LeetCode 54 螺旋矩阵
题目描述
螺旋矩阵
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
示例 1:
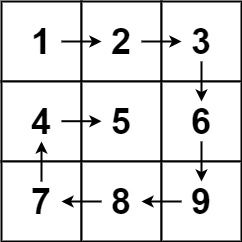
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
示例 2:
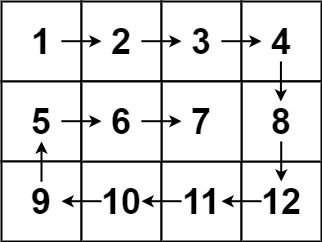
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
输出:[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
提示:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
解法
解法1:模拟
模拟螺旋矩阵的路径:初始位置是矩阵的左上角,初始方向是向右,当路径超出界限或者进入之前访问过的位置时,顺时针旋转,进入下一个方向。
判断路径是否进入之前访问过的位置需要使用一个与输入矩阵大小相同的辅助矩阵 visited,其中的每个元素表示该位置是否被访问过。当一个元素被访问时,将 visited中的对应位置的元素设为已访问。
如何判断路径是否结束?由于矩阵中的每个元素都被访问一次,因此路径的长度即为矩阵中的元素数量,当路径的长度达到矩阵中的元素数量时即为完整路径,将该路径返回。
java代码:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> order = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return order;
}
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rows][columns];
int total = rows * columns;
int row = 0, column = 0;
int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
int directionIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {
order.add(matrix[row][column]);
visited[row][column] = true;
int nextRow = row + directions[directionIndex][0];
int nextColumn = column + directions[directionIndex][1];
// 寻找下一个方向
if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= rows || nextColumn < 0 || nextColumn >= columns || visited[nextRow][nextColumn]) {
directionIndex = (directionIndex + 1) % 4;
}
row += directions[directionIndex][0];
column += directions[directionIndex][1];
}
return order;
}
}
复杂度
- ,间复杂度:
O(mn),其中 m 和 n 分别是输入矩阵的行数和列数 - 空间复杂度:
O(mn),需要创建一个大小为 m×n 的辅助矩阵 visited
解法2:按层模拟
可以将矩阵看成若干层,首先输出最外层的元素,其次输出次外层的元素,直到输出最内层的元素。
定义矩阵的第 k 层是到最近边界距离为 k 的所有顶点。例如,下图矩阵最外层元素都是第 1 层,次外层元素都是第 2 层,剩下的元素都是第 3 层。
[[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1],
[1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 2, 1],
[1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]
对于每层,从左上方开始以顺时针的顺序遍历所有元素。假设当前层的左上角位于 (top,left),右下角位于 (bottom,right),按照如下顺序遍历当前层的元素。
- 从左到右遍历上侧元素,依次为 (top,left) 到 (top,right)。
- 从上到下遍历右侧元素,依次为 (top+1,right) 到 (bottom,right)。
- 如果 left< right 且 top< bottom (因为如果有等于,说明只剩一行或一列,只要遍历上面两个即可),则从右到左遍历下侧元素,依次为 (bottom,right−1) 到 (bottom,left+1),以及从下到上遍历左侧元素,依次为 (bottom,left) 到 (top+1,left)。
遍历完当前层的元素之后,将 left 和 top分别增加 1,将 right 和 bottom分别减少 1,进入下一层继续遍历,直到遍历完所有元素为止。
遍历完所有元素的条件是left > right 或者 top > bottom
java代码:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> order = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return order;
}
// 初始化上下左右值
int left = 0, right = matrix[0].length - 1, top = 0, bottom = matrix.length - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
// 从左上向右遍历
for (int col = left; col <= right; col++) {
order.add(matrix[top][col]);
}
// 从右上向下遍历
for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) {
order.add(matrix[row][right]);
}
// 如果不是单行或单列
if (left< right && top< bottom) {
// 从右下向左遍历
for (int col = right - 1; col >= left; col--) {
order.add(matrix[bottom][col]);
}
// 从左下向上遍历
for (int row = bottom -1; row > top; row--) {
order.add(matrix[row][left]);
}
}
left ++;
right --;
top ++;
bottom --;
}
return order;
}
}