2.5 第四章 堆与拷贝构造函数
一 、程序阅读题
1、给出下面程序输出结果。
#include
class example
{int a;
public:
example(int b=5){a=b++;}
void print(){a=a+1;cout <
void print()const
{cout<
};
void main()
{example x;
const example y(2);
x.print();
y.print();
}
解析:example x;先实例化一个对象x,因为没有传参,所以默认走example(int b=5){a=b++;}着函数,后自加为先赋值a=5后b再自加为6,所以会调用void print()函数,里面a+1后a=6,所有打印出a的值为6
const example y(2);加了const修饰,表示参数不能被修改,实例化一个常对象,所以会调用void print()const函数,因为传了一个参数2,所有走example(int b=5){a=b++;}这条语句后a
=2,b再自加为3,输出直接调用void print()const函数,打印出a的值为2
2、运行程序,写出程序执行的结果。
#include
class Location
{ public:
int X,Y;
void init(int initX,int initY);
int GetX();
int GetY();
};
void Location::init (int initX,int initY)
{X=initX;
Y=initY;
}
int Location::GetX()
{return X;
}
int Location::GetY()
{return Y;
}
void display(Location& rL)
{cout<
}
void main()
{
Location A[5]={{5,5},{3,3},{1,1},{2,2},{4,4}};
Location *rA=A;
A[3].init(7,3);
rA->init(7,8);
for (int i=0;i<5;i++)
display(*(rA++));
}
解析:Location A[5]={{5,5},{3,3},{1,1},{2,2},{4,4}};这句实例化一个对象数组,再用Location *rA=A;这句定义一个指针指向这个数组的首地址即A[0],A[3].init(7,3);这句将A[3]的值改为{7,3},rA->init(7,8);这句直接把首地址A[0]改为{7,8},所以循环打印出来的结果为:
3. 给出下面程序输出结果。
#include
int a[8]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
void fun(int *pa,int n);
void main()
{int m=8;
fun(a,m);
cout<
}
void fun(int *pa,int n)
{for (int i=0;i
*(pa+7)+=*(pa+i);
}
解析:int a[8]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};定义一个全局的数组a[8]里填充7个数,再调用fun
函数给*(pa+7)即a[7]进行赋值,循环执行*(pa+7)+=*(pa+i);语句,第一次将*a的值1给a[7]就是a[7]+=a[0]=0+1=1,第二次a[7]+=*(a+1)就是原本的值加上a[1]=1+2=3,循环到i=6截止,即实现a[7]为a[0]到a[6]值的总和,所以a[7]最后的值是1+2+3+4+5+6+7=28:![]()
4. 给出下面程序输出结果。
#include
class A
{
int *a;
public:
A(int x=0):a(new int(x)){}
~A() {delete a;}
int getA() {return *a;}
void setA(int x) {*a=x;}
};
void main()
{
A x1,x2(3);
A *p=&x2;
(*p).setA(x2.getA()+5);
x1.setA(10+x1.getA());
cout<
}
解析:A x1,x2(3);这句用类A实例化两个对象,x1没有传参,所以调用A(int x=0)函数默认参数x=0,后将x的值赋给x1,即x1=0,x2传了一个参数3,即x=3,赋给x2,即x2=3,A *p=&x2;这句实例化一个指针指向对象x2。(*p).setA(x2.getA()+5);这句先看里面的x2.getA()+5就是将x2的值+5,所有就等于是(*p).setA(8);,即将*p指向的x2的值改为8,所以x2.getA()打印出的值为8,同理,x1.setA(10+x1.getA());;这句先看里面的10+x1.getA(),10加是x1的值,即10+0=0,所以就等于是x1.setA(10),集即将x1的值改为10,所有以x1.getA()打印出来的值为10,因此打印的结果为10 8:![]()
5. 阅读下面的程序,写出运行结果:
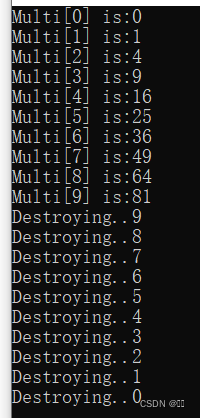
| #include < iostream.> using namespace std; class Samp { public: void Set_i_j(int a, int b){i=a,j=b;} ~Samp() { cout <<"Destroying.." << i < } int GetMulti () { return i * j; } protected: int i; int j; }; int main () { Samp * p; p = new Samp[l0]; if(!p) { cout << "Allocation error \ n"; return; } for(int j =0; j p[j]. Set_i_j (j, j); for(int k=0; k cout <<"Multi[" < delete [ ] p; return 0; } |
解析:Samp * p;先实例化一个指针对象,并用p = new Samp[l0];申请10个数据类型的空内存,Set_i_j(int a, int b)函数是将传过去的参数给GetMulti ()函数使用:将两个参数进行乘法运算,返回运算的结果,for(int j =0; j
6. 写出下面程序的运行结果,请用增加拷贝构造函数的方法避免存在的问题。
| #include < iostream> using namespace std; class Vector { public: Vector (int s = 100); int& Elem(int ndx); void Display(); void Set (); ~Vector (); protected: int size; int* buffer; } Vector::Vector (int s) { buffer = new int [size = s]; for(int i = O; i buffer [i] = i* i; } int& Vector:: Elem(int ndx) { if(ndx< 0 || ndx> = size) { cout << "error in index" < exit (1); } return buffer [ndx]; } void Vector::Display () { for(int j =0; j< size; j ++) cout << buffer[j] < } void Vector:: Set () { for(int j =0; j buffer[j] = j + 1; } Vector:: ~ Vector() { delete [] buffer; } int main() { Vector a(10); Vector b(a); a. Set (); b. Display (); return 0; } 运行结果: |
#include
using namespace std;
class Vector
{
public:
Vector(int s=100);
Vector(const Vector &other);//声明增加的拷贝构造函数
int &Elem(int ndx);
void Display();
void Set();
~Vector();
protected:
int size;
int *buffer;
};
Vector::Vector(int s)
{
buffer=new int[size=s];
for(int i=0;i=size)
{
cout << "error in index" < 7.读下面的程序与运行结果,添上一个拷贝构造函数来完善整个程序。
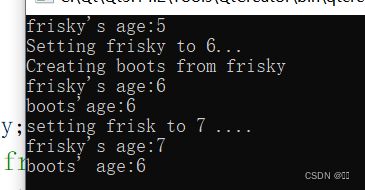
| #include < iostream> using namespace std; class CAT { public: CAT(); CAT(const CAT&); ~CAT(); int GetAge() const (return * itsAge;) void SetAge(int age) { * itsAge = age; } protected: int * itsAge; }; CAT::CAT () { itsAge = new int; *itsAge = 5; } CAT::~CAT () { delete itsAge; itsAge = 0; } void main() { CAT frisky; cout << "frisky's age:" << frisky. GetAge() < cout <<"Setting frisky to 6... \ n"; frisky. SetAge ( 6 ); cout << "Creating boots from frisky \ n"; CAT boots(frisky); cout <<"frisky's age:" << frisky. GetAge() < cout << "boots'age:" << boons. GetAge () < cout << "setting frisk,, to 7 .... n"; frisky. SetAge (7); cout <<"frisky"s age:" << frisky. GetAge() < cout <<"boots' age:" << boots. GetAge() < } |
运行结果为:
frisky's age:5
Setting frisky to 6...
Creating boots from frisky
frisky's age:6
boots' age:6
Setting frisky to 7...
frisky's age:7
boots' age:6
#include
using namespace std;
class CAT
{
public:
CAT();
CAT(const CAT&other);//声明增加的拷贝构造函数
~CAT();
int GetAge()const{return *itsAge;}
void SetAge(int age) {*itsAge=age;}
protected:
int *itsAge;
};
CAT::CAT ()
{
itsAge=new int;
*itsAge=5;
}
CAT::CAT(const CAT&other) //增加的拷贝构造函数
{
itsAge = new int; // 分配新的内存空间
*itsAge = *other.itsAge; // 拷贝年龄值
}
CAT::~CAT ()
{
delete itsAge;
itsAge=0;
}
int main()
{
CAT frisky;
cout << "frisky's age:" << frisky.GetAge() < 运行结果: