【BI&AI】Lecture10 - Motor System2
Motor System2
专业术语
descending spinal tracts 下行脊髓束
corticospinal tract 锥体束
reticulospinal tract 脊髓脑干束
vestibulospinal tract 脊髓脑干侧脊束
precentral gyrus 前中央回
population coding 群体编码
basal ganglia 基底节
thalamus 丘脑
Posterior parietal cortex 后顶叶皮层
Prefrontal cortex 前额叶皮层
Cerebellum 小脑
Three hierarchical levels of movement control
-
最低层次(low):局部控制。在这个层次上,控制发生在肌肉水平,以实现特定的运动。这包括单个肌肉纤维的收缩和放松,局部的肌肉协调和反射性运动。 -
中层次(middle):模式生成器。在这个层次上,控制发生在中枢神经系统中的模式生成器(Pattern Generators)中。这些模式生成器是一组神经元网络,能够产生周期性的运动模式,例如步态模式或呼吸模式。模式生成器可以自主地产生这些周期性运动,而不需要持续的输入信号。 -
最高层次(high):高级运动控制。在这个层次上,控制发生在大脑皮层和下丘脑等高级结构中。这些结构负责整体的运动规划、协调和调节。它们接收来自感觉系统的信息,并将其与内部模型和目标进行比较,然后生成相应的指令来控制模式生成器和局部控制。
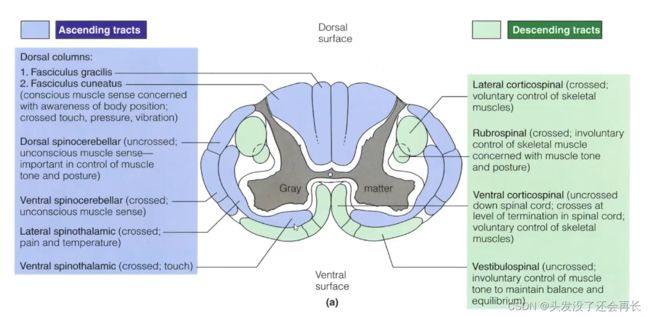
Descending Spinal Tracts
在上一篇文章中,已经解释了脊髓中的运动神经元是如何控制肌肉的,并且Alpha神经元接受的输入有一个来自于大脑的上位神经元,那大脑的上位运动神经元如何将信息传递给Alpha运动神经元的呢?
信息传递离不开一个重要的结构:下行脊髓束(descending spinal tracts)
下行脊髓束是从大脑皮层或脑干中的神经核发出的神经纤维,向下穿过脊髓,将运动指令传递给脊髓的运动神经元。这些运动指令控制着肌肉的收缩和运动,实现身体的运动和姿势调整。
下行脊髓束可以分为多个不同的通路,每个通路负责不同的运动控制。常见的下行脊髓束包括锥体束(corticospinal tract)、脊髓小脑束(rubrospinal tract)、脊髓脑干束(reticulospinal tract)、脊髓脑干侧脊束(vestibulospinal tract)等等。
- 侧面通路(lateral pathways) 参与了远端肌肉的自主运动,并直接受到大脑皮层控制,主要由锥体束(corticospinal tract)和脊髓红核束(rubrospinal tract)组成。侧面通路是下行脊髓束的一部分,负责控制肢体的
精细运动。 - 腹外侧通路(ventromedial pathways) 参与姿势和运动的控制,受脑干控制,主要由前庭脊髓束(vestibulospinal tract)、视脊髓束(tectospinal tract)、延髓网状脊髓束(medullary reticulospinal tract)和脑桥网状脊髓束(pontine reticulospinal tract)组成。在神经解剖学中,腹外侧通路是下行脊髓束的一部分,主要负责
控制姿势和运动。
如下图所示:


Ascending Tracts and Descending Tracts
在神经解剖学中,脊髓束是指通过脊髓向下传递神经信号的神经纤维束。脊髓束分为上行和下行两类。"descending spinal tracts" 特指下行脊髓束,"ascending spinal tracts" 特指上行脊髓束。
在体感系统中,主要介绍了上行通路,如何将感觉信息通过脊髓传递到大脑,而运动系统中,我们了解了下行通路,如何将大脑信息通过脊髓传递来控制肌肉运动。
Lateral pathway
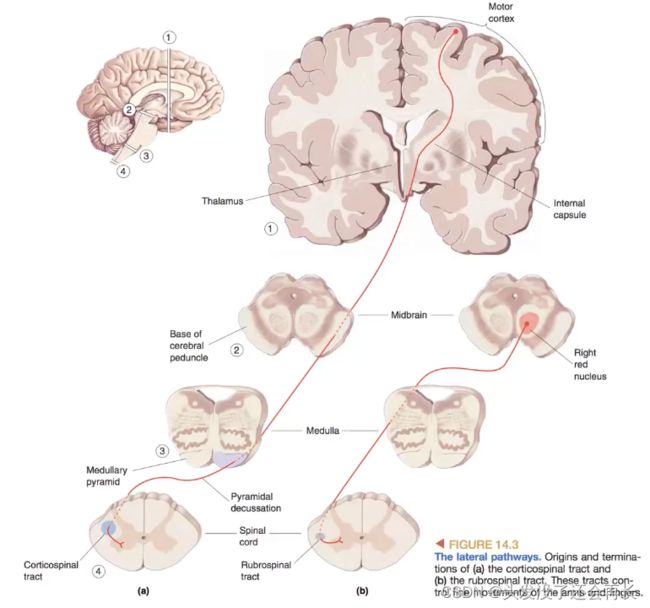
侧面通路由锥体束(corticospinal tract)和脊髓红核束(rubrospinal tract)组成,这两个组成部分在下行通路中有两个路径,如下图所示:
- 锥体束(corticospinal tract) 是侧面通路的主要组成部分,它起源于
大脑皮层的运动区域,通过脊髓的背侧束和腹侧束向下传递神经信号,最终连接到脊髓的运动神经元。锥体束被称为直接皮层控制途径,负责控制精确的、有意识的肌肉运动。 - 脊髓红核束(rubrospinal tract) 也是侧面通路的一部分,它起源于
脊髓红核,通过脊髓向下运行,最终连接到脊髓的运动神经元。脊髓红核束在运动调节和协调方面起着重要作用。
The Ventromedial Pathways
- The Vestibulospinal Tract:
- to keep the head balanced on the shoulders as the body moves through space
- to turn the head in response to new sensory stimuli
- The Tectospinal Tract:
- to direct the head and eyes to move
- The Pontine Reticulospinal Tract:
- to enhance the antigravity reflexes of the spinal cord
- to maintain a standing posture by resisting the effects of gravity
- The Medullary Reticulospinal Tract:
- to liberate the antigravity muscles from reflex control
Summary of Lateral and Ventromedial Pathways
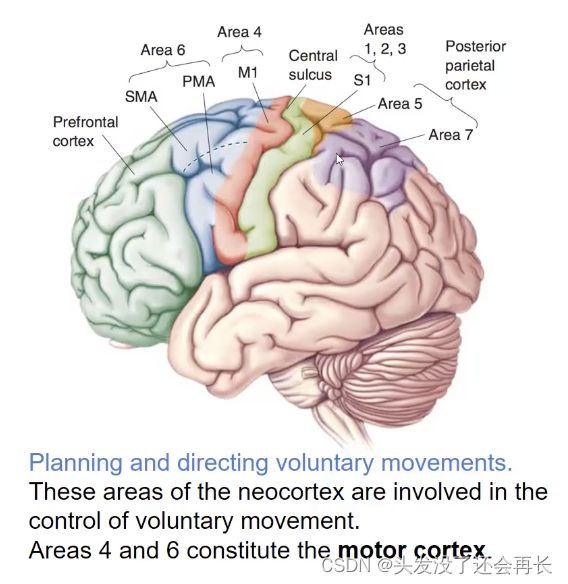
Brain regions in motor system
The control of voluntary movement engages almost all of the neocortex
在进行目标导向的运动(Goal-directed movementt)时,我们需要准确地知道自己身体在空间中的位置,也就是身体的姿势和位置信息。这种位置感知来源于多种感觉系统的综合,包括视觉、前庭感觉(平衡感觉)和本体感觉(肌肉、关节和皮肤的感觉)。
此外,我们还需要明确知道我们打算前往的目标位置。
最后,为了实现目标导向的运动,我们需要选择和执行一个计划,以达到目标位置。这涉及到大脑的高级认知和决策过程,包括选择适当的动作序列、调节肌肉的活动和协调不同身体部位的运动。
Somatotopic motor map in M1
神经外科医生Wilder Penfield在接受手术以切除被认为引发癫痫发作的脑部组织的患者身上,进行了皮层电刺激实验。
他发现在前中央回(precentral gyrus)的第4区进行微弱的电刺激会引起对侧身体特定区域的肌肉抽动(a twitch of the muscles)。
Somatotopic motor map in M1: from FMRI
使用非侵入式的F MRI观察身体的某一个位置运动时,大脑皮层的活动位置。

Premotor area(PMA)and Supplementary motor area(SMA)
前运动区(PMA)位于大脑皮层的前中央回附近,与主运动皮层(Primary Motor Cortex)相邻。它是运动计划和准备的关键区域,在执行动作之前对运动进行编码和规划。PMA参与协调和控制复杂的动作序列,包括手部和手臂的精细运动,以及手眼协调和物体操作等。
辅助运动区(SMA)位于大脑皮层的中央前回,与前运动区(PMA)相邻。SMA在运动计划和执行中起着重要作用,特别是与意愿驱动的自由动作和序列动作相关。SMA参与协调和整合运动的序列,尤其是在没有外部刺激的情况下自发生成动作序列。

Posterior Parietal and Prefrontal Cortex
Posterior parietal cortex(后顶叶皮层)
- Area 5 gets inputs from Areas 3, 1 and 2(sensory cortex)
- Area 7 get inputs from high-order visual areas(such as MT)
Prefrontal cortex(前额叶皮层) - The
parietal lobesare extensively interconnected with regions in theanterior frontal lobesthat in humans are throught to be important for abstract thought, decision making, and anticipation of the consequences of action.(顶叶与前额叶的区域之间有广泛的相互连接,这些区域在人类中被认为对抽象思维、决策制定和预测行动后果至关重要。)

Basal Ganglia
基底节(Basal Ganglia)是大脑深部的一组神经核团,包括纹状体(Caudate Nucleus)、腹侧核(Putamen)、球状核(Globus Pallidus)、苍白球(Subthalamic Nucleus)和黑质(Substantia Nigra)。它们与大脑皮层、丘脑和脑干等区域之间形成复杂的神经回路。
基底节在运动控制、学习、情绪调节和认知功能等方面起着重要作用。它们参与调节和调制运动的执行,帮助协调肌肉群的活动,维持运动的平衡和流畅性。此外,基底节还参与了注意力、意志力、决策制定、情绪调节和记忆等高级认知功能。
Summary of Lateral and Ventromedial Pathways
知道了大脑皮层在运动系统中的分布,我们可以细化两个运动通路在运动皮层的详细区域,如下图所示。我们需要记住的一点是,运动系统在spinal code中涉及到许多的feedback,是各种信息的整合,只有这样才能实现精细的控制。
所以大脑设计了许多的反馈,下图中蓝色回路就是一个重要部分,运动执行会通过basal ganglia,通过thalamus直接反馈到motor cortex。
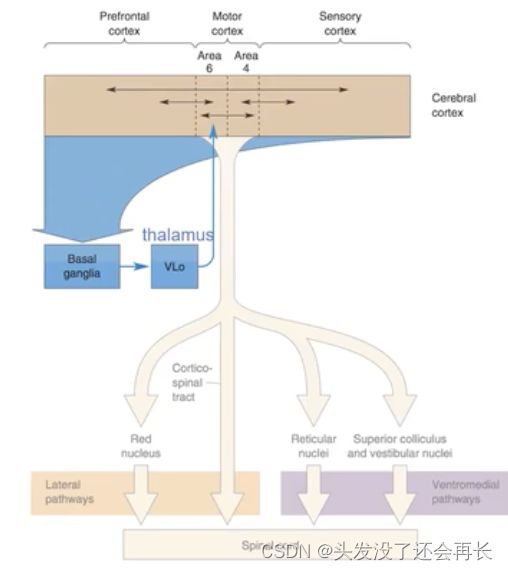
The initiation of movement by M1
由M1发起运动的过程,运动皮层激活下位运动神经元的途径起源于M1的皮层第V层(Layer V)。第V层拥有金字塔形神经元的群体,其中一些神经元可能非常大。
在人类中,第V层的许多大型皮质脊髓细胞投射到下位运动神经元的池中,并通过单突触兴奋它们。
一个单独的皮质脊髓神经元可能对拮抗肌肉产生协调作用。M1中的第V层金字塔细胞主要接收两个来源的输入:其他皮质区域(other cortical areas)和丘脑(thalamus)。

The population coding of movement in M1
在M1中,运动的群体编码(population coding)指的是多个神经元的活动模式共同编码和表示特定的运动。通过对大量神经元的活动进行综合分析,可以捕捉到特定运动的群体编码。这种群体编码可以提供更全面和精确的运动信息,超过了单个神经元的能力。
Cerebellum
- Not directly involved in initiation of motor activity
- Fine-tuning of motor control
- Motor learning
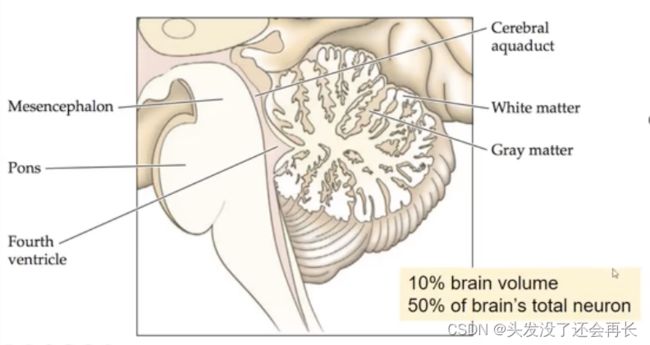
小脑接收来自整个身体的本体感觉(proprioceptive)、前庭感觉(vestibular)以及其他感觉输入,同时还接收来自运动皮层和关联皮层的巨大投射。
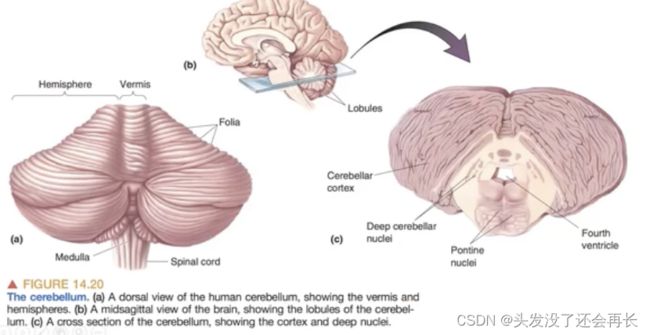
Efferent and Afferent pathway of the cerebellum
小脑的出路(efferent)和入路(afferent)途径是指与小脑之间传递信息的神经通路。
入路(afferent pathway)是指将信息从其他神经系统传递到小脑的通路。出路(efferent pathway)是指从小脑传递信息到其他神经系统的通路,从而影响运动和认知功能。


