Linux进程控制:进程创建与等待
目录
一、fork函数
1.1fork函数的调用与功能
1.2fork函数的返回值与写实拷贝
1.3fork的常规用法与失败原因
二、进程终止
2.1进程的退出场景和常见退出方法
2.2_exit函数与exit函数
2.2.1_exit函数
2.2.2exit函数
2.3return退出
三、进程等待
3.1wait及waitpid的方法
3.2获取子进程status
四、xshell实操
4.1阻塞等待方式
4.2非阻塞等待方式
一、fork函数
1.1fork函数的调用与功能
在linux中fork函数时非常重要的函数,它从已存在进程中创建一个新进程。新进程为子进程,而原进程为父进程。
#include
pid_t fork(void);
//返回值:自进程中返回0,父进程返回子进程id,出错返回-1
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
printf("Before: pid is %d\n", getpid());
return 0;
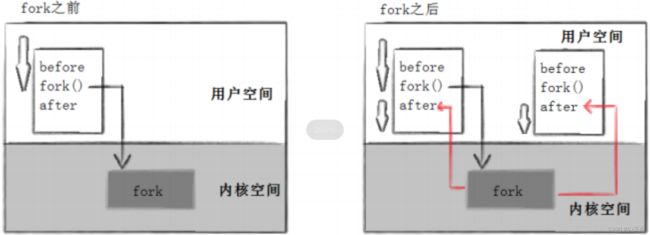
} 1.进程调用fork,当控制转移到内核中的fork代码后,内核做:
2.分配新的内存块和内核数据结构给子进程。
3.将父进程部分数据结构内容拷贝至子进程。
4.添加子进程到系统进程列表当中。
5.fork返回,开始调度器调度。
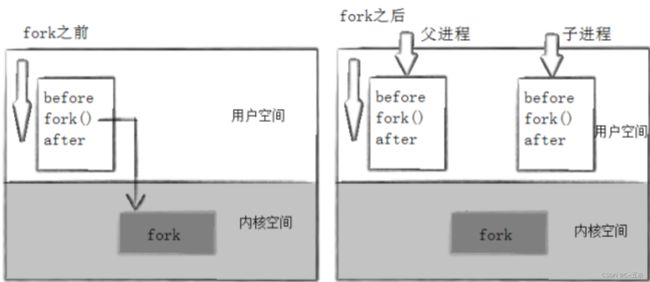
当一个进程调用fork之后,就有两个二进制代码相同的进程。而且它们都运行到相同的地方。但每个进程都将可以 开始它们自己的旅程,看如下程序:
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
printf("Before: pid is %d\n", getpid());
if ((pid = fork()) == -1)perror("fork()"), exit(1);
printf("After:pid is %d, fork return %d\n", getpid(), pid);
sleep(1);
return 0;
}
//XShell下运行结果:
//[root@localhost linux]# ./a.out
//Before: pid is 43676
//After:pid is 43676, fork return 43677
//After:pid is 43677, fork return 0 这里看到了三行输出,一行before,两行after。进程43676先打印before消息,然后它有打印after。另一个after消息有43677打印的。注意到进程43677没有打印before,为什么呢?如下图所示:
所以, fork 之前父进程独立执行, fork 之后,父子两个执行流分别执行。注意, fork 之后,谁先执行完全由调度器决定。
1.2fork函数的返回值与写实拷贝
一、子进程返回0,
二、父进程返回的是子进程的pid。
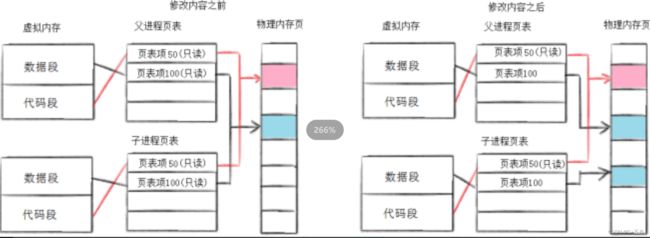
三、写诗拷贝:通常,父子代码共享,父子再不写入时,数据也是共享的,当任意一方试图写入,便以写时拷贝的方式各自一份副
1.3fork的常规用法与失败原因
常规用法:
1.一个父进程希望复制自己,使父子进程同时执行不同的代码段。例如,父进程等待客户端请求,生成子进程来处理请求。
2.一个进程要执行一个不同的程序。例如子进程从fork返回后,调用exec函数。
例如在使用xshell时的shell,用户每输入一条指令shell就会执行一条并在屏幕上进行打印,但执行完一条以后shell会停滞等待用户输入下一条指令,而不会直接结束进程,此处就用到了父子进程。
失败原因:
1.系统中有太多的进程。
2.实际用户的进程数超过了限制。
二、进程终止
2.1进程的退出场景和常见退出方法
退出场景:
1.代码运行完毕,结果正确。
2.代码运行完毕,结果不正确。
3.代码异常终止。
常见退出方法:
一、正常终止(可以通过 echo $? 查看进程退出码):
1. 从main返回
2. 调用exit
3. _exit
二、异常退出:
ctrl + c,信号终止
2.2_exit函数与exit函数
2.2.1_exit函数
#include
void _exit(int status);
参数:status 定义了进程的终止状态,父进程通过wait来获取该值 说明:虽然status是int,但是仅有低8位可以被父进程所用。所以_exit(-1)时,在终端执行$?发现返回值是255。
2.2.2exit函数
#include
void exit(int status); exit最后也会调用_exit, 但在调用_exit之前,还做了其他工作:
1. 执行用户通过 atexit或on_exit定义的清理函数。
2. 关闭所有打开的流,所有的缓存数据均被写入。
3. 调用_exit。
实例演示 :
#include
#include
int main()
{
printf("hello");
exit(0);
}
运行结果:
[root@localhost linux] # . / a.out
hello[root@localhost linux]#
int main()
{
printf("hello");
_exit(0);
}
运行结果:
[root@localhost linux] # . / a.out
[root@localhost linux]# 2.3return退出
return是一种更常见的退出进程方法。执行return n等同于执行exit(n),因为调用main的运行时函数会将main的返回值当做 exit的参数。
三、进程等待
子进程退出,父进程如果不管不顾,就可能造成‘僵尸进程’的问题,进而造成内存泄漏。
另外,进程一旦变成僵尸状态,那就刀枪不入,“杀人不眨眼”的kill -9 也无能为力,因为谁也没有办法杀死一个已经死去的进程。
最后,父进程派给子进程的任务完成的如何,我们需要知道。如:子进程运行完成,结果对还是不对,或者是否正常退出。
父进程通过进程等待的方式,回收子进程资源,获取子进程退出信息
3.1wait及waitpid的方法
#include
#include
pid_t wait(int*status);
返回值:
成功返回被等待进程pid,失败返回-1。
参数:
输出型参数,获取子进程退出状态,不关心则可以设置成为NULL pid_ t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int options);
返回值:
当正常返回的时候waitpid返回收集到的子进程的进程ID;
如果设置了选项WNOHANG,而调用中waitpid发现没有已退出的子进程可收集,则返回0;
如果调用中出错,则返回-1,这时errno会被设置成相应的值以指示错误所在;
参数:
pid:
Pid=-1,等待任一个子进程。与wait等效。
Pid>0.等待其进程ID与pid相等的子进程。
status:
WIFEXITED(status): 若为正常终止子进程返回的状态,则为真。(查看进程是否是正常退出)
WEXITSTATUS(status): 若WIFEXITED非零,提取子进程退出码。(查看进程的退出码)
options:
WNOHANG: 若pid指定的子进程没有结束,则waitpid()函数返回0,不予以等待。若正常结束,则返回该子进
程的ID。 如果子进程已经退出,调用wait/waitpid时,wait/waitpid会立即返回,并且释放资源,获得子进程退出信息。
如果在任意时刻调用wait/waitpid,子进程存在且正常运行,则进程可能阻塞。
如果不存在该子进程,则立即出错返回。
3.2获取子进程status
wait和waitpid,都有一个status参数,该参数是一个输出型参数,由操作系统填充。
如果传递NULL,表示不关心子进程的退出状态信息。
否则,操作系统会根据该参数,将子进程的退出信息反馈给父进程。
status不能简单的当作整形来看待,可以当作位图来看待,具体细节如下图(只研究status低16比特位):
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
if ((pid = fork()) == -1)
perror("fork"), exit(1);
if (pid == 0) {
sleep(20);
exit(10);
}
else {
int st;
int ret = wait(&st);
if (ret > 0 && (st & 0X7F) == 0) { // 正常退出
printf("child exit code:%d\n", (st >> 8) & 0XFF);
}
else if (ret > 0) { // 异常退出
printf("sig code : %d\n", st & 0X7F);
}
}
return 0;
} 测试结果:
[root@localhost linux]# ./a.out //等20秒退出
child exit code:10
[root@localhost linux]# ./a.out //在其他终端kill掉
sig code : 9四、xshell实操
4.1阻塞等待方式
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
printf("%s fork error\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 1;
}
else if (pid == 0) { //child
printf("child is run, pid is : %d\n", getpid());
sleep(5);
exit(257);
}
else {
int status = 0;
pid_t ret = waitpid(-1, &status, 0);//阻塞式等待,等待5S
printf("this is test for wait\n");
if (WIFEXITED(status) && ret == pid) {
printf("wait child 5s success, child return code is :%d.\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
else {
printf("wait child failed, return.\n");
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
[root@localhost linux]# ./a.out
child is run, pid is : 55119
this is test for wait
wait child 5s success, child return code is :1.
4.2非阻塞等待方式
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
printf("%s fork error\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 1;
}
else if (pid == 0) { //child
printf("child is run, pid is : %d\n", getpid());
sleep(5);
exit(1);
}
else {
int status = 0;
pid_t ret = 0;
do
{
ret = waitpid(-1, &status, WNOHANG);//非阻塞式等待
if (ret == 0) {
printf("child is running\n");
}
sleep(1);
} while (ret == 0);
if (WIFEXITED(status) && ret == pid) {
printf("wait child 5s success, child return code is :%d.\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
else {
printf("wait child failed, return.\n");
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}