黑马Java——面向对象
目录
1.类和对象
1.2 类的定义
1.1 类和对象的理解
2.封装
2.1封装
2.2private关键字
3.就近原则和this关键字
4.构造方法
构造方法的注意事项
5.标准的javabean类
6.三种情况的对象内存图
6.1单个对象内存图
6.2多个对象内存图
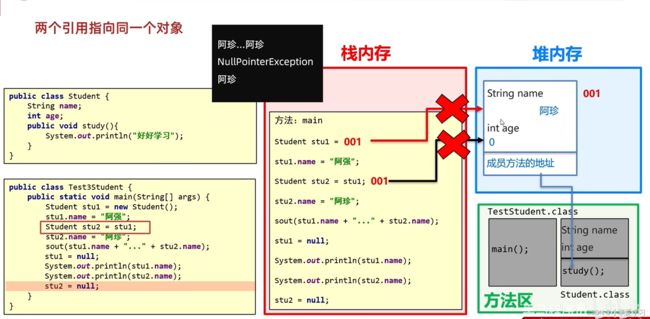
6.3两个引用指向同一个对象
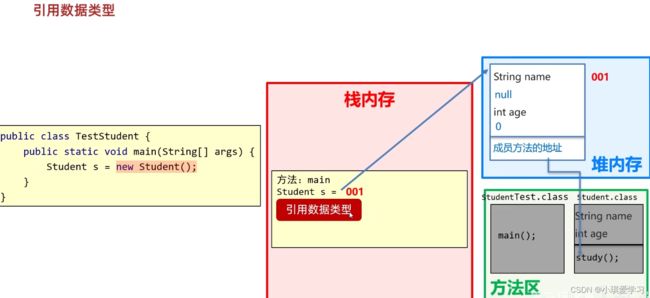
7.基本数据类型和引用数据类型编辑
8.this的内存原理
8.1this
编辑8.2成员变量与局部变量的区别
9.面向对象综合练习
9.1文字版格斗游戏
9.2文字版格斗游戏进阶
9.3对象数组商品
9.4对象数组(汽车)
9.5对象数组(手机)
9.6对象数组(女朋友)
9.7复杂的对象数组操作
要求1:再次添加一个学生对象,并在添加的时候进行学号的唯一性判断。
要求3:通过id删除学生信息
要求5:查询数组id为“heima002”的学生,如果存在,则将他的年龄+1岁
Alt+左键(选中,批量修改)
Alt+insert(生成构造方法快捷方式)/Alt+Fn+insert——>constractor/grtter and setter——>全选
插件PTG,一秒生成标准javabean(在idea中的 setting——>plugins——>搜索ptg下载安装)
PTG用法:右键点击空白处——>ptg to javabean
1.类和对象
1.2 类的定义
类的组成是由属性和行为两部分组成
-
1.1 类和对象的理解
客观存在的事物皆为对象 ,所以我们也常常说万物皆对象。
-
类
-
类的理解
-
类是对现实生活中一类具有共同属性和行为的事物的抽象
-
类是对象的数据类型,类是具有相同属性和行为的一组对象的集合
-
简单理解:类就是对现实事物的一种描述
-
-
类的组成
-
属性:指事物的特征,例如:手机事物(品牌,价格,尺寸)
-
行为:指事物能执行的操作,例如:手机事物(打电话,发短信)
-
-
-
类和对象的关系
-
类:类是对现实生活中一类具有共同属性和行为的事物的抽象
-
对象:是能够看得到摸的着的真实存在的实体
-
简单理解:类是对事物的一种描述,对象则为具体存在的事物
-
-
属性:在类中通过成员变量来体现(类中方法外的变量)
-
行为:在类中通过成员方法来体现(和前面的方法相比去掉static关键字即可)
如何定义类及如何得到类的对象及如何使用对象:
定义类的补充注意事项:
- 用来描述一类事物的类,专业方法叫做Javabean类。在Javabean类中,是不写main方法的。
- 在之前,编写main方法的类,叫做测试类。我们可以在测试类中创建javabean类的对象并进行赋值调用。
-
类名首字母建议大写,需要见名知意,驼峰模式。
-
一个Java文件中可以定义多个class类,且只能一个类是public修饰,而且public修饰的类名必须成为代码文件名。(实际开发中建议一个文件定义一个calss类)。
-
成员变量的完整定义格式是:修饰符 数据类型 变量名称 = 初始化值一般无需定义初始化值,存在默认值。
2.封装
2.1封装
封装就是告诉我们,如何正确设计对象的属性和方法。
对象代表什么,就要封装对应数据,并为数据提供相应行为。
-
封装概述 是面向对象三大特征之一(封装,继承,多态)
对象代表什么,就得封装对应的数据,并提供数据对应的行为
-
封装代码实现 将类的某些信息隐藏在类内部,不允许外部程序直接访问,而是通过该类提供的方法来实现对隐藏信息的操作和访问 成员变量private,提供对应的getXxx()/setXxx()方法
-
封装的好处:编程简单,降低学习成本
2.2private关键字
- private关键字是一个权限修饰符
- 可以用来修饰成员(成员变量和成员方法)
- 被private修饰的成员,只能在本类进行访问
- 针对private修饰的成员变量,如果需要被其他类使用,提供相应的操作
- 提供“get变量名()”方法,用于获取成员变量的值,方法用public修饰
- 提供“set变量名(参数)”方法,用于设置成员变量的值,方法用public修饰
示例代码:
/*
学生类
*/
class Student {
//成员变量
String name;
private int age;
//提供get/set方法
public void setAge(int a) {
if(a<0 || a>120) {
System.out.println("你给的年龄有误");
} else {
age = a;
}
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
//成员方法
public void show() {
System.out.println(name + "," + age);
}
}
/*
学生测试类
*/
public class StudentDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象
Student s = new Student();
//给成员变量赋值
s.name = "林青霞";
s.setAge(30);
//调用show方法
s.show();
}
}/*
学生类
*/
class Student {
//成员变量
String name;
private int age;
//提供get/set方法
public void setAge(int a) {
if(a<0 || a>120) {
System.out.println("你给的年龄有误");
} else {
age = a;
}
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
//成员方法
public void show() {
System.out.println(name + "," + age);
}
}
/*
学生测试类
*/
public class StudentDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象
Student s = new Student();
//给成员变量赋值
s.name = "林青霞";
s.setAge(30);
//调用show方法
s.show();
}
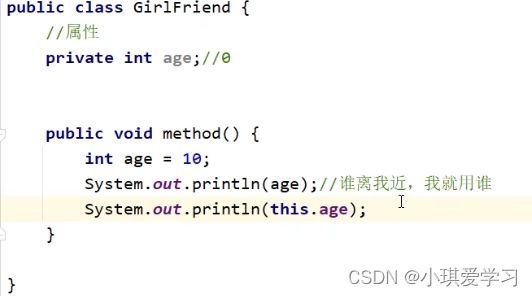
}3.就近原则和this关键字
成员变量:变量定义在方法内。
局部变量:变量定义在类中。
如果说和成员变量的名字一样就就近原则谁理我近,我用谁
System.out.println(age);//先找局部,局部没有,再找成员变量
System.out.println(this.age);//直接使用成员变量的age-
this修饰的变量用于指代成员变量,其主要作用是(区分局部变量和成员变量的重名问题)
-
方法的形参如果与成员变量同名,不带this修饰的变量指的是形参,而不是成员变量
-
方法的形参没有与成员变量同名,不带this修饰的变量指的是成员变量
-
当两种变量同名,使用变量时,触发就近原则。 用this.age就打印的是局部变量的值。
形参name赋值给局部变量name。
4.构造方法
构造方法也叫作构造器、构造函数
作用:在创建对象的时候给成员变量进行赋值的。
构造方法是一种特殊的方法
作用:创建对象 Student stu = new Student();
格式:
public class 类名{
修饰符 类名( 参数 ) {
方法;
}
}
功能:主要是完成对象数据的初始化
构造方法作用:创建对象的时候,由虚拟机自动调用(不是手动调用),给成员变量进行初始化。
成员方法与构造方法区别:
(1)构造方法主要用来给对象的数据进行初始化。
(2)成员方法一般实现对类中成员变量的操作(修改值,获取值),提供某些功能,有返回类型,可以为void类型。
(3)构造方法通过new运算符调用,成员方法通过对象调用。
构造方法的注意事项
-
构造方法的定义
如果没有定义构造方法,系统将给出一个默认的无参数构造方法 如果定义了构造方法,系统将不再提供默认的构造方法
-
构造方法的重载
如果自定义了带参构造方法,还要使用无参数构造方法,就必须再写一个无参数构造方法
-
推荐的使用方式
无论是否使用,都手工书写无参数构造方法,和带全部参数的构造方法
-
重要功能!
可以使用带参构造,为成员变量进行初始化
5.标准的javabean类
Alt+insert(生成构造方法快捷方式)/Alt+Fn+insert——>constractor/grtter and setter——>全选
插件PTG,一秒生成标准javabean(在idea中的 setting——>plugins——>搜索ptg下载安装)
PTG用法:右键点击空白处——>ptg to javabean
① 类名需要见名知意
② 成员变量使用private修饰
③ 提供至少两个构造方法
-
无参构造方法
-
带全部参数的构造方法
④ get和set方法
提供每一个成员变量对应的setXxx()/getXxx()
⑤ 如果还有其他行为,也需要写上
6.三种情况的对象内存图
6.1单个对象内存图
当所有都执行完后,study方法会先出栈,然后是main方法出栈,并且main里的变量会消失,因为没有变量再指向堆内存的这个空间(对象),这个空间也会消失。
6.2多个对象内存图
创建第二个对象的时候,不会重新加载class文件,而且在堆内存开辟的空间与第一个对象开辟的堆内存互不影响。
6.3两个引用指向同一个对象
7.基本数据类型和引用数据类型

基本数据类型:在变量中存储的是真实的数据值,存储在自己的空间中,与其它空间无关。
引用数据类型:创建的对象、数组,都是引用数据类型。引用其他空间数据。
8.this的内存原理
8.1this
this的作用:区分局部变量和成员变量。
this的本质:所在方法调用者的地址值。
 8.2成员变量与局部变量的区别
8.2成员变量与局部变量的区别
9.面向对象综合练习
9.1文字版格斗游戏
需求:
格斗游戏,每个游戏角色的姓名,血量,都不相同,在选定人物的时候(new对象的时候),这些信息就应该被确定下来。
举例:
程序运行之后结果为:
姓名为:乔峰 血量为:100
姓名为:鸠摩智 血量为:100
乔峰举起拳头打了鸠摩智一下,造成了XX点伤害,鸠摩智还剩下XXX点血。
鸠摩智举起拳头打了鸠摩智一下,造成了XX点伤害,乔峰还剩下XXX点血。
乔峰举起拳头打了鸠摩智一下,造成了XX点伤害,鸠摩智还剩下XXX点血。
鸠摩智举起拳头打了鸠摩智一下,造成了XX点伤害,乔峰还剩下XXX点血。
乔峰K.O.了鸠摩智
public class GameTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建第一个角色
Role r1 = new Role("乔峰",100);
//2.创建第二个角色
Role r2 = new Role("鸠摩智",100);
//3.开始格斗 回合制游戏
while(true){
//r1开始攻击r2
r1.attack(r2);
//判断r2的剩余血量
if(r2.getBlood() == 0){
System.out.println(r1.getName() + " K.O了" + r2.getName());
break;
}
//r2开始攻击r1
r2.attack(r1);
if(r1.getBlood() == 0){
System.out.println(r2.getName() + " K.O了" + r1.getName());
break;
}
}
}
}
public class Role {
private String name;
private int blood;
public Role() {
}
public Role(String name, int blood) {
this.name = name;
this.blood = blood;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getBlood() {
return blood;
}
public void setBlood(int blood) {
this.blood = blood;
}
//定义一个方法用于攻击别人
//思考:谁攻击谁?
//Role r1 = new Role();
//Role r2 = new Role();
//r1.攻击(r2);
//方法的调用者去攻击参数
public void attack(Role role) {
//计算造成的伤害 1 ~ 20
Random r = new Random();
int hurt = r.nextInt(20) + 1;
//剩余血量
int remainBoold = role.getBlood() - hurt;
//对剩余血量做一个验证,如果为负数了,就修改为0
remainBoold = remainBoold < 0 ? 0 : remainBoold;
//修改一下挨揍的人的血量
role.setBlood(remainBoold);
//this表示方法的调用者
System.out.println(this.getName() + "举起拳头,打了" + role.getName() + "一下," +
"造成了" + hurt + "点伤害," + role.getName() + "还剩下了" + remainBoold + "点血");
}
}9.2文字版格斗游戏进阶
在上一个的基础上,我想看到人物的性别和长相,打斗的时候我想看到武功招式。
举例:
程序运行之后结果为:
姓名为:乔峰 血量为:100 性别为:男 长相为:气宇轩昂
姓名为:鸠摩智 血量为:100 性别为:男 长相为:气宇轩昂
乔峰使出了一招【背心钉】,转到对方的身后,一掌向鸠摩智背心的灵台穴拍去。给鸠摩智造成一处瘀伤。
鸠摩智使出了一招【游空探爪】,飞起身形自半空中变掌为抓锁向乔峰。结果乔峰退了半步,毫发无损。
。。。。
乔峰K.O.了鸠摩智
分析:
长相是提前定义好的,提前放在一个数组当中,程序运行之后,从数组中随机获取。
package com.yaqi.test2;
public class GameTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建第一个角色
Role r1 = new Role("乔峰", 100, '男');
//2.创建第二个角色
Role r2 = new Role("鸠摩智", 100, '男');
//展示一下角色信息
r1.showRoleInfo();
r2.showRoleInfo();
//3.开始格斗,回合制游戏
while (true) {
//r1开始进攻r2
r1.atttack(r2);
//判断r2的剩余血量
if (r2.getBlood() == 0) {
System.out.println(r1.getName() + "K.O了" + r2.getName());
break;
}
//r2开始进攻r1
r2.atttack(r1);
//判断r1的血量
if (r1.getBlood() == 0) {
System.out.println(r2.getName() + "K.O了" + r1.getName());
break;
}
}
}
}
package com.yaqi.test2;
import java.util.Random;
public class Role {
private String name;
private int blood;
private char gender;
private String face;//长相是随机的
String[] boyfaces = {"风流俊雅", "气宇轩昂", "相貌英俊", "五官端正", "相貌平平", "一塌糊涂", "面目狰狞"};
String[] girlfaces = {"美奂绝伦", "沉鱼落雁", "婷婷玉立", "身材娇好", "相貌平平", "相貌简陋", "惨不忍睹"};
//attack 攻击描述:
String[] attacks_desc = {
"%s使出了一招【背心钉】,转到对方的身后,一掌向%s背心的灵台穴拍去。",
"%s使出了一招【游空探爪】,飞起身形自半空中变掌为抓锁向%s。",
"%s大喝一声,身形下伏,一招【劈雷坠地】,捶向%s双腿。",
"%s运气于掌,一瞬间掌心变得血红,一式【掌心雷】,推向%s。",
"%s阴手翻起阳手跟进,一招【没遮拦】,结结实实的捶向%s。",
"%s上步抢身,招中套招,一招【劈挂连环】,连环攻向%s。"
};
//injured 受伤描述:
String[] injureds_desc = {
"结果%s退了半步,毫发无损",
"结果给%s造成一处瘀伤",
"结果一击命中,%s痛得弯下腰",
"结果%s痛苦地闷哼了一声,显然受了点内伤",
"结果%s摇摇晃晃,一跤摔倒在地",
"结果%s脸色一下变得惨白,连退了好几步",
"结果『轰』的一声,%s口中鲜血狂喷而出",
"结果%s一声惨叫,像滩软泥般塌了下去"
};
public Role() {
}
public Role(String name, int blood, char gender) {
this.name = name;
this.blood = blood;
this.gender = gender;
//随机长相
setFace(gender);
}
public char getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(char gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getFace() {
return face;
}
public void setFace(char gender) {
Random r = new Random();
//长相是随机的
if (gender == '男') {
//从boyfaces里面随机长相
int index = r.nextInt(boyfaces.length);
this.face = boyfaces[index];
} else if (gender == '女') {
//从girlfaces里面随机长相
int index = r.nextInt(girlfaces.length);
this.face = girlfaces[index];
} else {
this.face = "面目狰狞";
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getBlood() {
return blood;
}
public void setBlood(int blood) {
this.blood = blood;
}
//定义一个方法用于攻击别人
//思考:谁攻击谁?
//Role r1 = new Role();
//Role r2 = new Role();
//r1.攻击(r2);
//方法的调用者去攻击参数
public void atttack(Role role) {
Random r = new Random();
int index = r.nextInt(attacks_desc.length);
String kungFu = attacks_desc[index];
//输出一个攻击效果
System.out.printf(kungFu, this.getName(), role.getName());
//计算造成的伤害1~20
int hurt = r.nextInt(20) + 1;
//剩余血量
int remainBoold = role.getBlood() - hurt;
//对剩余血量做一个验证,如果为负数了,就修改为0
remainBoold = remainBoold < 0 ? 0 : remainBoold;
//修改一些挨揍的人的血量
role.setBlood(remainBoold);
//受伤的描述
//受伤的描述
//血量> 90 0索引的描述
//80 ~ 90 1索引的描述
//70 ~ 80 2索引的描述
//60 ~ 70 3索引的描述
//40 ~ 60 4索引的描述
//20 ~ 40 5索引的描述
//10 ~ 20 6索引的描述
//小于10的 7索引的描述
if (remainBoold > 90) {
System.out.printf(injureds_desc[0], role.getName());
} else if (remainBoold > 80 && remainBoold <= 90) {
System.out.printf(injureds_desc[1], role.getName());
} else if (remainBoold > 70 && remainBoold <= 80) {
System.out.printf(injureds_desc[2], role.getName());
} else if (remainBoold > 60 && remainBoold <= 70) {
System.out.printf(injureds_desc[3], role.getName());
} else if (remainBoold > 40 && remainBoold <= 60) {
System.out.printf(injureds_desc[4], role.getName());
} else if (remainBoold > 20 && remainBoold <= 40) {
System.out.printf(injureds_desc[5], role.getName());
} else if (remainBoold > 10 && remainBoold <= 20) {
System.out.printf(injureds_desc[6], role.getName());
} else {
System.out.printf(injureds_desc[7], role.getName());
}
System.out.println();
}
public void showRoleInfo() {
System.out.println("姓名为:" + getName());
System.out.println("血量为:" + getBlood());
System.out.println("性别为:" + getGender());
System.out.println("长相为:" + getFace());
}
}
9.3对象数组商品
需求:
定义数组存储3个商品对象。
商品的属性:商品的id,名字,价格,库存。
创建三个商品对象,并把商品对象存入到数组当中。
代码示例:
package com.yaqi.test3;
public class Goods {
private String id;
private String name;
private double price;
private int count;
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(String id, String name, double price, int count) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.count = count;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
}
package com.yaqi.test3;
public class GoodsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个数组
Goods[] arr = new Goods[3];
//2.创建三个商品对象
Goods g1 = new Goods("001","华为P40",5999.9,100);
Goods g2 = new Goods("002","保温杯",227.0,50);
Goods g3 = new Goods("003","枸杞",12.7,70);
//3.把商品添加到数组中
arr[0] = g1;
arr[1] = g2;
arr[2] = g3;
//4.遍历
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//i索引arr[i]元素
Goods goods = arr[i];
System.out.println(goods.getId()+","+goods.getName()+","+goods.getPrice()+","+goods.getCount());
}
}
}
9.4对象数组(汽车)
需求:
定义数组存储3部汽车对象。
汽车的属性:品牌,价格,颜色。
创建三个汽车对象,数据通过键盘录入而来,并把数据存入到数组当中。
package com.yaqi.test5;
public class Car {
private String brand;//品牌
private int price;//价格
private String color;//颜色
public Car() {
}
public Car(String brand, int price, String color) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
this.color = color;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
package com.yaqi.test5;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CarTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个数组用来存储3个汽车对象
Car[] arr = new Car[3];
//2.创建汽车对象,数据来自键盘录入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//创建汽车对象
Car c = new Car();
//录入品牌
System.out.println("请输入汽车品牌");
String brand = sc.next();
c.setBrand(brand);
//录入价格
System.out.println("请输入汽车价格");
int price = sc.nextInt();
c.setPrice(price);
//录入汽车颜色
System.out.println("请输入汽车颜色");
String color = sc.next();
c.setColor(color);
//把汽车对象放到数组中
arr[i] = c;//[c,c,c]
}
//3.遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
Car car = arr[i];
System.out.println(car.getBrand()+","+car.getPrice()+","+car.getColor());
}
}
}
9.5对象数组(手机)
需求 :
定义数组存储3部手机对象。
手机的属性:品牌,价格,颜色。
要求,计算出三部手机的平均价格
package com.yaqi.test6;
public class Phone {
private String brand;//品牌
private int price;//价格
private String color;//颜色
public Phone() {
}
public Phone(String brand, int price, String color) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
this.color = color;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
package com.yaqi.test6;
public class PhoneTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个数组
Phone[] arr = new Phone[3];
//2.创建手机的对象
Phone p1 = new Phone("小米",1999,"白色");
Phone p2 = new Phone("华为",4999,"蓝色");
Phone p3 = new Phone("魅族",3999,"红色");
//3.把手机对象添加到数组当中
arr[0] = p1;
arr[1] = p2;
arr[2] = p3;
//4.获取三部手机的平均价格
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//i索引 arr[i] 元素(手机对象)
Phone phone = arr[i];
sum = sum + phone.getPrice();
}
//5.求平均价格
//数据不写死,尽量不写死
//int avg = sum / arr.length;
double avg2 = sum * 1.0 / arr.length;
System.out.println(avg2);//3665.6666666666665
}
}
9.6对象数组(女朋友)
需求:
定义数组存储4个女朋友的对象
女朋友的属性:姓名、年龄、性别、爱好
要求1:计算出四女朋友的平均年龄
要求2:统计年龄比平均值低的女朋友有几个?并把她们的所有信息打印出来。
代码示例:
package com.yaqi.test7;
public class GrilFriend {
private String name;//姓名
private int age;//年龄
private String gender;//性别
private String hobby;//爱好
public GrilFriend() {
}
public GrilFriend(String name, int age, String gender, String hobby) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getHobby() {
return hobby;
}
public void setHobby(String hobby) {
this.hobby = hobby;
}
}
package com.yaqi.test7;
public class GrilFriendTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.定义数组用来存入女朋友的对象
GrilFriend[] arr = new GrilFriend[4];
//2.创建女朋友对象
GrilFriend gf1 = new GrilFriend("小诗诗", 18, "萌妹子", "吃零食");
GrilFriend gf2 = new GrilFriend("小丹丹", 19, "萌妹子", "玩游戏");
GrilFriend gf3 = new GrilFriend("小慧慧", 20, "萌妹子", "看书");
GrilFriend gf4 = new GrilFriend("小莉莉", 21, "萌妹子", "睡觉");
//3.把对象添加到数组中
arr[0] = gf1;
arr[1] = gf2;
arr[2] = gf3;
arr[3] = gf4;
//4.求和
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//i索引 arr[i] 元素(女朋友对象)
GrilFriend gf = arr[i];
//累加
sum = sum + gf.getAge();
}
//5.平均值
int avg = sum / arr.length;
//6.统计年龄比平均值低的有几个,打印他们的信息
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
GrilFriend gf = arr[i];
if (gf.getAge() < avg) {
count++;
System.out.println(gf.getName() + "," + gf.getAge() + "," + gf.getGender() + "," + gf.getHobby());
}
}
System.out.println(count+"个");
}
}
9.7复杂的对象数组操作
定义一个长度为3的数组,数组存储1~3名学生对象作为初始数据,学生对象的学号,姓名各不相同。
学生的属性:学号,姓名,年龄。
要求1:再次添加一个学生对象,并在添加的时候进行学号的唯一性判断。
要求2:添加完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
要求3:通过id删除学生信息
如果存在,则删除,如果不存在,则提示删除失败。
要求4:删除完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
要求5:查询数组id为“heima002”的学生,如果存在,则将他的年龄+1岁
代码示例:
-
要求1:再次添加一个学生对象,并在添加的时候进行学号的唯一性判断。
- 要求2:添加完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
package com.yaqi.test8;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.yaqi.test8;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*定义一个长度为3的数组,数组存储1~3名学生对象作为初始数据,学生对象的学号,姓名各不相同。
学生的属性:学号,姓名,年龄。
要求1:再次添加一个学生对象,并在添加的时候进行学号的唯一性判断。
要求2:添加完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
要求3:通过id删除学生信息
如果存在,则删除,如果不存在,则提示删除失败。
要求4:删除完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
要求5:查询数组id为“2”的学生,如果存在,则将他的年龄+1岁
*/
//1.创建一个数组用来存储学生对象
Student[] arr = new Student[3];
//2.创建学生对象添加到数组当中
Student stu1 = new Student(001, "张三", 23);
Student stu2 = new Student(002, "李四", 24);
Student stu3 = new Student(003, "王五", 25);
//3.把学生对象添加到数组当中
arr[0] = stu1;
arr[1] = stu2;
arr[2] = stu3;
//要求1:再次添加一个学生对象,并在添加的时候进行学号的唯一性判断。
Student stu4 = new Student(004, "小汪", 25);
//唯一性判断
//已存在 --- 不用添加
//不存在 --- 就可以把学生对象添加进数组
boolean flag = contains(arr, stu4.getId());
if (flag) {
//已存在 --- 不用添加
System.out.println("当前id重复,请修改id后再进行添加");
} else {
//不存在 --- 就可以把学生对象添加进数组
//把stu4添加到数组当中
//1.数组已经存满 --- 只能创建一个新的数组,新数组的长度 = 老数组 + 1
//2.数组没有存满 --- 直接添加
int count = getCount(arr);
if (count == arr.length) {
//已经存满
Student[] newArr = creatNewArr(arr);
//把stu4添加进去
newArr[count] = stu4;
//要求2:添加完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
printArr(newArr);
} else {
//没有存满
//[stu1,stu2,null]
//getCount获取到的是2,表示数组当中已经有了2个元素
//还有一层意思:如果下一次要添加数据,就是添加到2索引的位置
arr[count] = stu4;
//要求2:添加完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
printArr(arr);
}
}
}
//遍历方法
public static void printArr(Student[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
Student stu = arr[i];
if (stu != null) {
System.out.println(stu.getId() + ", " + stu.getName() + ", " + stu.getAge());
}
}
}
//创建一个新的数组,长度 = 老数组的长度 + 1
//然后把老数组的元素,拷贝到新数组当中
public static Student[] creatNewArr(Student[] arr) {
Student[] newArr = new Student[arr.length + 1];
//循环遍历得到老数组中的每一个元素
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//把老数组中的元素添加到新数组当中
newArr[i] = arr[i];
}
//把新数组返回
return newArr;
}
//定义一个方法判断数组中已经存了几个元素
public static int getCount(Student[] arr) {
//定义一个计数器用来统计
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] != null) {
count++;
}
}
//当循环结束之后,我就知道了数组中一共有几个元素
return count;
}
//判断唯一性方法
//1.我要干嘛? 唯一性判断
//2.我干这件事情,需要什么才能完成? 数组 id
//3.调用处是否需要继续使用方法的结果? 必须返回
public static boolean contains(Student[] arr, int id) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//依次获取到数组里面的每一个学生对象
Student stu = arr[i];
if (stu != null) {
//获取数组中学生对象的id
int sid = stu.getId();
//比较
if (sid == id) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
-
要求3:通过id删除学生信息
- 如果存在,则删除,如果不存在,则提示删除失败。
package com.yaqi.test8;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*定义一个长度为3的数组,数组存储1~3名学生对象作为初始数据,学生对象的学号,姓名各不相同。
学生的属性:学号,姓名,年龄。
要求3:通过id删除学生信息
如果存在,则删除,如果不存在,则提示删除失败。
要求4:删除完毕之后,遍历所有学生信息。
*/
//1.创建一个数组用来存储学生对象
Student[] arr = new Student[3];
//2.创建学生对象并添加到数组当中
Student stu1 = new Student(1, "zhangsan", 23);
Student stu2 = new Student(2, "lisi", 24);
Student stu3 = new Student(3, "wangwu", 25);
//3.把学生对象添加到数组当中
arr[0] = stu1;
arr[1] = stu2;
arr[2] = stu3;
/*要求3:通过id删除学生信息
如果存在,则删除,如果不存在,则提示删除失败。*/
//要找到id在数组中对应的索引
int index = getIndex(arr, 2);
if (index >= 0){
//如果存在,则删除
arr[index] = null;
//遍历数组
printArr(arr);
}else{
//如果不存在,则提示删除失败
System.out.println("当前id不存在,删除失败");
}
}
//1.我要干嘛? 找到id在数组中的索引
//2.我需要什么? 数组 id
//3.调用处是否需要继续使用方法的结果? 要
public static int getIndex(Student[] arr , int id){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//依次得到每一个学生对象
Student stu = arr[i];
//对stu进行一个非空判断
if(stu != null){
int sid = stu.getId();
if(sid == id){
return i;
}
}
}
//当循环结束之后,还没有找到就表示不存在
return -1;
}
public static void printArr(Student[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
Student stu = arr[i];
if(stu != null){
System.out.println(stu.getId() + ", " + stu.getName() + ", " + stu.getAge());
}
}
}
}
-
要求5:查询数组id为“heima002”的学生,如果存在,则将他的年龄+1岁
package com.yaqi.test8;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*定义一个长度为3的数组,数组存储1~3名学生对象作为初始数据,学生对象的学号,姓名各不相同。
学生的属性:学号,姓名,年龄。
要求5:查询数组id为“2”的学生,如果存在,则将他的年龄+1岁*/
//1.创建一个数组用来存储学生对象
Student[] arr = new Student[3];
//2.创建学生对象并添加到数组当中
Student stu1 = new Student(1, "zhangsan", 23);
Student stu2 = new Student(2, "lisi", 24);
Student stu3 = new Student(3, "wangwu", 25);
//3.把学生对象添加到数组当中
arr[0] = stu1;
arr[1] = stu2;
arr[2] = stu3;
//4.先要找到id为2的学生对于的索引
int index = getIndex(arr, 2);
//5.判断索引
if(index >= 0){
//存在, 则将他的年龄+1岁
Student stu = arr[index];
//把原来的年龄拿出来
int newAge = stu.getAge() + 1;
//把+1之后的年龄塞回去
stu.setAge(newAge);
//遍历数组
printArr(arr);
}else{
//不存在,则直接提示
System.out.println("当前id不存在,修改失败");
}
}
//1.我要干嘛? 找到id在数组中的索引
//2.我需要什么? 数组 id
//3.调用处是否需要继续使用方法的结果? 要
public static int getIndex(Student[] arr , int id){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//依次得到每一个学生对象
Student stu = arr[i];
//对stu进行一个非空判断
if(stu != null){
int sid = stu.getId();
if(sid == id){
return i;
}
}
}
//当循环结束之后,还没有找到就表示不存在
return -1;
}
public static void printArr(Student[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
Student stu = arr[i];
if(stu != null){
System.out.println(stu.getId() + ", " + stu.getName() + ", " + stu.getAge());
}
}
}
}