Mysql的读写分离(SparingBoot 程序自我设计实现版)
SparingBoot 程序自我设计实现版的读写分离
需先进行主从复制请参考另一篇《Mysql的主从复制和读写分离(中间件Mycal版)》
思路
所谓的手写读写分离,需要用户自定义一个动态的数据源,该数据源可以根据当前上下文中调用方法是读或者是写方法决定返回主库的链接还是从库的链接。这里我们使用Spring提供的一个代理数据源AbstractRoutingDataSource接口
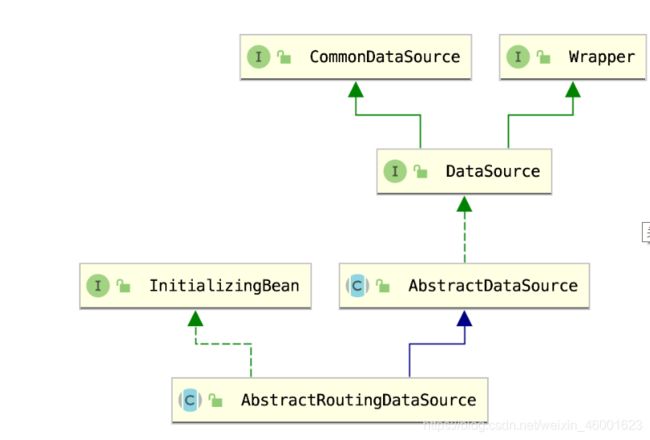
这是AbstractRoutingDataSource接口的血统图
该接口需要用户完善一个determineCurrentLookupKey抽象法,系统会根据这个抽象返回值决定使用系统中定义的数据源。
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
其次该类还有两个属性需要指定defaultTargetDataSource和targetDataSources,其中defaultTargetDataSource需要指定为Master数据源。targetDataSources是一个Map需要将所有的数据源添加到该Map中,以后系统会根据determineCurrentLookupKey方法的返回值作为key从targetDataSources查找相应的实际数据源。如果找不到则使用defaultTargetDataSource指定的数据源。
实现的步骤
1,用JAVA 配置 自定义配置数据源来替换系统的数据源
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ExecutorType;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
//java 配置
@Configuration
public class UserDefineDatasourceConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.sparktwo")//主~写
public DataSource sparkTwoDataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.mysql01")//从 1~读
public DataSource mysql01DataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.mysql02")//从 2~读
public DataSource mysql02DataSource(){
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
//@Qualifier的意思是合格者,通过这个标示,表明了哪个实现类才是我们所需要的
@Bean
public DataSource proxyDataSource(@Qualifier("sparkTwoDataSource") DataSource sparkTwoDataSource,
@Qualifier("mysql01DataSource") DataSource mysql01DataSource,
@Qualifier("mysql02DataSource") DataSource mysql02DataSource
){
DataSourceProxy proxy = new DataSourceProxy();
proxy.setDefaultTargetDataSource(sparkTwoDataSource);//设置默认数据源
Map mappedDataSource=new HashMap<>();
mappedDataSource.put("sparkTwo",sparkTwoDataSource);
mappedDataSource.put("mysql01",mysql01DataSource);
mappedDataSource.put("mysql02",mysql02DataSource);
proxy.setTargetDataSources(mappedDataSource); //注册所有数据源
return proxy;
}
/**
* 当自定义数据源,用户必须覆盖SqlSessionFactory创建
* @param dataSource
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("proxyDataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.baizhi.entity");//实体类所在位置
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:com/baizhi/mapper/UserDao*.xml"));
return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject();
}
/**
* 当自定义数据源,用户必须覆盖SqlSessionTemplate,开启BATCH处理模式
* @param sqlSessionFactory
* @return
*/
@Bean//等同与之前配置的的开启mybatis 的批处理
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType.BATCH);
}
/***
* 当自定义数据源,用户必须注入,否则事务控制不生效
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager(@Qualifier("proxyDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
2,自定义配置切面来判断那些是读操作那些是写操作
需要先导依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-aop
1.5.8.RELEASE
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Aspect //代表切面
@Component //交给工厂
@Order(0) //控制切面顺序,保证在事务切面之前运行切面 正数数字越小代表优先级越高
public class ServiceMethodAOP {
//环绕通知,execution(* com.baizhi.service..*.*(..))表示对整个业务层所有方法都环绕
@Around("execution(* com.baizhi.service..*.*(..))")
public Object methodInterceptor(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
Object result = null;
try{
//获取当前的方法信息
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();//拿到方法对象
//判断方法上是否存在注解@SlaveDB
boolean present = method.isAnnotationPresent(SlaveDB.class);
if(present){
//读
OperTypeContextHolder.setOperType(OperType.READ);
}else{
//写
OperTypeContextHolder.setOperType(OperType.WRIRTE);
}
result= pjp.proceed();//把方法查到的数据传出去
//清除线程变量
OperTypeContextHolder.clear();
}catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
3,自定义动态数据源类,属于代理数据源,负责负载均衡
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class DataSourceProxy extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
/**
* 实现了负载均衡策略
* */
private String masterDBKey="sparkTwo";//写 数据源的key
private List slaveDBKeys= Arrays.asList("mysql01","mysql02");//读 数据源的key
private static final AtomicInteger round=new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
OperType operType = OperTypeContextHolder.getOperType();
String dbkey=null;
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("mysql01");
list.add("mysql02");
if (operType.equals(OperType.WRIRTE)){
//写操作
dbkey ="sparkTwo";
}else{
//读
// 轮询
int andIncrement = round.getAndIncrement();//每次来自动加一
//因为一直加可能会加到int值变成负数所以
if(andIncrement<0){
round.set(0);//让round的值重新为零
}
// round.get();取出它的值
int i= round.get()%slaveDBKeys.size();
dbkey=slaveDBKeys.get(i);
}
return dbkey;
}
}
A,自定义注解 用来标识那些方法为读
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 注解@Retention可以用来修饰注解,是注解的注解,称为元注解。
* Retention注解有一个属性value,是RetentionPolicy类型的,Enum RetentionPolicy是一个枚举类型,
* 这个枚举决定了Retention注解应该如何去保持,也可理解为Rentention 搭配 RententionPolicy使用。RetentionPolicy有3个值:CLASS RUNTIME SOURCE
* 按生命周期来划分可分为3类:
* 1、RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:注解只保留在源文件,当Java文件编译成class文件的时候,注解被遗弃;
* 2、RetentionPolicy.CLASS:注解被保留到class文件,但jvm加载class文件时候被遗弃,这是默认的生命周期;
* 3、RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在;
* 这3个生命周期分别对应于:Java源文件(.java文件) ---> .class文件 ---> 内存中的字节码。
*/
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
/**
* @Target:注解的作用目标
* @Target(ElementType.TYPE)—— 接口、类、枚举、注解
* @Target(ElementType.FIELD)—— 字段、枚举的常量
* @Target(ElementType.METHOD)—— 方法
* @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)—— 方法参数
* @Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) —— 构造函数
* @Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)—— 局部变量
* @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)—— 注解
* @Target(ElementType.PACKAGE)—— 包
* */
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface SlaveDB {
}
B 枚举类型 用来传递那些是写那些是读
public enum OperType {
WRIRTE,READ;
}
C 记录操作类型的自定义类
/**
* 通过线程本地变量传递操作类型
* ThreadLocal 线程本地变量,在一个线程里,我们可以通过它来传递信息
*/
public class OperTypeContextHolder {
//常量 名全大写
private static final ThreadLocal OPER_TYPE_THREAD_LOCAL=new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setOperType(OperType operType){
OPER_TYPE_THREAD_LOCAL.set(operType);
}
public static OperType getOperType(){
return OPER_TYPE_THREAD_LOCAL.get();
}
public static void clear(){//清空
OPER_TYPE_THREAD_LOCAL.remove();
}
}
最后别忘了在application.properties 配置文件配置
配置自定义数据源
spring.datasource.sparktwo.username=root
spring.datasource.sparktwo.password=root
spring.datasource.sparktwo.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.sparktwo.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://SparkTwo:3306/text?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.mysql01.username=root
spring.datasource.mysql01.password=root
spring.datasource.mysql01.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.mysql01.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://Mysql01:3306/text?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.mysql02.username=root
spring.datasource.mysql02.password=root
spring.datasource.mysql02.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.mysql02.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://Mysql02:3306/text?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false