【数据结构】链表的一些面试题
简单不先于复杂,而是在复杂之后。
链表面试题
- 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有结点。OJ链接
//1.常规方法 struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) { struct ListNode* cur = head, *prev = NULL; while(cur) { if(cur->val == val) { //1.头删 //2.非头删 if(cur == head) { head = head->next; free(cur); cur = head; } else { prev-> next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = prev-> next; } } else { prev = cur; cur = cur->next; } } return head; }//2.新思路 //创建一个新链表,把非val的结点尾插到新链表 struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) { struct ListNode* newhead =NULL, *cur = head, *tail = NULL; while(cur) { if(cur->val != val) { if(tail == NULL) { newhead = tail = cur; } else { tail->next = cur; tail = tail->next; } cur = cur->next; } else { struct ListNode* del = cur; cur = cur->next; free(del); } } //最后的节点是val就会出现此问题 if(tail) { tail->next = NULL; } return newhead; }小技巧:在涉及到链表的题的时候调试不太方便,我们需要快速构建一个链表。
int main() { struct ListNode* n1 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); assert(n1); struct ListNode* n2 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); assert(n2); struct ListNode* n3 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); assert(n3); struct ListNode* n4 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); assert(n4); struct ListNode* n5 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); assert(n5); struct ListNode* n6 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); assert(n6); struct ListNode* n7 = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); assert(n7); n1->next = n2; n2->next = n3; n3->next = n4; n4->next = n5; n5->next = n6; n6->next = n7; n7->next = NULL; n1->val = 1; n2->val = 2; n3->val = 6; n4->val = 3; n5->val = 4; n6->val = 5; n7->val = 6; return 0; }带哨兵位的链表:
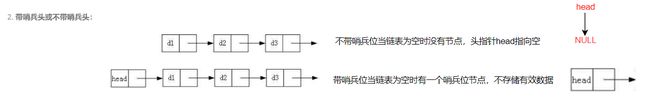
- 哨兵节点(Sentinel Node): 这是一个特殊的节点,它不包含实际数据,仅用于简化代码逻辑。哨兵节点通常作为链表的头部存在,这意味着链表中始终有一个节点,即使链表为空。哨兵节点的存在简化了对链表头部的特殊处理,因为无论链表是否为空,我们都可以始终通过哨兵节点来引导链表的访问。
- 优点: 哨兵节点可以简化代码实现,避免在对头部进行操作时需要额外的条件检查。
不带哨兵位的链表:
- 特殊处理头部: 在不使用哨兵节点的情况下,需要特殊处理链表头部,因为在空链表或者插入第一个节点时,需要进行额外的条件检查,以确保正确处理链表头部。
- 优点: 节省了一个节点的空间开销,因为没有用于哨兵的额外节点。
带哨兵位和不带哨兵位的区别:
//利用带哨兵位的头节点的链表可以免去判空的步骤 struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) { struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* guard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); struct ListNode* tail = guard; while(cur) { if(cur->val != val) { tail->next = cur; tail = tail->next; cur = cur->next; } else { struct ListNode* del = cur; cur = cur->next; free(del); } } //最后的节点是val就会出现此问题 if(tail) { tail->next = NULL; } head = guard->next; free(guard); return head; }替代之前实现单链表时候传参用的二级指针有两种方式:
- 返回新的链表头指针
- 设计为带哨兵位的链表
(单链表在实际应用中很少带头,OJ题链表基本不带头)
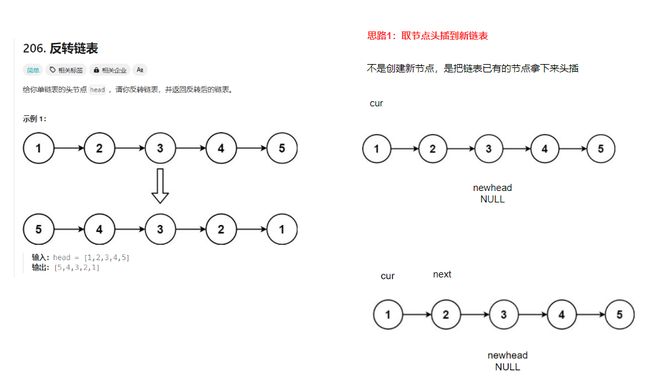
- 反转一个单链表。OJ链接
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* newhead = NULL; while(cur) { struct ListNode* next = cur->next; cur->next = newhead; newhead = cur; cur = next; } return newhead; }//思路2:将链表的指针指向反转 struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* prev = NULL; struct ListNode* cur = head; while(cur) { struct ListNode* next = cur->next; cur->next = prev; //迭代器 prev = cur; cur = next; } return prev; }
- 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。OJ链接
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* fast,*slow; fast = slow = head; while(fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } return slow; }
- 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。OJ链接
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) { // write code here struct ListNode* slow, *fast; slow = fast = pListHead; while(k--) { //判断k大于链表长度 if(!fast) { return NULL; } fast = fast->next; } while(fast) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; } return slow; }
- 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有结点组成的。OJ链接
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) { struct ListNode* guard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); guard->next = NULL; struct ListNode* tail = guard; struct ListNode* cur1 = list1, *cur2 = list2; while(cur1 && cur2) { if(cur1->val < cur2->val) { tail->next = cur1; cur1 = cur1->next; } else { tail->next = cur2; cur2 = cur2->next; } tail = tail->next; } if(cur1) tail->next = cur1; if(cur2) tail->next = cur2; struct ListNode* head = guard->next; free(guard); return head; }
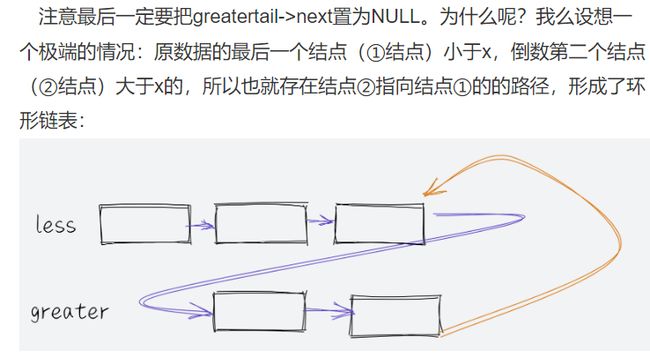
- 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大小或等于x的结点之前。OJ链接
class Partition { public: ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) { // write code here struct ListNode* lessTail,*lessGuard,*greaterTail,*greaterGuard; lessTail = lessGuard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); greaterTail = greaterGuard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); struct ListNode* cur = pHead; greaterGuard->next = NULL; lessGuard->next = NULL; while(cur) { if(cur->val < x) { lessTail->next = cur; lessTail = lessTail->next; } else { greaterTail->next = cur; greaterTail = greaterTail->next; } cur = cur->next; } lessTail->next = greaterGuard->next; greaterTail->next = NULL; pHead = lessGuard->next; free(greaterGuard); free(lessGuard); return pHead; } };
- 链表的回文结构。OJ链表
class PalindromeList { public: struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* fast, *slow; fast = slow = head; while (fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } return slow; } struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* prev = NULL; struct ListNode* cur = head; while (cur) { struct ListNode* next = cur->next; cur->next = prev; //迭代器 prev = cur; cur = next; } return prev; } bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head) { // write code here struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(head); struct ListNode* rmid = reverseList(mid); while(head && rmid) { if(head->val != rmid->val) return false; head = head->next; rmid = rmid->next; } return true; } };
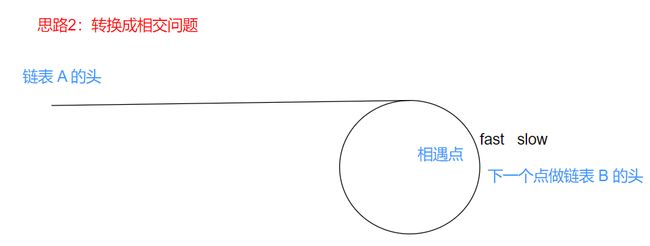
- 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。OJ链表
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) { struct ListNode* curA = headA, *curB = headB; if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL) { return NULL; } int lenA = 1; while(curA->next) { curA = curA->next; lenA++; } int lenB = 1; while(curB->next) { curB = curB->next; lenB++; } if(curA != curB) { return NULL; } struct ListNode* longList = headA,*shortList = headB; if(lenA < lenB) { longList = headB; shortList = headA; } int gap = abs(lenA - lenB); while(gap--) { longList = longList->next; } while(longList != shortList) { longList = longList->next; shortList = shortList->next; } return longList; }
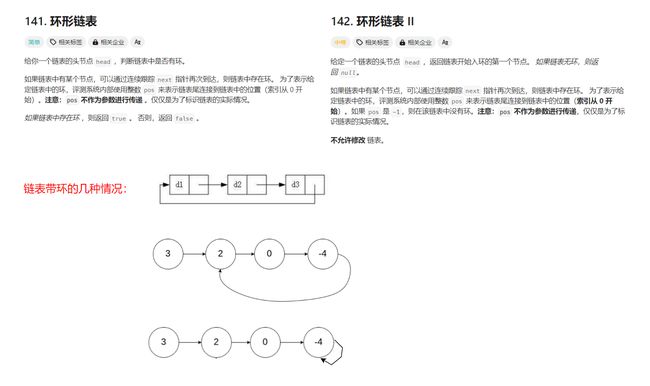
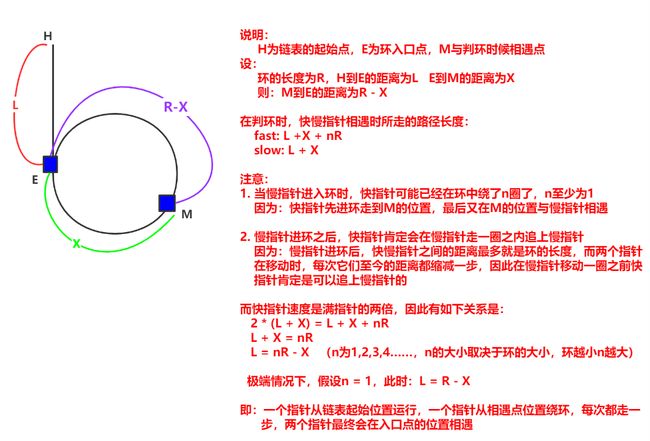
- 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。OJ链表
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode* fast, *slow; fast = slow = head; while(fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if(slow == fast) return true; } return false; }【思路】
快慢指针,即慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,两个指针从链表起始位置开始运行,如果链表带环则一定会在环中相遇,否则快指针率先走到链表的末尾。
【扩展问题】
- 为什么快指针每次走两步,慢指针走一步可以?
假设链表带环,两个指针最后都会进入环,快指针先进环,慢指针后进环。当慢指针刚进环时,可能就和快指针相遇了,最差情况下两个指针之间的距离刚好就是环的长度。
此时,两个指针每移动一次,之间的距离就缩小一步,不会出现每次刚好是套圈的情况,因此:在慢指针走到一圈之前,快指针肯定是可以追上慢指针的,即相遇。
快指针一次走3步,走4步,…n步行吗?
快指针一次走 3 步:
假设slow进环后,fast和slow之间差距N,追赶距离就是N,每追赶一次,之间的距离缩小2步
如果N是偶数,距离一定会减少到0,也就是两个指针相遇;
如果N是奇数,距离会减少到1,fast会越过slow指针,fast和slow之间得距离变成了-1,也就是C-1,(C-1是环长度),如果C-1是偶数,再追一圈就可以追上,如果C-1是奇数,永远追不上;
- 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个结点。如果链表无环,则返回 NULL。OJ链接
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head; while(fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if(slow == fast) { struct ListNode* meet = slow; while(meet != head) { meet = meet->next; head = head->next; } return meet; } } return NULL; }
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) { struct ListNode* curA = headA, *curB = headB; int lenA = 1; while(curA->next) { curA = curA->next; lenA++; } int lenB = 1; while(curB->next) { curB = curB->next; lenB++; } if(curA != curB) { return NULL; } struct ListNode* longList = headA, *shortList = headB; if(lenA < lenB) { longList = headB; shortList = headA; } int gap = abs(lenA - lenB); while(gap--) { longList = longList->next; } while(longList != shortList) { longList = longList->next; shortList = shortList->next; } return longList; } struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode* slow, *fast; slow = fast = head; while(fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if(slow == fast) { struct ListNode* meet = slow; struct ListNode* next = meet->next; meet->next = NULL; struct ListNode* entry = getIntersectionNode(head,next); meet->next = next; return entry; } } return NULL; }
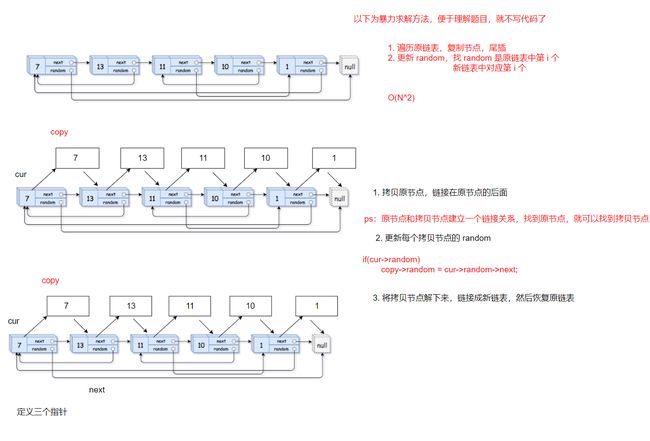
- 给定一个链表,每个结点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何结点或空结点。
要求返回这个链表的深度拷贝。OJ链接
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) { // 1.插入copy节点 struct Node* cur = head; struct Node* copy; struct Node* next; while(cur) { // 复制链接 next = cur->next; copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); copy->val = cur->val; cur->next = copy; copy->next = next; // 迭代往后走 cur = next; } //2. 更新copy->random cur = head; while(cur) { copy = cur->next; if(cur->random == NULL) copy->random = NULL; else copy->random = cur->random->next; //迭代 cur = copy->next; } //3. copy节点要解下来链接在一起,然后恢复原链表 struct Node* copyHead = NULL, *copyTail = NULL; cur = head; while(cur) { copy = cur->next; next = copy->next; //取节点尾插 if(copyTail == NULL) { copyHead = copyTail = copy; } else { copyTail->next = copy; copyTail = copyTail->next; } //恢复原链表链接 cur->next = next; //迭代 cur = next; } return copyHead; }
- 其他。ps:链表的题当前因为难度及知识面等等原因还不适合当前学习,下面有OJ链接。
Leetcode OJ链接 + 牛客 OJ链接