SpringBoot源码解读与原理分析(二十)IOC容器的刷新(一)
文章目录
- 7 IOC容器的刷新
-
- 7.1 初始化前的预处理
-
- 7.1.1 初始化属性配置
- 7.1.2 初始化早期事件的集合
- 7.2 初始化BeanFactory
-
- 7.2.1 注解驱动的refreshBeanFactory
- 7.2.2 XML驱动的refreshBeanFactory
- 7.2.3 获取BeanFactory
- 7.3 BeanFactory的预处理配置
-
- 7.3.1 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
-
- 7.3.1.1 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor的作用
- 7.3.1.2 ignoreDependencyInterface
- 7.3.2 自动注入的支持
- 7.3.3 ApplicationListenerDetector
7 IOC容器的刷新
上一章完整介绍了SpringBoot应用的启动过程,其中有一个关键步骤,其内部设计相当复杂,即IOC容器的刷新。
代码清单1:SpringApplication.java
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//...
//6.3.3 初始化IOC容器
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//6.3.4 刷新IOC容器
refreshContext(context);
//...
}
通过查看源码,refreshContext方法最终会调用AbstractApplicationContext中的refresh方法。
在 SpringBoot源码解读与原理分析(十三)IOC容器的启动流程 中已经从大体上梳理了IOC容器刷新一共做了13件事情,这一章详细梳理这13件事情具体是怎么做的。注意,这一章会分多篇文章来梳理,这篇文章先梳理前面三个步骤(7.1-7.3)。
代码清单2:AbstractApplicationContext.java
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 7.1 初始化前的预处理
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 7.2 获取BeanFactory,加载所有bean的定义信息(未实例化)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 7.3 BeanFactory的预处理配置
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 7.4 准备BeanFactory完成后进行的后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 7.5 执行BeanFactory创建后的后置处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 7.6 注册Bean的后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 7.7 初始化MessageSource
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 7.8 初始化事件广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 7.9 子类的多态onRefresh
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 7.10 注册监听器
registerListeners();
// 至此,BeanFactory创建完成
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 7.11 初始化所有剩下的单实例
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 7.12 完成容器的创建工作
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
// 7.13 清理缓存
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
7.1 初始化前的预处理
// 7.1 初始化前的预处理
prepareRefresh();
代码清单3:AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
// 记录刷新动作执行的事件
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 标记当前IOC容器已激活
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
} else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
// 7.1.1 初始化属性配置
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
// 属性校验
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
// 监听器的初始化(兼顾可以反复刷新的IOC容器)
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
} else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
// 7.1.2 初始化早期事件的结合
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
由 代码清单3 可知,初始化前的预处理阶段的大多数动作都是前置性准备,有两个步骤比较关键。
7.1.1 初始化属性配置
代码清单4:AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected void initPropertySources() {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
由 代码清单4 可知,initPropertySources是一个模板方法,默认不会做任何事情,而是留给子类重写。
在 SpringBoot源码解读与原理分析(十九)IOC容器的创建与初始化 6.3.2 创建IOC容器 中提到,SpringBoot会根据已经推断好的Web类型区分创建不同的ApplicationContext落地实现类。基于Servlet的落地实现类是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。
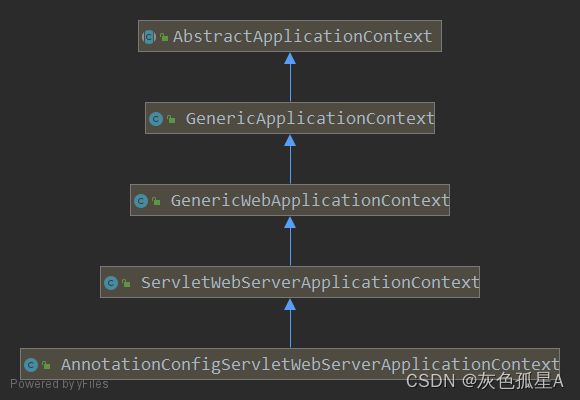
借助IDEA可以得到AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext与AbstractApplicationContext的继承关系:
在GenericWebApplicationContext类中重写了initPropertySources方法:
代码清单5:GenericWebApplicationContext.java
@Override
protected void initPropertySources() {
ConfigurableEnvironment env = getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(this.servletContext, null);
}
}
代码清单6:StandardServletEnvironment.java
@Override
public void initPropertySources(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig);
}
由 代码清单5、6 可知,initPropertySources方法会获取一个ConfigurableWebEnvironment,并配置当前的ServletContext。
代码清单7:WebApplicationContextUtils.java
public static void initServletPropertySources(MutablePropertySources sources,
@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
Assert.notNull(sources, "'propertySources' must not be null");
String name = StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (servletContext != null && sources.get(name) instanceof StubPropertySource) {
// 将ServletContext当作一个属性配置源注入Environment中
sources.replace(name, new ServletContextPropertySource(name, servletContext));
}
name = StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (servletConfig != null && sources.get(name) instanceof StubPropertySource) {
// 将ServletConfig当作一个属性配置源注入Environment中
sources.replace(name, new ServletConfigPropertySource(name, servletConfig));
}
}
由 代码清单7 可知,WebApplicationContextUtils的静态initServletPropertySources方法是将ServletContext和ServletConfig封装为PropertySource,存入Environment内置的聚合对象MutablePropertySources中。每次从Environment中获取配置属性时,实际是从MutablePropertySources中取值,而MutablePropertySources会遍历自身聚合的所有PropertySource并尝试获取指定的配置属性。
7.1.2 初始化早期事件的集合
代码清单8:AbstractApplicationContext.java
/** ApplicationEvents published before the multicaster setup. */
@Nullable
private Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyApplicationEvents;
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
由 代码清单8 中的注释可以了解到,earlyApplicationEvents用于保存事件广播器初始化之前的早期事件,一旦事件广播器可用,这些保存的事件将被广播。换句话说,在监听机制可用之前,可能会产生一些事件需要广播,earlyApplicationEvents把这些事件暂存起来,等到监听机制可用再逐一广播,以确保所有监听器都监听到自己本应该监听到的事件。
7.2 初始化BeanFactory
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 7.2 获取BeanFactory,加载所有bean的定义信息(未实例化)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
代码清单9:AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
// 刷新BeanFactory
refreshBeanFactory();
// 获取BeanFactory
return getBeanFactory();
}
protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
由 代码清单9 可知,初始化BeanFactory分为两步:刷新BeanFactory;获取BeanFactory。
刷新BeanFactory的refreshBeanFactory方法本身是一个抽象方法,需要子类实现。借助IDEA可得GenericApplicationContext和AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext均实现了这个方法,分别对应基于注解驱动的IOC容器和基于XML配置文件驱动的IOC容器。
7.2.1 注解驱动的refreshBeanFactory
代码清单10:GenericApplicationContext.java
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
}
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
}
由 代码清单10 可知,基于注解驱动的refreshBeanFactory仅仅设置了BeanFactory的序列化ID。
7.2.2 XML驱动的refreshBeanFactory
由于SpringBoot已不再使用这种方式,简单了解。
代码清单11:AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
// 如果BeanFactory已存在,则先销毁Bean和关闭BeanFactory
// 因为基于XML驱动的IOC容器是可刷新的,内部的Bean也是可以重新加载的
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 创建BeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 自定义配置BeanFactory
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 解析、加载XML中定义的BeanDefinition
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
7.2.3 获取BeanFactory
代码清单12:AbstractApplicationContext.java
public abstract ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
由 代码清单12 可知,getBeanFactory方法是一个模板方法,由子类实现。
代码清单13:GenericApplicationContext.java
private final DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
@Override
public final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return this.beanFactory;
}
由 代码清单13 可知,在子类GenericApplicationContext中实现了这个方法,返回一个DefaultListableBeanFactory对象。也就是说,此时BeanFactory的落地实现就是一个DefaultListableBeanFactory。
7.3 BeanFactory的预处理配置
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 7.3 BeanFactory的预处理配置
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
代码清单14:AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
// 设置BeanFactory的类加载器、表达式解析器等
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 7.3.1 配置一个可回调注入ApplicationContext的BeanPostProcessor
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 忽略几种依赖接口
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
// 7.3.2 自动注入的支持
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
// 7.3.3 配置一个可加载所有监听器的组件
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
// LoadTimeWeaver的支持
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
// 向BeanFactory中注册Environment、系统配置属性、系统环境的信息
// Environment本身对于BeanFactory来讲也是一个Bean
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
7.3.1 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
7.3.1.1 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor的作用
代码清单15:ApplicationContextAwareProcessor.java
@Override
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 如果被处理的Bean不是指定的Aware类型接口,则不予处理
if (!(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)){
return bean;
}
// ...
// 执行Aware接口的回调注入
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return bean;
}
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
// 判断实现的接口,进行强转并调用setter方法
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
由 代码清单15 可知,ApplicationContextAwareProcessor实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,它会判断一个bean对象所属类是实现了指定的内置Aware系列接口。只要检测到bean对象所属类有一个Aware系列接口实现,就会尝试将其强转为对应的Aware接口,并调接口对应的setter方法完成Aware接口的回调注入。
7.3.1.2 ignoreDependencyInterface
从上面的分析可知,Aware系列接口的注入使用的是BeanPostProcessor注入的方式,因此使用ignoreDependencyInterface是为了放弃这些Aware接口在BeanFactory中实现的自动依赖注入,
7.3.2 自动注入的支持
处理完Aware类型的接口后,接下来是向BeanFactory注册几个接口类型与指定对象的映射关系。
代码清单16:AbstractApplicationContext.java
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
代码清单17:DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
private final Map<Class<?>, Object> resolvableDependencies = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
@Override
public void registerResolvableDependency(Class<?> dependencyType, @Nullable Object autowiredValue) {
Assert.notNull(dependencyType, "Dependency type must not be null");
if (autowiredValue != null) {
if (!(autowiredValue instanceof ObjectFactory || dependencyType.isInstance(autowiredValue))) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Value [" + autowiredValue +
"] does not implement specified dependency type [" + dependencyType.getName() + "]");
}
this.resolvableDependencies.put(dependencyType, autowiredValue);
}
}
由 代码清单16、17 可知,registerResolvableDependency方法的作用是使BeanFactory遇到指定类型的对象需要注入时,直接使用映射的对象进行注入。Map集合resolvableDependencies就是负责存储指定类型和对应实现类的集合,后续进行依赖注入时,遇到指定的类型就可以直接从这个Map集合中提取。
7.3.3 ApplicationListenerDetector
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
// 7.3.3 配置一个可加载所有监听器的组件
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
处理完依赖类型后,prepareBeanFactory方法会向BeanFactory注册一个后置处理器ApplicationListenerDetector。
BeanPostProcessorthat detects beans which implement theApplicationListenerinterface. This catches beans that can’t reliably be detected bygetBeanNamesForTypeand related operations which only work against top-level beans.
ApplicationListenerDetector是一个用于检测实现了ApplicationListener接口的Bean的后置处理器,它可以捕获通过getBeanNamesForType方法以及仅对顶级Bean有效的相关操作无法可靠地检测到的Bean。
由javadoc可知,ApplicationListenerDetector的作用是在bean对象初始化阶段检测当前bean对象是否是ApplicationListener,如果是则会进行一些额外的处理:将该bean对象加入到ApplicationContext的监听器集合中。
代码清单18:ApplicationListenerDetector.java
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) {
// potentially not detected as a listener by getBeanNamesForType retrieval
Boolean flag = this.singletonNames.get(beanName);
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(flag)) {
// singleton bean (top-level or inner): register on the fly
// 如果当前bean对象是ApplicationListener且是一个单实例对象
// 则将该bean对象加入到ApplicationContext的监听器集合中
this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean);
}
else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(flag)) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && !this.applicationContext.containsBean(beanName)) {
// inner bean with other scope - can't reliably process events
logger.warn("Inner bean '" + beanName + "' implements ApplicationListener interface " +
"but is not reachable for event multicasting by its containing ApplicationContext " +
"because it does not have singleton scope. Only top-level listener beans are allowed " +
"to be of non-singleton scope.");
}
this.singletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
}
return bean;
}
另外,ApplicationListenerDetector实现了DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,说明其还有对bean对象销毁阶段的处理(postProcessBeforeDestruction方法)。
代码清单19:ApplicationListenerDetector.java
class ApplicationListenerDetector implements DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor, MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) {
try {
// 将监听器类型的bean对象逐个从事件广播器中移除
ApplicationEventMulticaster multicaster = this.applicationContext.getApplicationEventMulticaster();
multicaster.removeApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean);
multicaster.removeApplicationListenerBean(beanName);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// ApplicationEventMulticaster not initialized yet - no need to remove a listener
}
}
}
}
由 代码清单19 可知,ApplicationListenerDetector会在bean对象销毁阶段将监听器类型的bean对象逐个从事件广播器中移除。
至此,IOC容器的刷新完成了前面三步,分别是初始化前的预处理、初始化BeanFactory以及BeanFactory的预处理配置。
本节完,更多内容请查阅分类专栏:SpringBoot源码解读与原理分析