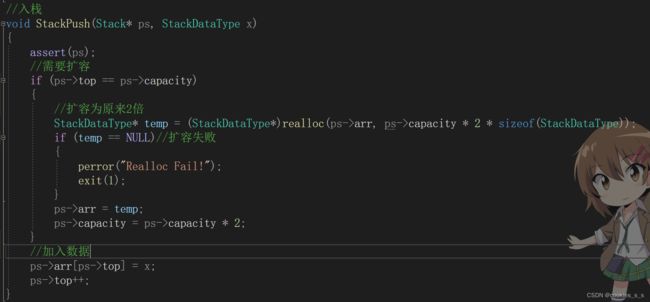
文章目录堆结构基础与函数接口堆的核心性质函数签名与核心接口std::is_heapstd::is_heap_until实现原理深度剖析std::is_heap的验证逻辑std::is_heap_until的定位策略算法优化细节代码实践与案例分析基础用法演示自定义比较器实现最小堆检查边缘情况处理性能分析与实际应用时间复杂度对比典型应用场景与手动实现的对比注意事项与最佳实践迭代器要求比较器设计C++标
- C++ 11 Lambda表达式和min_element()与max_element()的使用_c++ lamda函数 min_element((1)
2401_84976182
程序员c语言c++学习
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上CC++开发知识点,真正体系化!由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新如果你需要这些资料,可以戳这里获取#include#include#includeusingnamespacestd;boolcmp(int
- C++ 11 Lambda表达式和min_element()与max_element()的使用_c++ lamda函数 min_element(
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加戳这里获取一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!intmain(){vectormyvec{3,
- 冒泡、选择、插入排序:三大基础排序算法深度解析(C语言实现)
xienda
算法排序算法数据结构
在算法学习道路上,排序算法是每位程序员必须掌握的基石。本文将深入解析冒泡排序、选择排序和插入排序这三种基础排序算法,通过C语言代码实现和对比分析,帮助读者彻底理解它们的差异与应用场景。算法原理与代码实现1.冒泡排序(BubbleSort)工作原理:通过重复比较相邻元素,将较大元素逐步"冒泡"到数组末尾。voidbubbleSort(intarr[],intn){ for(inti=0;iarr[
- Leetcode 148. 排序链表
文章目录前引题目代码(首刷看题解)代码(8.9二刷部分看解析)代码(9.15三刷部分看解析)前引综合性比较强的一道题,要求时间复杂度必须O(logn)才能通过,最适合链表的排序算法就是归并。这里采用自顶向下的方法步骤:找到链表中点(双指针)对两个子链表排序(递归,直到只有一个结点,记得将子链表最后指向nullptr)归并(引入dummy结点)题目Leetcode148.排序链表代码(首刷看题解)c
- 全面触摸屏输入法设计与实现
长野君
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:触摸屏输入法是针对触摸设备优化的文字输入方案,包括虚拟键盘、手写、语音识别和手势等多种输入方式。本方案通过提供主程序文件、用户手册、界面截图、示例图、说明文本和音效文件,旨在为用户提供一个完整的、多样的文字输入体验。开发者通过持续优化算法和用户界面,使用户在无物理键盘环境下也能高效准确地进行文字输入。1.触摸屏输入法概述简介在现代信息技术飞速发展的今天,触摸屏
- 嵌入式系统LCD显示模块编程实践
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:本文档提供了一个具有800x480分辨率的3.5英寸液晶显示模块LW350AC9001的驱动程序代码,以及嵌入式系统中使用C/C++语言进行硬件编程的实践指南。该模块的2mm厚度使其适用于空间受限的便携式设备。内容包括驱动程序源代码、硬件控制接口使用方法,以及如何在嵌入式系统中进行图形处理、电源管理与性能优化。1.嵌入式系统原理1.1嵌入式系统概念嵌入式系统是
- FPGA小白到项目实战:Verilog+Vivado全流程通关指南(附光学类岗位技能映射)
阿牛的药铺
算法移植部署fpga开发verilog
FPGA小白到项目实战:Verilog+Vivado全流程通关指南(附光学类岗位技能映射)引言:为什么这个FPGA入门路线能帮你快速上岗?本文设计了一条**"Verilog语法→工具链操作→光学项目实战→岗位技能对标"的阶梯式学习路径。不同于泛泛而谈的FPGA教程,我们聚焦光学类产品开发**核心能力(时序接口设计、图像处理算法移植、高速接口应用),通过3个递进式项目(从LED闪烁到图像边缘检测),
- PyTorch & TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)
阿牛的药铺
算法移植部署pytorchtensorflowfpga开发
PyTorch&TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)引言:为什么算法移植工程师必须掌握框架基础?针对光学类产品算法FPGA移植岗位需求(如可见光/红外图像处理),深度学习框架是算法落地的"桥梁"——既要用PyTorch/TensorFlow验证算法可行性,又要将训练好的模型(如CNN、目标检测)转换为FPGA可部署的格式(ONNX、TFLite)。本文采用"
- 【超硬核】JVM源码解读:Java方法main在虚拟机上解释执行
HeapDump性能社区
java开发语言后端jvm
本文由HeapDump性能社区首席讲师鸠摩(马智)授权整理发布第1篇-关于Java虚拟机HotSpot,开篇说的简单点开讲Java运行时,这一篇讲一些简单的内容。我们写的主类中的main()方法是如何被Java虚拟机调用到的?在Java类中的一些方法会被由C/C++编写的HotSpot虚拟机的C/C++函数调用,不过由于Java方法与C/C++函数的调用约定不同,所以并不能直接调用,需要JavaC
- 算法学习笔记:17.蒙特卡洛算法 ——从原理到实战,涵盖 LeetCode 与考研 408 例题
在计算机科学和数学领域,蒙特卡洛算法(MonteCarloAlgorithm)以其独特的随机抽样思想,成为解决复杂问题的有力工具。从圆周率的计算到金融风险评估,从物理模拟到人工智能,蒙特卡洛算法都发挥着不可替代的作用。本文将深入剖析蒙特卡洛算法的思想、解题思路,结合实际应用场景与Java代码实现,并融入考研408的相关考点,穿插图片辅助理解,帮助你全面掌握这一重要算法。蒙特卡洛算法的基本概念蒙特卡
- 算法学习笔记:15.二分查找 ——从原理到实战,涵盖 LeetCode 与考研 408 例题
呆呆企鹅仔
算法学习算法学习笔记考研二分查找
在计算机科学的查找算法中,二分查找以其高效性占据着重要地位。它利用数据的有序性,通过不断缩小查找范围,将原本需要线性时间的查找过程优化为对数时间,成为处理大规模有序数据查找问题的首选算法。二分查找的基本概念二分查找(BinarySearch),又称折半查找,是一种在有序数据集合中查找特定元素的高效算法。其核心原理是:通过不断将查找范围减半,快速定位目标元素。与线性查找逐个遍历元素不同,二分查找依赖
- Python 脚本最佳实践2025版
前文可以直接把这篇文章喂给AI,可以放到AI角色设定里,也可以直接作为提示词.这样,你只管提需求,写脚本就让AI来.概述追求简洁和清晰:脚本应简单明了。使用函数(functions)、常量(constants)和适当的导入(import)实践来有逻辑地组织你的Python脚本。使用枚举(enumerations)和数据类(dataclasses)等数据结构高效管理脚本状态。通过命令行参数增强交互性
- (Python基础篇)字典的操作
EternityArt
基础篇python开发语言
一、引言在Python编程中,字典(Dictionary)是一种极具灵活性的数据结构,它通过“键-值对”(key-valuepair)的形式存储数据,如同现实生活中的字典——通过“词语(键)”快速查找“释义(值)”。相较于列表和元组的有序索引访问,字典的优势在于基于键的快速查找,这使得它在处理需要频繁通过唯一标识获取数据的场景中极为高效。掌握字典的操作,能让我们更高效地组织和管理复杂数据,是Pyt
- LeetCode算法题:电话号码的字母组合
吱屋猪_
算法leetcodejava
题目描述:给定一个仅包含数字2-9的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按任意顺序返回。给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意1不对应任何字母。2->"abc"3->"def"4->"ghi"5->"jkl"6->"mno"7->"pqrs"8->"tuv"9->"wxyz"例如,给定digits="23",返回["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd
- C++ 设计模式:抽象工厂(Abstract Factory)
冀晓武
C++设计模式c++设计模式抽象工厂模式
链接:C++设计模式链接:C++设计模式-工厂方法链接:C++设计模式-原型模式链接:C++设计模式-建造者模式抽象工厂(AbstractFactory)是一种创建型设计模式,它提供一个接口,用于创建一系列相关或相互依赖的对象,而无需指定它们的具体类。抽象工厂模式通常用于创建一组相关的产品对象,例如不同类型的机器人和它们的配件。1.问题分析在某些情况下,我们需要创建一组相关或相互依赖的对象,但我们
- 霍夫变换(Hough Transform)算法原来详解和纯C++代码实现以及OpenCV中的使用示例
点云SLAM
算法图形图像处理算法opencv图像处理与计算机视觉算法直线提取检测目标检测霍夫变换算法
霍夫变换(HoughTransform)是一种经典的图像处理与计算机视觉算法,广泛用于检测图像中的几何形状,例如直线、圆、椭圆等。其核心思想是将图像空间中的“点”映射到参数空间中的“曲线”,从而将形状检测问题转化为参数空间中的峰值检测问题。一、霍夫变换基本思想输入:边缘图像(如经过Canny边缘检测)输出:一组满足几何模型的形状(如直线、圆)关键思想:图像空间中的一个点→参数空间中的一个曲线参数空
- 用OpenCV标定相机内参应用示例(C++和Python)
下面是一个完整的使用OpenCV进行相机内参标定(CameraCalibration)的示例,包括C++和Python两个版本,基于棋盘格图案标定。一、目标:相机标定通过拍摄多张带有棋盘格图案的图像,估计相机的内参:相机矩阵(内参)K畸变系数distCoeffs可选外参(R,T)标定精度指标(如重投影误差)二、棋盘格参数设置(根据自己的棋盘格设置):棋盘格角点数:9x6(内角点,9列×6行);每个
- C++设计模式:简单工厂、工厂方法、抽象工厂
起个别名
C++算法c++
1.工厂模式的特点在我们现实生活中,买馒头和自己蒸馒头、去饭店点一份大盘鸡和自己养鸡,杀鸡,做大盘鸡,这是全然不同的两种体验:自己做麻烦,而且有失败的风险,需要自己承担后果。买现成的,可以忽略制作细节,方便快捷并且无风险,得到的肯定是美味的食物。对于后者,就相当于是一个加工厂,通过这个工厂我们就可以得到想要的东西,在程序设计中,这种模式就叫做工厂模式,工厂生成出的产品就是某个类的实例,也就是对象。
- Java三年经验程序员技术栈全景指南:从前端到架构,对标阿里美团全栈要求
可曾去过倒悬山
java前端架构
Java三年经验程序员技术栈全景指南:从前端到架构,对标阿里美团全栈要求三年经验是Java程序员的分水岭,技术栈深度决定你成为“业务码农”还是“架构师候选人”。本文整合阿里、美团、滴滴等大厂招聘要求,为你绘制可落地的进阶路线。一、Java核心:从语法糖到JVM底层三年经验与初级的核心差异在于系统级理解,大厂面试常考以下能力:JVM与性能调优内存模型(堆外内存、元空间)、GC算法(G1/ZGC适用场
- 被动降噪的概念及编程实现
CodeByte
人工智能算法javascript编程
被动降噪是指通过编程技术和算法,对输入的数据进行处理,以减少或消除其中的噪声。噪声可以是各种形式的干扰,例如来自传感器、通信信号或其他外部源的干扰。在本文中,我们将探讨被动降噪的意义以及如何使用编程来实现这一目标。被动降噪的意义:噪声对数据的准确性和可靠性产生负面影响。在许多应用领域,例如图像处理、音频处理和信号处理中,噪声的存在可能导致数据质量下降,使得后续的分析和处理变得困难。因此,被动降噪技
- 传统检测响应慢?陌讯多模态引擎提速90+FPS实战
2501_92473147
算法计算机视觉目标检测
开篇痛点:实时目标检测在安防监控中的核心挑战在安防监控领域,实时目标检测是保障公共安全的关键技术。然而,传统算法如YOLOv5或开源框架MMDetection常面临两大痛点:误报率高(复杂光照或遮挡场景下检测不稳定)和响应延迟(高分辨率视频流处理FPS低于30)。实测数据显示,城市交通监控系统误报率达15%,导致安保资源浪费;客户反馈表明,延迟超100ms时,目标跟踪可能失效。这些问题源于算法泛化
- 反光衣识别漏检率 30%?陌讯多尺度模型实测优化
在建筑工地、交通指挥等场景中,反光衣是保障作业人员安全的重要装备,对其进行精准识别是智能监控系统的核心功能之一。但传统视觉算法在实际应用中却屡屡碰壁:强光下反光衣易与背景混淆、远距离小目标漏检率高达30%、复杂场景下模型泛化能力不足[实测数据来源:某智慧工地项目2024年Q1日志]。这些问题直接导致安全监控系统预警滞后,给安全生产埋下隐患。一、技术解析:反光衣识别的核心难点与陌讯算法创新反光衣识别
- 【GESP】C++三级真题 luogu-B4359 [GESP202506 三级] 分糖果
CoderCodingNo
GESPc++java开发语言
GESPC++三级,2025年6月真题,模拟算法,难度★★☆☆☆。本次三级题目个人感觉比较简单。题目题解详见:【GESP】C++三级真题luogu-B4359[GESP202506三级]分糖果|OneCoder【GESP】C++三级真题luogu-B4359[GESP202506三级]分糖果|OneCoderGESPC++三级,2025年6月真题,模拟算法,难度★★☆☆☆。本次三级题目个人感觉比较
- C++设计秘籍:为什么所有参数都需类型转换时,非成员函数才是王道?
讳疾忌医丶
c++前端开发语言
当所有参数都需要类型转换时,为什么要选择非成员函数?在C++的世界里,有一个看似简单却蕴含深意的设计原则:当所有参数(包括被this指针所指的那个隐式参数)皆须进行类型转换时,请为此采用非成员函数实现。这个原则背后隐藏着C++类型系统的精妙设计,也揭示了成员函数与非成员函数在处理隐式类型转换时的本质差异。想象一下,你正在设计一个数学计算库,需要支持整数与有理数的混合运算。如果你天真地将所有操作都实
- 【华为机试】HJ61 放苹果
不爱熬夜的Coder
算法华为机试golang华为golang算法面试
文章目录HJ61放苹果描述输入描述输出描述示例1示例2解题思路算法分析问题本质分析状态定义与转移递推关系详解动态规划表构建算法流程图示例推导过程代码实现思路时间复杂度分析关键优化点边界情况处理递归解法对比实际应用场景测试用例分析算法特点数学原理完整题解代码HJ61放苹果描述我们需要将m个相同的苹果放入n个相同的盘子中,允许有的盘子空着不放。求解有多少种不同的分法。输入描述输入两个整数m,n(0B[
- 初始化列表与类型转换(C++)
2401_89195731
c++开发语言
初始化列表和构造函数体在C++中都是用于给类的成员变量赋初值区别:初始化列表是给每个成员变量定义初始化的地方,即使有成员变量没有给它显式在初始化列表初始化,它也会走初始化列表初始化时机初始化列表:在对象创建时,成员变量通过初始化列表被直接初始化,这发生在构造函数体执行之前。构造函数体内赋值:成员变量首先被默认初始化,然后在构造函数体内通过赋值语句进行赋值。性能差异初始化列表:通常更高效,因为它避免
- list的一些特性(C++)
2401_89195731
c++开发语言
C++STL库中的std::list是一个带头双向循环链表,使用之前需要包头文件,它和vector的使用高度类似。构造list支持多种构造方式默认构造函数:创建一个空的列表。拷贝构造函数:从另一个相同类型的列表创建一个新的列表。范围构造函数:从一对迭代器指定的范围内复制元素到新的列表中。初始值列表构造函数:使用初始化列表(initializerlist)创建一个包含指定元素的列表。填充构造函数:创
- .NET中的安全性之数字签名、数字证书、强签名程序集、反编译
hezudao25
NET.netassembly加密算法referenceheader
本文将探讨数字签名、数字证书、强签名程序集、反编译等以及它们在.NET中的运用(一些概念并不局限于.NET在其它技术、平台中也存在)。1.数字签名数字签名又称为公钥数字签名,或者电子签章等,它借助公钥加密技术实现。数字签名技术主要涉及公钥、私钥、非对称加密算法。1.1公钥与私钥公钥是公开的钥匙,私钥则是与公钥匹配的严格保护的私有密钥;私钥加密的信息只有公钥可以解开,反之亦然。在VisualStud
- QML与C++相互调用函数并获得返回值
cpp_learners
QMLc++QMLqt
这篇博客主要讲解在qml端如何直接调用c++的函数并获得返回值,在c++端如何直接调用qml的函数并获得返回值;主要以map或者jsonobject、list或者jsonarray为主!其他单个类型,常见的类型,例如QString、int等,就不演示了;一通百通。目录1准备工作1.1C++端1.2QML端2qml端直接调用c++端函数3c++端直接调用qml端函数3.1调用qml的qmlFuncO
- java封装继承多态等
麦田的设计者
javaeclipsejvmcencapsulatopn
最近一段时间看了很多的视频却忘记总结了,现在只能想到什么写什么了,希望能起到一个回忆巩固的作用。
1、final关键字
译为:最终的
&
- F5与集群的区别
bijian1013
weblogic集群F5
http请求配置不是通过集群,而是F5;集群是weblogic容器的,如果是ejb接口是通过集群。
F5同集群的差别,主要还是会话复制的问题,F5一把是分发http请求用的,因为http都是无状态的服务,无需关注会话问题,类似
- LeetCode[Math] - #7 Reverse Integer
Cwind
java题解MathLeetCodeAlgorithm
原题链接:#7 Reverse Integer
要求:
按位反转输入的数字
例1: 输入 x = 123, 返回 321
例2: 输入 x = -123, 返回 -321
难度:简单
分析:
对于一般情况,首先保存输入数字的符号,然后每次取输入的末位(x%10)作为输出的高位(result = result*10 + x%10)即可。但
- BufferedOutputStream
周凡杨
首先说一下这个大批量,是指有上千万的数据量。
例子:
有一张短信历史表,其数据有上千万条数据,要进行数据备份到文本文件,就是执行如下SQL然后将结果集写入到文件中!
select t.msisd
- linux下模拟按键输入和鼠标
被触发
linux
查看/dev/input/eventX是什么类型的事件, cat /proc/bus/input/devices
设备有着自己特殊的按键键码,我需要将一些标准的按键,比如0-9,X-Z等模拟成标准按键,比如KEY_0,KEY-Z等,所以需要用到按键 模拟,具体方法就是操作/dev/input/event1文件,向它写入个input_event结构体就可以模拟按键的输入了。
linux/in
- ContentProvider初体验
肆无忌惮_
ContentProvider
ContentProvider在安卓开发中非常重要。与Activity,Service,BroadcastReceiver并称安卓组件四大天王。
在android中的作用是用来对外共享数据。因为安卓程序的数据库文件存放在data/data/packagename里面,这里面的文件默认都是私有的,别的程序无法访问。
如果QQ游戏想访问手机QQ的帐号信息一键登录,那么就需要使用内容提供者COnte
- 关于Spring MVC项目(maven)中通过fileupload上传文件
843977358
mybatisspring mvc修改头像上传文件upload
Spring MVC 中通过fileupload上传文件,其中项目使用maven管理。
1.上传文件首先需要的是导入相关支持jar包:commons-fileupload.jar,commons-io.jar
因为我是用的maven管理项目,所以要在pom文件中配置(每个人的jar包位置根据实际情况定)
<!-- 文件上传 start by zhangyd-c --&g
- 使用svnkit api,纯java操作svn,实现svn提交,更新等操作
aigo
svnkit
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/hardwin/article/details/7963318
import java.io.File;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.tmatesoft.svn.core.SVNCommitInfo;
import org.tmateso
- 对比浏览器,casperjs,httpclient的Header信息
alleni123
爬虫crawlerheader
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException
{
String type=req.getParameter("type");
Enumeration es=re
- java.io操作 DataInputStream和DataOutputStream基本数据流
百合不是茶
java流
1,java中如果不保存整个对象,只保存类中的属性,那么我们可以使用本篇文章中的方法,如果要保存整个对象 先将类实例化 后面的文章将详细写到
2,DataInputStream 是java.io包中一个数据输入流允许应用程序以与机器无关方式从底层输入流中读取基本 Java 数据类型。应用程序可以使用数据输出流写入稍后由数据输入流读取的数据。
- 车辆保险理赔案例
bijian1013
车险
理赔案例:
一货运车,运输公司为车辆购买了机动车商业险和交强险,也买了安全生产责任险,运输一车烟花爆竹,在行驶途中发生爆炸,出现车毁、货损、司机亡、炸死一路人、炸毁一间民宅等惨剧,针对这几种情况,该如何赔付。
赔付建议和方案:
客户所买交强险在这里不起作用,因为交强险的赔付前提是:“机动车发生道路交通意外事故”;
如果是交通意外事故引发的爆炸,则优先适用交强险条款进行赔付,不足的部分由商业
- 学习Spring必学的Java基础知识(5)—注解
bijian1013
javaspring
文章来源:http://www.iteye.com/topic/1123823,整理在我的博客有两个目的:一个是原文确实很不错,通俗易懂,督促自已将博主的这一系列关于Spring文章都学完;另一个原因是为免原文被博主删除,在此记录,方便以后查找阅读。
有必要对
- 【Struts2一】Struts2 Hello World
bit1129
Hello world
Struts2 Hello World应用的基本步骤
创建Struts2的Hello World应用,包括如下几步:
1.配置web.xml
2.创建Action
3.创建struts.xml,配置Action
4.启动web server,通过浏览器访问
配置web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="
- 【Avro二】Avro RPC框架
bit1129
rpc
1. Avro RPC简介 1.1. RPC
RPC逻辑上分为二层,一是传输层,负责网络通信;二是协议层,将数据按照一定协议格式打包和解包
从序列化方式来看,Apache Thrift 和Google的Protocol Buffers和Avro应该是属于同一个级别的框架,都能跨语言,性能优秀,数据精简,但是Avro的动态模式(不用生成代码,而且性能很好)这个特点让人非常喜欢,比较适合R
- lua set get cookie
ronin47
lua cookie
lua:
local access_token = ngx.var.cookie_SGAccessToken
if access_token then
ngx.header["Set-Cookie"] = "SGAccessToken="..access_token.."; path=/;Max-Age=3000"
end
- java-打印不大于N的质数
bylijinnan
java
public class PrimeNumber {
/**
* 寻找不大于N的质数
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=100;
PrimeNumber pn=new PrimeNumber();
pn.printPrimeNumber(n);
System.out.print
- Spring源码学习-PropertyPlaceholderHelper
bylijinnan
javaspring
今天在看Spring 3.0.0.RELEASE的源码,发现PropertyPlaceholderHelper的一个bug
当时觉得奇怪,上网一搜,果然是个bug,不过早就有人发现了,且已经修复:
详见:
http://forum.spring.io/forum/spring-projects/container/88107-propertyplaceholderhelper-bug
- [逻辑与拓扑]布尔逻辑与拓扑结构的结合会产生什么?
comsci
拓扑
如果我们已经在一个工作流的节点中嵌入了可以进行逻辑推理的代码,那么成百上千个这样的节点如果组成一个拓扑网络,而这个网络是可以自动遍历的,非线性的拓扑计算模型和节点内部的布尔逻辑处理的结合,会产生什么样的结果呢?
是否可以形成一种新的模糊语言识别和处理模型呢? 大家有兴趣可以试试,用软件搞这些有个好处,就是花钱比较少,就算不成
- ITEYE 都换百度推广了
cuisuqiang
GoogleAdSense百度推广广告外快
以前ITEYE的广告都是谷歌的Google AdSense,现在都换成百度推广了。
为什么个人博客设置里面还是Google AdSense呢?
都知道Google AdSense不好申请,这在ITEYE上也不是讨论了一两天了,强烈建议ITEYE换掉Google AdSense。至少,用一个好申请的吧。
什么时候能从ITEYE上来点外快,哪怕少点
- 新浪微博技术架构分析
dalan_123
新浪微博架构
新浪微博在短短一年时间内从零发展到五千万用户,我们的基层架构也发展了几个版本。第一版就是是非常快的,我们可以非常快的实现我们的模块。我们看一下技术特点,微博这个产品从架构上来分析,它需要解决的是发表和订阅的问题。我们第一版采用的是推的消息模式,假如说我们一个明星用户他有10万个粉丝,那就是说用户发表一条微博的时候,我们把这个微博消息攒成10万份,这样就是很简单了,第一版的架构实际上就是这两行字。第
- 玩转ARP攻击
dcj3sjt126com
r
我写这片文章只是想让你明白深刻理解某一协议的好处。高手免看。如果有人利用这片文章所做的一切事情,盖不负责。 网上关于ARP的资料已经很多了,就不用我都说了。 用某一位高手的话来说,“我们能做的事情很多,唯一受限制的是我们的创造力和想象力”。 ARP也是如此。 以下讨论的机子有 一个要攻击的机子:10.5.4.178 硬件地址:52:54:4C:98
- PHP编码规范
dcj3sjt126com
编码规范
一、文件格式
1. 对于只含有 php 代码的文件,我们将在文件结尾处忽略掉 "?>" 。这是为了防止多余的空格或者其它字符影响到代码。例如:<?php$foo = 'foo';2. 缩进应该能够反映出代码的逻辑结果,尽量使用四个空格,禁止使用制表符TAB,因为这样能够保证有跨客户端编程器软件的灵活性。例
- linux 脱机管理(nohup)
eksliang
linux nohupnohup
脱机管理 nohup
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2166699
nohup可以让你在脱机或者注销系统后,还能够让工作继续进行。他的语法如下
nohup [命令与参数] --在终端机前台工作
nohup [命令与参数] & --在终端机后台工作
但是这个命令需要注意的是,nohup并不支持bash的内置命令,所
- BusinessObjects Enterprise Java SDK
greemranqq
javaBOSAPCrystal Reports
最近项目用到oracle_ADF 从SAP/BO 上调用 水晶报表,资料比较少,我做一个简单的分享,给和我一样的新手 提供更多的便利。
首先,我是尝试用JAVA JSP 去访问的。
官方API:http://devlibrary.businessobjects.com/BusinessObjectsxi/en/en/BOE_SDK/boesdk_ja
- 系统负载剧变下的管控策略
iamzhongyong
高并发
假如目前的系统有100台机器,能够支撑每天1亿的点击量(这个就简单比喻一下),然后系统流量剧变了要,我如何应对,系统有那些策略可以处理,这里总结了一下之前的一些做法。
1、水平扩展
这个最容易理解,加机器,这样的话对于系统刚刚开始的伸缩性设计要求比较高,能够非常灵活的添加机器,来应对流量的变化。
2、系统分组
假如系统服务的业务不同,有优先级高的,有优先级低的,那就让不同的业务调用提前分组
- BitTorrent DHT 协议中文翻译
justjavac
bit
前言
做了一个磁力链接和BT种子的搜索引擎 {Magnet & Torrent},因此把 DHT 协议重新看了一遍。
BEP: 5Title: DHT ProtocolVersion: 3dec52cb3ae103ce22358e3894b31cad47a6f22bLast-Modified: Tue Apr 2 16:51:45 2013 -070
- Ubuntu下Java环境的搭建
macroli
java工作ubuntu
配置命令:
$sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
再运行如下命令:
$sudo apt-get install sun-java6-jdk
待安装完毕后选择默认Java.
$sudo update- alternatives --config java
安装过程提示选择,输入“2”即可,然后按回车键确定。
- js字符串转日期(兼容IE所有版本)
qiaolevip
TODateStringIE
/**
* 字符串转时间(yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss)
* result (分钟)
*/
stringToDate : function(fDate){
var fullDate = fDate.split(" ")[0].split("-");
var fullTime = fDate.split("
- 【数据挖掘学习】关联规则算法Apriori的学习与SQL简单实现购物篮分析
superlxw1234
sql数据挖掘关联规则
关联规则挖掘用于寻找给定数据集中项之间的有趣的关联或相关关系。
关联规则揭示了数据项间的未知的依赖关系,根据所挖掘的关联关系,可以从一个数据对象的信息来推断另一个数据对象的信息。
例如购物篮分析。牛奶 ⇒ 面包 [支持度:3%,置信度:40%] 支持度3%:意味3%顾客同时购买牛奶和面包。 置信度40%:意味购买牛奶的顾客40%也购买面包。 规则的支持度和置信度是两个规则兴
- Spring 5.0 的系统需求,期待你的反馈
wiselyman
spring
Spring 5.0将在2016年发布。Spring5.0将支持JDK 9。
Spring 5.0的特性计划还在工作中,请保持关注,所以作者希望从使用者得到关于Spring 5.0系统需求方面的反馈。