AtCoder Beginner Contest 338(ABCDEF题)
A - Capitalized?
Problem Statement
You are given a non-empty string S S S consisting of uppercase and lowercase English letters. Determine whether the following condition is satisfied:
The first character of S S S is uppercase, and all other characters are lowercase.
Constraints
1 ≤ ∣ S ∣ ≤ 100 1 \leq |S| \leq 100 1≤∣S∣≤100 ( ∣ S ∣ |S| ∣S∣ is the length of the string S S S.)
Each character of S S S is an uppercase or lowercase English letter.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
S S S
Output
If the condition is satisfied, print Yes; otherwise, print No.
Sample Input 1
Capitalized
Sample Output 1
Yes
The first character C of Capitalized is uppercase, and all other characters apitalized are lowercase, so you should print Yes.
Sample Input 2
AtCoder
Sample Output 2
No
AtCoder contains an uppercase letter C that is not at the beginning, so you should print No.
Sample Input 3
yes
Sample Output 3
No
The first character y of yes is not uppercase, so you should print No.
Sample Input 4
A
Sample Output 4
Yes
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include B - Frequency
Problem Statement
You are given a string S S S consisting of lowercase English letters. Find the character that appears most frequently in S S S. If multiple such characters exist, report the one that comes earliest in alphabetical order.
Constraints
1 ≤ ∣ S ∣ ≤ 1000 1 \leq |S| \leq 1000 1≤∣S∣≤1000 ( ∣ S ∣ |S| ∣S∣ is the length of the string S S S.)
Each character in S S S is a lowercase English letter.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
$S$
Output
Among the characters that appear most frequently in S S S, print the one that comes earliest in alphabetical order.
Sample Input 1
frequency
Sample Output 1
e
In frequency, the letter e appears twice, which is more than any other character, so you should print e.
Sample Input 2
atcoder
Sample Output 2
a
In atcoder, each of the letters a, t, c, o, d, e, and r appears once, so you should print the earliest in alphabetical order, which is a.
Sample Input 3
pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
Sample Output 3
o
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include C - Leftover Recipes
Problem Statement
Your refrigerator has N N N kinds of ingredients. Let us call them ingredient 1 1 1, … \dots …, ingredient N N N. You have Q i Q_i Qi grams of ingredient i i i.
You can make two types of dishes. To make one serving of dish A, you need A i A_i Ai grams of each ingredient i i i ( 1 ≤ i ≤ N ) (1 \leq i \leq N) (1≤i≤N). To make one serving of dish B, you need B i B_i Bi grams of each ingredient i i i. You can only make an integer number of servings of each type of dish.
Using only the ingredients in the refrigerator, what is the maximum total number of servings of dishes you can make?
Constraints
1 ≤ N ≤ 10 1 \leq N \leq 10 1≤N≤10
1 ≤ Q i ≤ 1 0 6 1 \leq Q_i \leq 10^6 1≤Qi≤106
0 ≤ A i ≤ 1 0 6 0 \leq A_i \leq 10^6 0≤Ai≤106
There is an i i i such that A i ≥ 1 A_i \geq 1 Ai≥1.
0 ≤ B i ≤ 1 0 6 0 \leq B_i \leq 10^6 0≤Bi≤106
There is an i i i such that B i ≥ 1 B_i \geq 1 Bi≥1.
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N
Q 1 Q_1 Q1 Q 2 Q_2 Q2 … \dots … Q N Q_N QN
A 1 A_1 A1 A 2 A_2 A2 … \dots … A N A_N AN
B 1 B_1 B1 B 2 B_2 B2 … \dots … B N B_N BN
Output
Assuming that you can make a maximum total of S S S servings of dishes, print the integer S S S.
Sample Input 1
2
800 300
100 100
200 10
Sample Output 1
5
This refrigerator has 800 800 800 grams of ingredient 1 1 1 and 300 300 300 grams of ingredient 2 2 2.
You can make one serving of dish A with 100 100 100 grams of ingredient 1 1 1 and 100 100 100 grams of ingredient 2 2 2, and one serving of dish B with 200 200 200 grams of ingredient 1 1 1 and 10 10 10 grams of ingredient 2 2 2.
To make two servings of dish A and three servings of dish B, you need 100 × 2 + 200 × 3 = 800 100 \times 2 + 200 \times 3 = 800 100×2+200×3=800 grams of ingredient 1 1 1, and 100 × 2 + 10 × 3 = 230 100 \times 2 + 10 \times 3 = 230 100×2+10×3=230 grams of ingredient 2 2 2, neither of which exceeds the amount available in the refrigerator. In this way, you can make a total of five servings of dishes, but there is no way to make six, so the answer is 5 5 5.
Sample Input 2
2
800 300
100 0
0 10
Sample Output 2
38
You can make 8 8 8 servings of dish A with 800 800 800 grams of ingredient 1 1 1, and 30 30 30 servings of dish B with 300 300 300 grams of ingredient 2 2 2, for a total of 38 38 38 servings.
Sample Input 3
2
800 300
801 300
800 301
Sample Output 3
0
You cannot make any dishes.
Sample Input 4
10
1000000 1000000 1000000 1000000 1000000 1000000 1000000 1000000 1000000 1000000
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Sample Output 4
222222
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include D - Island Tour
Problem Statement
The AtCoder Archipelago consists of N N N islands connected by N N N bridges.
The islands are numbered from 1 1 1 to N N N, and the i i i-th bridge ( 1 ≤ i ≤ N − 1 1\leq i\leq N-1 1≤i≤N−1) connects islands i i i and i + 1 i+1 i+1 bidirectionally, while the N N N-th bridge connects islands N N N and 1 1 1 bidirectionally.
There is no way to travel between islands other than crossing the bridges.
On the islands, a tour that starts from island X 1 X_1 X1 and visits islands X 2 , X 3 , … , X M X_2, X_3, \dots, X_M X2,X3,…,XM in order is regularly conducted.
The tour may pass through islands other than those being visited, and the total number of times bridges are crossed during the tour is defined as the length of the tour.
More precisely, a tour is a sequence of l + 1 l+1 l+1 islands a 0 , a 1 , … , a l a_0, a_1, \dots, a_l a0,a1,…,al that satisfies all the following conditions, and its length is defined as l l l:
For all j ( 0 ≤ j ≤ l − 1 ) j\ (0\leq j\leq l-1) j (0≤j≤l−1), islands a j a_j aj and a j + 1 a_{j+1} aj+1 are directly connected by a bridge.
There are some KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 9: 0 = y_1 &̲lt; y_2 < \d… such that for all k ( 1 ≤ k ≤ M ) k\ (1\leq k\leq M) k (1≤k≤M), a y k = X k a_{y_k} = X_k ayk=Xk.
Due to financial difficulties, the islands will close one bridge to reduce maintenance costs.
Determine the minimum possible length of the tour when the bridge to be closed is chosen optimally.
Constraints
3 ≤ N ≤ 2 × 1 0 5 3\leq N \leq 2\times 10^5 3≤N≤2×105
2 ≤ M ≤ 2 × 1 0 5 2\leq M \leq 2\times 10^5 2≤M≤2×105
1 ≤ X k ≤ N 1\leq X_k\leq N 1≤Xk≤N
X k ≠ X k + 1 ( 1 ≤ k ≤ M − 1 ) X_k\neq X_{k+1}\ (1\leq k\leq M-1) Xk=Xk+1 (1≤k≤M−1)
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N M M M
X 1 X_1 X1 X 2 X_2 X2 … \dots … X M X_M XM
Output
Print the answer as an integer.
Sample Input 1
3 3
1 3 2
Sample Output 1
2
If the first bridge is closed: By taking the sequence of islands ( a 0 , a 1 , a 2 ) = ( 1 , 3 , 2 ) (a_0, a_1, a_2) = (1, 3, 2) (a0,a1,a2)=(1,3,2), it is possible to visit islands 1 , 3 , 2 1, 3, 2 1,3,2 in order, and a tour of length 2 2 2 can be conducted. There is no shorter tour.
If the second bridge is closed: By taking the sequence of islands ( a 0 , a 1 , a 2 , a 3 ) = ( 1 , 3 , 1 , 2 ) (a_0, a_1, a_2, a_3) = (1, 3, 1, 2) (a0,a1,a2,a3)=(1,3,1,2), it is possible to visit islands 1 , 3 , 2 1, 3, 2 1,3,2 in order, and a tour of length 3 3 3 can be conducted. There is no shorter tour.
If the third bridge is closed: By taking the sequence of islands ( a 0 , a 1 , a 2 , a 3 ) = ( 1 , 2 , 3 , 2 ) (a_0, a_1, a_2, a_3) = (1, 2, 3, 2) (a0,a1,a2,a3)=(1,2,3,2), it is possible to visit islands 1 , 3 , 2 1, 3, 2 1,3,2 in order, and a tour of length 3 3 3 can be conducted. There is no shorter tour.
Therefore, the minimum possible length of the tour when the bridge to be closed is chosen optimally is 2 2 2.
The following figure shows, from left to right, the cases when bridges 1 , 2 , 3 1, 2, 3 1,2,3 are closed, respectively. The circles with numbers represent islands, the lines connecting the circles represent bridges, and the blue arrows represent the shortest tour routes.
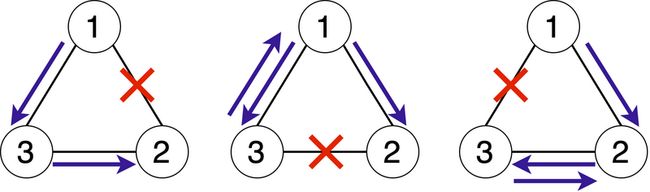
Sample Input 2
4 5
2 4 2 4 2
Sample Output 2
8
The same island may appear multiple times in X 1 , X 2 , … , X M X_1, X_2, \dots, X_M X1,X2,…,XM.
Sample Input 3
163054 10
62874 19143 77750 111403 29327 56303 6659 18896 64175 26369
Sample Output 3
390009
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include E - Chords
Problem Statement
There are 2 N 2N 2N points placed at equal intervals on a circle, numbered 1 1 1 to 2 N 2N 2N in a clockwise direction starting from a certain point.
There are also N N N chords on the circle, with the i i i-th chord connecting points A i A_i Ai and B i B_i Bi.
It is guaranteed that all the values A 1 , … , A N , B 1 , … , B N A_1,\dots,A_N,B_1,\dots,B_N A1,…,AN,B1,…,BN are distinct.
Determine whether there is an intersection between the chords.
Constraints
2 ≤ N ≤ 2 × 1 0 5 2\leq N \leq 2\times 10^5 2≤N≤2×105
1 ≤ A i , B i ≤ 2 N 1\leq A_i,B_i \leq 2N 1≤Ai,Bi≤2N
A 1 , … , A N , B 1 , … , B N A_1,\dots,A_N,B_1,\dots,B_N A1,…,AN,B1,…,BN are all distinct
All input values are integers
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N
A 1 A_1 A1 B 1 B_1 B1
A 2 A_2 A2 B 2 B_2 B2
⋮ \vdots ⋮
A N A_N AN B N B_N BN
Output
If there is an intersection between the chords, print Yes; otherwise, print No.
Sample Input 1
3
1 3
4 2
5 6
Sample Output 1
Yes
 As shown in the figure, chord $1$ (the line segment connecting points $1$ and $3$) and chord $2$ (the line segment connecting points $4$ and $2$) intersect, so print
As shown in the figure, chord $1$ (the line segment connecting points $1$ and $3$) and chord $2$ (the line segment connecting points $4$ and $2$) intersect, so print Yes. ## Sample Input 2 ``` 3 6 1 4 3 2 5 ``` ## Sample Output 2 ``` No ```  As shown in the figure, there is no intersection between the chords, so print
As shown in the figure, there is no intersection between the chords, so print No. ## Sample Input 3 ``` 4 2 4 3 7 8 6 5 1 ``` ## Sample Output 3 ``` Yes ```
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include F - Negative Traveling Salesman
Problem Statement
There is a weighted simple directed graph with N N N vertices and M M M edges.
The vertices are numbered 1 1 1 to N N N, and the i i i-th edge has a weight of W i W_i Wi and extends from vertex U i U_i Ui to vertex V i V_i Vi.
The weights can be negative, but the graph does not contain negative cycles.
Determine whether there is a walk that visits each vertex at least once. If such a walk exists, find the minimum total weight of the edges traversed.
If the same edge is traversed multiple times, the weight of that edge is added for each traversal.
Here, “a walk that visits each vertex at least once” is a sequence of vertices v 1 , v 2 , … , v k v_1,v_2,\dots,v_k v1,v2,…,vk that satisfies both of the following conditions:
For every i i i ( 1 ≤ i ≤ k − 1 ) (1\leq i\leq k-1) (1≤i≤k−1), there is an edge extending from vertex v i v_i vi to vertex v i + 1 v_{i+1} vi+1.
For every j ( 1 ≤ j ≤ N ) j\ (1\leq j\leq N) j (1≤j≤N), there is i i i ( 1 ≤ i ≤ k ) (1\leq i\leq k) (1≤i≤k) such that v i = j v_i=j vi=j.
Constraints
2 ≤ N ≤ 20 2\leq N \leq 20 2≤N≤20
1 ≤ M ≤ N ( N − 1 ) 1\leq M \leq N(N-1) 1≤M≤N(N−1)
1 ≤ U i , V i ≤ N 1\leq U_i,V_i \leq N 1≤Ui,Vi≤N
U i ≠ V i U_i \neq V_i Ui=Vi
( U i , V i ) ≠ ( U j , V j ) (U_i,V_i) \neq (U_j,V_j) (Ui,Vi)=(Uj,Vj) for i ≠ j i\neq j i=j
− 1 0 6 ≤ W i ≤ 1 0 6 -10^6\leq W_i \leq 10^6 −106≤Wi≤106
The given graph does not contain negative cycles.
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N M M M
U 1 U_1 U1 V 1 V_1 V1 W 1 W_1 W1
U 2 U_2 U2 V 2 V_2 V2 W 2 W_2 W2
⋮ \vdots ⋮
U M U_M UM V M V_M VM W M W_M WM
Output
If there is a walk that visits each vertex at least once, print the minimum total weight of the edges traversed. Otherwise, print No.
Sample Input 1
3 4
1 2 5
2 1 -3
2 3 -4
3 1 100
Sample Output 1
-2
By following the vertices in the order 2 → 1 → 2 → 3 2\rightarrow 1\rightarrow 2\rightarrow 3 2→1→2→3, you can visit all vertices at least once, and the total weight of the edges traversed is ( − 3 ) + 5 + ( − 4 ) = − 2 (-3)+5+(-4)=-2 (−3)+5+(−4)=−2.
This is the minimum.
Sample Input 2
3 2
1 2 0
2 1 0
Sample Output 2
No
There is no walk that visits all vertices at least once.
Sample Input 3
5 9
1 2 -246288
4 5 -222742
3 1 246288
3 4 947824
5 2 -178721
4 3 -947824
5 4 756570
2 5 707902
5 1 36781
Sample Output 3
-449429
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include 视频题解
Atcoder Beginner Contest 338
最后祝大家早日![]()