算法基础——位运算,双指针,排序,二分
目录
1.位运算
与:&
或:|
取反:~
异或:^或者是一个圈里有个加号的图像
移位:<<或者>>
例题:二进制中1的个数
例题:我们需要0
编辑
2.排序sort
例题:【模板】排序(1)
例题:【模板】排序(2)
桶排序:
例题:【模板】排序(3)
3.双指针
例题:最长连续不重复子序列
4.二分
例题:查找
1.位运算
位运算是以每一位的形式来进行的
与:&
只有两个都为1才是1
3为011
4为100
所以3&4 = 000 = 0
或:|
只要有一个为1则是1
取反:~
与非类似,但非是一个逻辑运算,只要一个数大于0,对它!结果都为0
而取反是按位来进行的
~1 = 0
~0 = 1
异或:^或者是一个圈里有个加号的图像
只要两个不同就为1,举例:
1^0为1,0^1为1
移位:<<或者>>
将所有位往左移或者往右移,过界会直接溢出,所以一般只对正数做这个操作,因为左移时最高一位的符号位会溢出
举例:3为00011,<<3为00110,变为6,乘以了2
同理,右移就是除以2
例题:二进制中1的个数
#include
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 2e9 + 10;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
while(n--)
{
ll a;
ll ans = 0;
cin >> a;
while(a)
{
if(a & 1) ans++;
a >>= 1;
}
cout << ans << ' ';
}
return 0;
} 例题:我们需要0
奇数个x异或的结果为x
#include
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 2e9 + 10;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
ll a;
cin >> a;
ans ^= a;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
} 2.排序sort
stl里面的sort
sort是一个左闭右开的区间
例题:【模板】排序(1)
使用sort升序排序好后
使用unique可以将重复的元素移动到最后面,再让下标指向最后面的第一个重复的位置的下标
在使用erase从这个下标开始删除到尾部,就可以得到一个排序去重的序列
#include
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 2e9 + 10;
vector v;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
v.push_back(x);
}
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
v.erase(unique(v.begin(),v.end()),v.end());
for(auto &ele : v)
cout << ele << ' ';
return 0;
} 例题:【模板】排序(2)
#include
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
struct book
{
int h,s,w;
bool operator <(const book &b)const
{
if(h == b.h && s == b.s) return w > b.w;
if(h == b.h) return s > b.s;
return h > b.h;
}
}b[N];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> b[i].h >> b[i].s >> b[i].w;
sort(b,b + n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << b[i].h << ' ' << b[i].s << ' ' << b[i].w << '\n';
return 0;
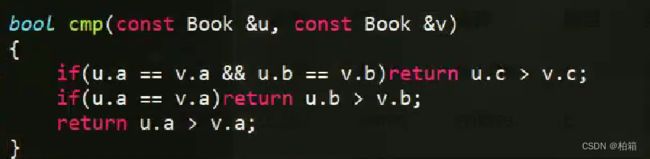
} 用cmp比较也可以
桶排序:
数组很长,数据范围很小
例题:【模板】排序(3)
#include
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 3e6 + 10;
int a[N];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
a[x]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= 2e5; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < a[i]; j++)
cout << i << ' ';
}
return 0;
} 3.双指针
例题:最长连续不重复子序列
这里用了桶的思想
#include
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N],c[N];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
c[i] = 0;
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 1,j = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
while(j < n && c[a[j + 1]] == 0)
c[a[++j]]++;
ans = max(ans,j - i + 1ll);
c[a[i]]--;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
return 0;
} 4.二分
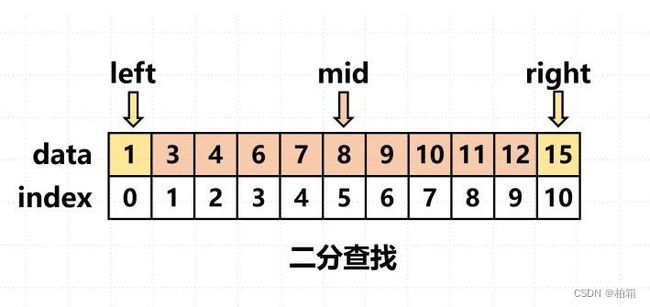
例题:查找
#include
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
ll a[N],c[N];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int n,q;
cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
while(q--)
{
int left = 1,right = n,found = 0;
int x;
cin >> x;
int mid;
while(left <= right && !found)
{
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(a[mid] > x) right = mid - 1;
if(a[mid] < x) left = mid + 1;
if(a[mid] == x) found = 1;
}
if(found) cout << mid << ' ';
else cout << -1 << ' ';
}
return 0;
}