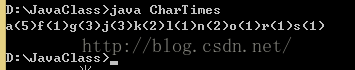黑马程序员——集合——Collection、List、set、Map
------Java培训、Android培训、iOS培训、.Net培训、期待与您交流! -------
集合
集合:
1.容器—用于存储对象(不可以存储基本类型,要用包装类来存储)的容器。
2.集合的长度可变(相当于是一个可变长度的数组,但是数组中可以存储基本数据类型),且存入的类型可以不同(但是貌似很少存不同类型的)。
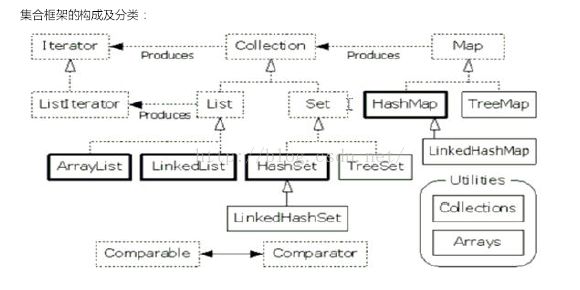
集合框架:
学习集合要从集合的最共性的方法开始学起—
一、Collection接口
Collection常见方法:
增:
boolean add(Object obj);//添加一个Element;
boolean addAll(Collection col);//添加一个集合中所有的Elements进入新集合中
删;
boolean remove(Object obj);//删除指定的Element;
boolean removeAll(Collection col);//删除和旧集合中相同的Elements;
void clear();//清空集合;
查:
判断
boolean contains(Object obj);//查询集合中是否含有obj这个Element
boolean containsAll(Collection col);//查询集合中是否有旧集合中的所有Elements
boolean isEmpty();//集合是否为空
获取:
intsize();//获取集合的长度
Iteratoriterator();//迭代器
//迭代器的概念:迭代器必须依靠具体的集合对象存在,不同的集合对象会有不同的底层数据结构(后续文章中会详细介绍),而Iterator的实现方法也不尽相同。程序员只要懂得使用迭代器来取出集合中的Elements就可以了,对底层的实现方法可以不用理会,这就是面对对象的方法的一个很好的使用。
其他:
boolean retainAll(Collection col);//取出两个集合的交集;
Object[] toArray();//将集合转换为数组
//
/*
下面使用一个ArrayList(Collection一个实现类)来使用上述的方法。
*/
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Collection col = new ArrayList();
Collection col1 = new ArrayList();
sampleColMethod(col);
}
public static void sampleColMethod(Collection col){
//增:
col.add("Element1");
col.add("Element2");
col.add("Element3");
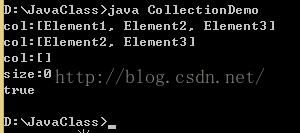
System.out.println("col:"+col);//result:col:[Element1,Element2,Element3]
//删
col.remove("Element1");
System.out.println("col:"+col);//result:col:[Element2,Element3]
col.clear();//清空集合
System.out.println("col:"+col);//result:col:[]
System.out.println("size:"+col.size());//result:size:0;
System.out.println(col.isEmpty());//result:true;
}
public static void otherColMethod(Collection col,Collection col1){
col.add("element1");
col.add("element2");
col.add("element3");
col.add("element4");
col1.add("element1");
col1.add("element5");
col1.add("element6");
System.out.println("col:"+col);
System.out.println("col1:"+col1);
//增
col.addAll(col1);//添加成功返回true,添加失败返回false,并将新的集合写到col中
//相同的元素是否会添加进去???
//删
col.removeAll(col1);//删除成功返回true,删除失败返回false,并将新集合写到col中
System.out.println("col:"+col);
//取交集
col.retainAll(col1);//取交集成功(包括空集),返回true,失败返回false。新集合写入到col中
System.out.println("col和col1的交集:"+col);
}
/*、
重点:Iterator的使用
*/
import java.util.*;
public class IteratorDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Collection col = new ArrayList();
col.add("element1");
col.add("element2");
col.add("element3");
//开始迭代
//使用iterator方法可以获取该集合的迭代器
Iterator it1 = col.iterator();
while(it1.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it1.next());
}
//上面的方法比较容易理解,演示的时候会使用该写法,开发过程中应该使用下述方法、
System.out.println("使用for循环来迭代集合");
for(Iterator it2 = col.iterator();it2.hasNext();){
System.out.println(it2.next());
}
}
}
Collection接口下有两个子接口:
|--List:有序,元素都有索引,允许元素重复。
|--set:元素不能重复,无序。
下面开始介绍
二、List接口
List特有的常见方法:
//增
void add(index,element);//在索引值为index的位置插入元素element;
void add(index,collection);//在索引值为index的位置插入一个集合,集合元素从index开始依次向后排序;
//删
Object remove(index);//删除索引为index上的元素;
//改
Object remove(index,element);//使用element来替换掉索引为index上的元素
//查
//获取
Object get(index);//获取索引为index上的元素
int indexOf(object);//获取元素为object的索引,如果有多个,则返回第一个
int lastIndexOf(object);//获取元素为object的最后一个索引;
List subList(from,to);//切取集合,并返回。留头不留尾。
/*
以下对List集合进行一下简单的演示
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ListDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("element1");
list.add("element2");
list.add("element3");
System.out.println(list);
//插入元素
list.add(1,"ELEMENT1");
//删除元素
list.remove(2);
System.out.println("list:"+list);
//修改元素
list.set(0,"ELEMENT2");
//截取集合、
System.out.println("subList:"+list.subList(0,1));
}
}
list特有的迭代器演示:相比于Collection中共性的迭代器,List的迭代器新增了一些特有的方法
ListIterator
void add(element);//将指定元素插入到列表中
boolean hasNext();
boolean hasPrevious();//反向遍历集合
E next();//返回列表的下一个元素
int nextIndex();//返回列表的下一个元素的索引
E previous();//返回列表的前一个元素
int previousIndex();//返回列表的前一个元素的索引
void remove();//删除列表中由next或者previous返回的元素
void set(element);//用指定的元素element来替换列表中由next或previous返回的元素
示例:
import java.util.*;
public class ListIteratorDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("element1");
list.add("element2");
list.add("element3");
list.add("element4");
ListIterator listIt1 = list.listIterator();
while(listIt1.hasNext()){
if("element2".equals(listIt1.next())){
listIt1.set("ELEMENT2");
System.out.println(listIt1.nextIndex());
}
}
System.out.println("LIST:"+list);
}
//向前迭代的使用方法和正向顺序的迭代使用方法一样,这里就不做演示,有兴趣可以自己验证一下
}
result:

在迭代器的过程中,是禁止使用集合自身的方法操作集合中的元素的,很容易产生异常:java.util.ConcurrentModificationException.
List接口的几个常用的实现类:
|--Vector:数组数据结构,同步—〉增删查都很慢;
|--ArrayList:数组数据结构,非同步--〉查询快,增删相对于链表结构的较慢,替代了Vector
|--LinkedList:链表数据结构,非同步—〉增删快,查询慢。
LinkedList常用特有方法:
//增
addFirst();
addLast();
/*jdk1.6以后,上述方法改成:
offerFirst();
offerLast();//只是名字变了,功能是一样的
*/
//查
//获取
getFirst();//获取但不移除,如果链表为空,抛出NoSuchElementException。
getLast();//同上
/*
新方法
peekFirst();//获取但不移除,如果链表为空,返回null;
peekLast();//同上
*/
//删
removeFirst();//获取并移除,如果链表为空,抛出NoSuchElementException
removeLast();//同上
/*
新方法、
pollFirst();//获取并移除,如果链表为空,返回null;
pollLast();//同上
*/
示例
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedListDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
LinkedList link = new LinkedList();
link.addFirst("element1");
link.addFirst("element2");
link.addFirst("element3");
link.addFirst("element4");
Iterator it = link.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
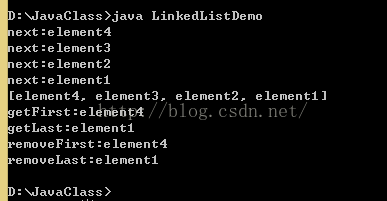
System.out.println("next:"+it.next());
}
System.out.println(link);
System.out.println("getFirst:"+link.getFirst());//获取但不删除
System.out.println("getLast:"+link.getLast());
System.out.println("removeFirst:"+link.removeFirst());//获取并删除
System.out.println("removeLast:"+link.removeLast());
//删除全部元素
while(!link.isEmpty()){
link.removeFirst();
}
}
}
/*
了解了LinkedList的这些方法,用其来模拟一个堆栈或者队列数据结构
*/
import java.util.*;
class Duilie{
private LinkedList link;
public Duilie(){
link = new LinkedList();
}
public void duilieAdd(Object obj){
link.offerLast(obj);
}
public Object duilieGet(){
return link.removeLast();
}
public boolean isNull(){
return link.isEmpty();
}
}
public class DuilieTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Duilie dl = new Duilie();
dl.duilieAdd("element1");
dl.duilieAdd("element2");
dl.duilieAdd("element3");
dl.duilieAdd("element4");
while(!dl.isNull()){
System.out.println(dl.duilieGet());
}
}
}
set
Set:元素不可重复,无序
|--HashSet:哈希表结构,非同步
|--TreeSet:二叉树结构,可以对Set集合中的元素进行排序,非同步
import java.util.*;
public class HashSetDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
hs.add("element1");
hs.add("element2");
hs.add("element3");
hs.add("element4");
for(Iterator it = hs.iterator();it.hasNext();){
System.out.println(it.next());
/*result:打印时无序的
element1
element2
element3
element4
*/
}
}
}
HashSet判断元素相同的条件:
1:判断两个元素的哈希值是否相同。如果两个元素的哈希值相同,则判断两个元素相同
2:判断哈希值相同的方法,是判断hashCode方法得到的值是否相同。
3:判断元素内容是否相同,使用的是equals方法。
/*
举个例子来说明上面的一段话
*/
import java.util.*;
//我们定义一个Person类,代替之前的"element"
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
public String toString(){
return name+":"+age;
}
public int hashCode(){
return name.hashCode()+age*23;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if(this == obj)
return true;
if(!(obj instanceof Person))
throw new ClassCastException("类型错误");
Person p = (Person)obj;
return this.name.equals(p.name)&&this.age == p.age;
}
}
public class HashSetTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
HashSet hs = new HashSet();
hs.add(new Person("zs1",12));
hs.add(new Person("zs1",13));
hs.add(new Person("zs2",12));
hs.add(new Person("zs3",14));
hs.add(new Person("zs1",12));
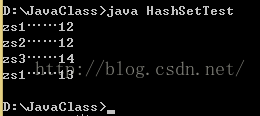
for(Iterator it = hs.iterator();it.hasNext();){
Person p = (Person)it.next();
System.out.println(p.getName()+"……"+p.getAge());
}
}
}
result:
/*
除去ArrayList中的重复元素
*/
import java.util.*;
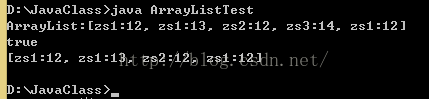
public class ArrayListTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(new Person("zs1",12));
al.add(new Person("zs1",13));
al.add(new Person("zs2",12));
al.add(new Person("zs3",14));
al.add(new Person("zs1",12));
System.out.println("ArrayList:"+al);
//remove底层用的也是equals方法
System.out.println(al.remove(new Person("zs3",14)));
System.out.println(al);
}
//能不能让得到的类型也不会改变呢?还是Person类,是要用到泛型吗??
public static ArrayList getSingleElement(ArrayList al){
ArrayList tempAl = new ArrayList();
Iterator it = al.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object obj = it.next();
//contains底层用的是equals方法
if(!(tempAl.contains(obj))){
tempAl.add(obj);
}
}
return tempAl;
}
}
result:
/*
如果你想得到一个有序的set集合,可以考虑是使用linkedHashSet
*/
import java.util.*;
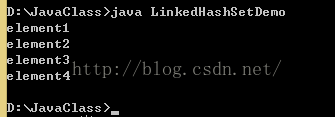
public class LinkedHashSetDemo{
public static void main(String [] args){
HashSet hs = new LinkedHashSet();
hs.add("element1");
hs.add("element2");
hs.add("element3");
hs.add("element4");
for(Iterator it = hs.iterator();it.hasNext();)
{
System.out.println(it.next());
}
/*result:
element1
element2
element3
element4
*/
}
}
result:
TreeSet判断元素的惟一性的方法:compareTo方法的返回值,当返回值为0时,就是相同元素,不存。
//定义一个类,实现Comparable接口,重写接口的CompareTo方法。就可以让该类按照我们重写的方法进行判断元素相同与否。
import java.util.*;
class Person implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
public int hashCode(){
return name.hashCode()+age*23;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
//传人两个相同的对象
if(this == obj)
return true;
if(!(obj instanceof Person))
throw new ClassCastException("类型错误");
Person p = (Person)obj;
return this.name.equals(p.name)&&this.age == p.age;
}
public int compareTo(Object o){
Person p = (Person)o;
//先按照年龄排序,在按照姓名排序,以免年龄相同的人没有存进去??????
int temp = this.age-p.age;
return temp == 0?this.name.compareTo(p.name):temp;//这里的this.name是字符串,String类也实现了Comparable方法
}
}
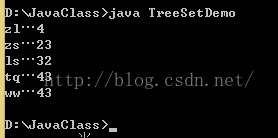
public class TreeSetDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet();
//Person对象年龄从小到大进行排序
ts.add(new Person("zs",23));
ts.add(new Person("ls",32));
ts.add(new Person("ww",43));
ts.add(new Person("zl",4));
ts.add(new Person("tq",43));
Iterator it = ts.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Person p = (Person)it.next();
System.out.println(p.getName()+"…"+p.getAge());
}
}
}
result:
如果不按照对象中具备的自然顺序进行排序或者对象中不具备自然排序。怎么办?
TreeSet集合排序的第二种排序方式:
//让集合自身具备比较功能,定义一个类实现Comparator接口,覆盖compare方法,将该类对象作为参数传递给TreeSet集合的构造函数。
import java.util.*;
//创建一个根据Person类的name进行排序的比较器
class ComparatorByName implements Comparator{
public int compare(Object obj1,Object obj2){
Person p1 = (Person)obj1;
Person p2 = (Person)obj2;
int temp = p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
return temp == 0?p1.getAge()-p2.getAge():temp;
}
}
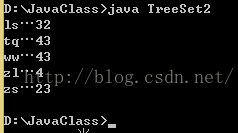
public class TreeSet2{
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(new ComparatorByName());
ts.add(new Person("zs",23));
ts.add(new Person("ls",32));
ts.add(new Person("ww",43));
ts.add(new Person("zl",4));
ts.add(new Person("tq",43));
Iterator it = ts.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Person p = (Person)it.next();
System.out.println(p.getName()+"…"+p.getAge());
}
}
}
result:
如果自定义类实现了Comparable接口,并且TreeSet的构造函数中传入了比较器,那么将以比较器的比较规则为准。
Map
Map:一次添加一对元素,Collection一次添加一个元素
被称为双列集合,Collection被称为单列集合
Map中存储的元素是按照键值对的形式。
Map集合中的键是唯一的。
常用方法
//增
value put(key,value);//返回前一个和key关联的值,如果没有返回null。
//删
void clear();//清空集合
value remove(Object key);//根据制定的key删除这个键值对
//查
判断
booleancontainsKey(key);//根据键查询,如果有返回true
booleancontainsValue(value);//根据值查询,如果有返回true
booleanisEmpty();//是否为空
获取
valueget(key);//通过键获取值,如果没有返回null
intsize();//获取键值对的个数
/*
上述方法的简单应用
*/
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Map map = new HashMap ();
method(map);
}
public static void sop(Object obj){
System.out.println(obj);
}
public static void method(Map map){
//增
sop("增------------------------");
sop(map.put(1,"小明"));
sop(map.put(1,"小红"));
sop(map.put(2,"小红"));
map.put(3,"小花");
sop(map);
//删
sop("删-----------------------");
sop("remove会返回被移除的对象:"+map.remove(3));
sop(map);
//查
//判断
sop("判断-------------------");
sop ("containsKey:"+map.containsKey(1));
sop("containsValue:"+map.containsValue("小花"));
//获取
sop("获取");
sop("get:"+map.get(3));
sop("size:"+map.size());
}
}
result:
//获取Map集合并打印
/*
方式1:
*/
import java.util.*;
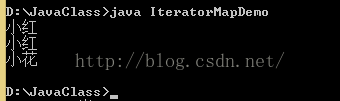
public class IteratorMapDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Map map = new HashMap ();
map.put(1,"小明");
map.put(1,"小红");
map.put(2,"小红");
map.put(3,"小花");
method(map);
}
public static void method(Map map){
//取出map集合中的所有元素
//方式1:通过个KeySet方法获取map中所有的键所在的set集合,在通过set的迭代器获取每一个键,再对每一个键通过map集合的get方法获取到相对应的值即可。
Set set = map.keySet();
Iterator it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String str = map.get(it.next());
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
result:
/*
方式2:
*/
import java.util.*;
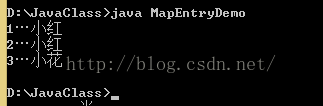
public class MapEntryDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Map map= new HashMap ();
map.put(1,"小明");
map.put(1,"小红");
map.put(2,"小红");
map.put(3,"小花");
method(map);
}
public static void method(Map map){
/*
通过Map转换成set集合就可以迭代
找到另一个方法,entrySet
该方法将键和值得映射关系作为对象存储到了Set集合中,
*/
Set> entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator> it = entrySet.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry me = it.next();
Integer key = me.getKey();
String value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"…"+value);
}
}
}
result:
/*
方式3,获取所有值组成集合
*/
import java.util.*;
public class MapValueDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Map map= new HashMap ();
map.put(1,"小明");
map.put(1,"小红");
map.put(2,"小红");
map.put(3,"小花");
method(map);
}
public static void method(Map map){
/*
只能打印出值,没办法打印出键
*/
Collection values = map.values();
Iterator it = values.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
result:
Map的常用子类
|--HashMap:哈希表结构,非同步,允许null作为键,作为值
|--Hashtable:内部结构是哈希表,同步,不允许null作为键,null作为值
|--Properties:用来存储键值对型的配置文件的信息,可以和IO技术相结合
|--TreeMap:二叉树,非同步,可以对Map集合中的键进行排序。
//HashSet实现Set接口,由哈希表(实际上是一个HashMap实例)支持的
package com.leaf.test;
import java.util.*;
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
public int hashCode(){
return name.hashCode()+age*23;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if(this == obj)
return true;
if(this == null)
return false;
if(getClass()!=obj.getClass())
return false;
Person other = (Person)obj;
if(age != other.getAge())
return false;
if(name == null){
if(other.getName() !=null)
return false;
}else if(!name.equals(other.getName()))
return false;
return true;
}
}
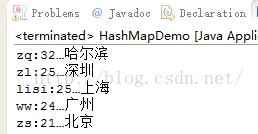
public class HashMapDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
//将人和出生地联系在一起
HashMap hm = new HashMap();
hm.put(new Person("lisi",25),"上海");
hm.put(new Person("zs",21),"北京");
hm.put(new Person("ww",24),"广州");
hm.put(new Person("zl",25),"深圳");
hm.put(new Person("zq",32),"哈尔滨");
Iterator it = hm.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Person key = it.next();
String value = hm.get(key);
System.out.println(key.getName()+":"+key.getAge()+"…"+value);
}
}
}
result:
注:使用LinkedHashMap存储元素,会得到和存入顺序一样的集合。有兴趣的可以自己演示。
练习:
取出一个字符串中每个字母出现的次数并打印,打印结果a(1)b(2)…
思路:
查看题目,发现字母和字母次数右移对应关系,所以使用Map集合来存储这种关系。
打印结果有顺序,按照abc从小到大的顺序,可以使用TreeSet
演示:
import java.util.*;
class CharTimes
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = "agaojgnkalgjnkrasjfa";
getCharTime(str);
}
public static void getCharTime(String str){
Map map = new TreeMap();
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0;i> set= map.entrySet();
Iterator> it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry me = it.next();
Character ch = me.getKey();
builder.append(ch).append("(");
Integer in = me.getValue();
builder.append(in).append(")");
}
System.out.println(builder.toString());
}
}