反射的学习
一个例子引出反射
根据配置文件 re.properties指定信息 创建对象并调用方法 classfullpath=com.haojie.spring.Cat method=hi
package com.haojie.spring;
/**
* @Author: lihaojie
* @Description: 根据配置文件 re.properties指定信息 创建对象并调用方法
* classfullpath=com.haojie.spring.Cat
* method=hi
* @DateTime: 2024/1/18 14:19
**/
public class Cat {
private String name = "招财猫";
public void hi() {
System.out.println("hi " + name);
}
public void cry() {
System.out.println(name + "喵喵叫");
}
}
package com.haojie.spring.reflection;
/**
* @Author: lihaojie
* @Description: 反射问题的引入
* @DateTime: 2024/1/18 14:23
**/
import com.haojie.spring.Cat;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* 根据配置文件 re.properties指定信息 创建对象并调用方法
* classfullpath=com.haojie.spring.Cat
* method=hi
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class ReflectionQuestion {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
// 传统方式 new对象,然后调方法
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.hi();
// 尝试做一下
// 1、先读入re.properties,使用IO的properties类
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("H:\\04-Workspace\\springstudy\\spring\\src\\main\\resources\\re.properties"));
String classfullpath = (String) properties.get("classfullpath");
String methodName = (String) properties.get("method");
System.out.println(classfullpath);
System.out.println(methodName);
// 2、创建对象 传统的方法却行不通了
// 3、使用反射机制解决
// 3.1、加载类 返回Class类型的对象
Class cls = Class.forName(classfullpath);
// 3.2、通过cls可以得到加载 com.haojie.spring.Cat 对象实例
Object o = cls.newInstance();
System.out.println(o.getClass()); // 得到o的运行时类型(class com.haojie.spring.Cat)
// 3.3、通过反射得到方法对象
// 使用getMethod得到你加载的类 com.haojie.spring.Cat 的指定方法 对象
// 即 在反射中 可以把方法也视为对象 万物皆对象
Method method = cls.getMethod(methodName);
// 3.4、通过方法对象来实现调用方法
method.invoke(o); // hi 招财猫
}
}
1、什么是反射?
反射机制允许程序在执行期间借助于Reflection API取得任何类的内部信息(比如成员变量、构造器、成员方法等等),并能操作对象的属性及方法。反射在设计模式和框架底层都会用到
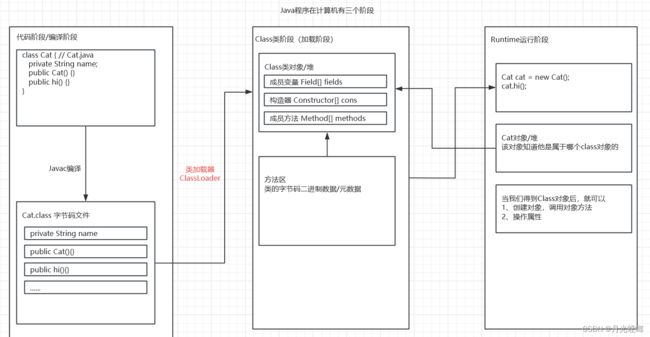
加载完类后,在堆中就会产生一个Class类型的对象(一个类只会有一个Class对象),这个对象包含了类的完整结构信息,通过这个对象得到类的结构,这个对象就像是一面镜子,透过这个镜子可以看到类的结构,所以,形象的称之为:反射
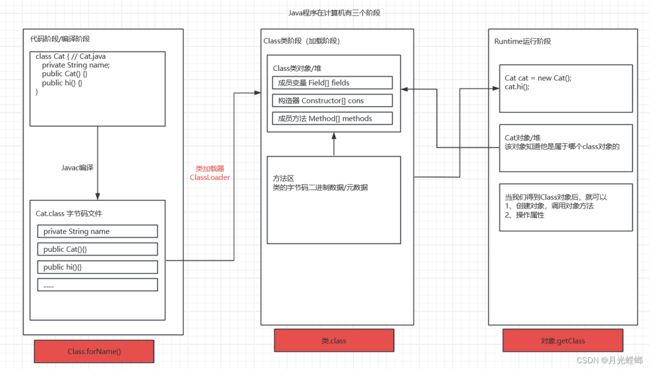
Java反射机制原理图:
Java反射机制可以完成:
1、在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
2、在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
3、在运行时得到任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
4、在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员变量和方法
5、生成动态代理
2、如何使用反射?
package com.haojie.spring.reflection;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @Author: lihaojie
* @Description:
* @DateTime: 2024/1/18 16:01
**/
public class Reflection01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("H:\\04-Workspace\\springstudy\\spring\\src\\main\\resources\\re.properties"));
String classfullpath = (String) properties.get("classfullpath");
String methodName = (String) properties.get("method");
// 3、使用反射机制解决
// 3.1、加载类 返回Class类型的对象
Class cls = Class.forName(classfullpath);
// 3.2、通过cls可以得到加载 com.haojie.spring.Cat 对象实例
Object o = cls.newInstance();
System.out.println(o.getClass()); // 得到o的运行时类型(class com.haojie.spring.Cat)
// 3.3、通过反射得到方法对象
// 使用getMethod得到你加载的类 com.haojie.spring.Cat 的指定方法 对象
// 即 在反射中 可以把方法也视为对象 万物皆对象
Method method = cls.getMethod(methodName);
// 3.4、通过方法对象来实现调用方法
method.invoke(o); // hi 招财猫
// 得到name字段
// getField不能得到私有的属性
// 要想得到private的属性
// Field name = cls.getField("name");
Field age = cls.getField("age");
Integer ageReal = (Integer) age.get(o);
System.out.println(ageReal); // 反射:成员变量对象.get(对象)
// 得到构造器 构造器又可以帮我们创建对象
Constructor constructorNoParam = cls.getConstructor();// ()中可以指定构造器参数类型,不写返回的就是无参构造器
System.out.println(constructorNoParam); // com.haojie.spring.Cat()
Constructor constructorHasParam = cls.getConstructor(String.class);// ()中可以指定构造器参数类型,不写返回的就是无参构造器
System.out.println(constructorHasParam); // com.haojie.spring.Cat()
}
}
反射的优缺点:
package com.haojie.spring.reflection;
import com.haojie.spring.Cat;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @Author: lihaojie
* @Description: 测试 反射调用的性能 和优化方案
* @DateTime: 2024/1/18 16:29
**/
public class Reflection02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 传统方法调用hi耗时4ms
* 使用反射调用hi耗时1325ms
* 差别确实挺大的
* 优化方案:关闭访问检查
*
*/
m1();
m2();
}
// 传统方法来调用 hi
public static void m1() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Cat cat = new Cat();
for (int i = 0; i < 900000000; i++) {
cat.hi();
}
System.out.println("传统方法调用hi耗时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
}
// 反射机制调用方法 hi
public static void m2() throws Exception{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Class cls = Class.forName("com.haojie.spring.Cat");
Object o = cls.newInstance();
Method hi = cls.getMethod("hi");
for (int i = 0; i < 900000000; i++) {
hi.invoke(o);
}
System.out.println("使用反射调用hi耗时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
}
}
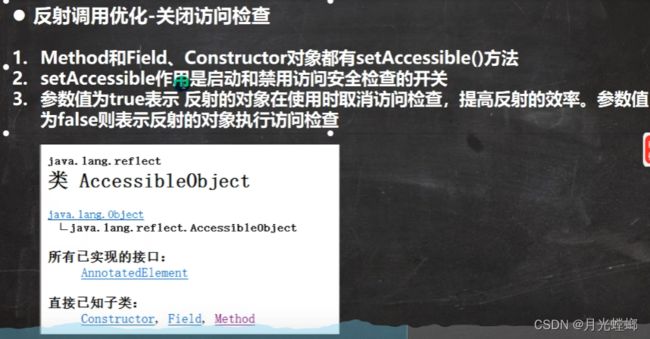
从下面的例子可以看出,关闭掉访问检查后效率提升了一半!
package com.haojie.spring.reflection;
import com.haojie.spring.Cat;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @Author: lihaojie
* @Description: 测试 反射调用的性能 和优化方案
* @DateTime: 2024/1/18 16:29
**/
public class Reflection02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 传统方法调用hi耗时4ms
* 使用反射调用hi耗时1325ms
* 差别确实挺大的
* 优化方案:关闭访问检查
*
*/
m1();
m2();
m2Up(); // 传统方法调用hi耗时4ms 使用反射调用hi耗时742ms 提升了一半
}
// 传统方法来调用 hi
public static void m1() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Cat cat = new Cat();
for (int i = 0; i < 900000000; i++) {
cat.hi();
}
System.out.println("传统方法调用hi耗时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
}
// 反射机制调用方法 hi
public static void m2() throws Exception{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Class cls = Class.forName("com.haojie.spring.Cat");
Object o = cls.newInstance();
Method hi = cls.getMethod("hi");
for (int i = 0; i < 900000000; i++) {
hi.invoke(o);
}
System.out.println("使用反射调用hi耗时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
}
// 反射机制调用优化方法 hi
public static void m2Up() throws Exception{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Class cls = Class.forName("com.haojie.spring.Cat");
Object o = cls.newInstance();
Method hi = cls.getMethod("hi");
hi.setAccessible(true); // 在反射调用方法时 取消访问检测
for (int i = 0; i < 900000000; i++) {
hi.invoke(o);
}
System.out.println("使用反射调用hi耗时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
}
}
3、Class类
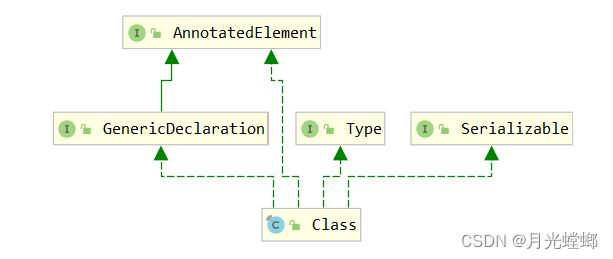
1、Class也是类,因此也继承Object类
2、Class类对象不是new出来的,而是系统创建出来的
// Class类对象不是new出来的,而是系统创建出来的
// 1、传统new对象的方法
/**
* public Class loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
* return loadClass(name, false);
* }
*/
// Cat cat = new Cat();
// 2、用反射的方式
Class cls = Class.forName("com.haojie.spring.reflection.class_.Class01");
Object o = cls.newInstance();3、对于某个类的Class类对象,在内存中只有一份,因为类只加载一次
Class cls1 = Class.forName("com.haojie.spring.reflection.class_.Class01");
Class cls2 = Class.forName("com.haojie.spring.reflection.class_.Class01");
System.out.println(cls1.hashCode()); // 1950409828
System.out.println(cls2.hashCode()); // 19504098284、每个实例都知道自己是由哪个Class生成
5、通过一个Class对象可以完整地得到一个类的完整结构,通过一系列的API
6、Class对象是存放在堆中的
7、类的字节码二进制数据,是放在方法区的
3.1、Class类的常用方法
package com.haojie.spring.reflection.class_;
import com.haojie.spring.Car;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* @Author: lihaojie
* @Description: 演示Class类的一些常用方法
* @DateTime: 2024/1/19 10:35
**/
public class Class02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String classAllPath = "com.haojie.spring.Car";
// 1、获取到Car类对应的Class对象
// 表示不确定的Java类型
Class cls = Class.forName(classAllPath);
// 2、输出Class
System.out.println(cls); // 显示cls对象,是哪一个类的Class对象 class com.haojie.spring.Car
System.out.println(cls.getClass()); // java.lang.Class cls运行类型
// 3、得到包名
System.out.println(cls.getPackage().getName()); // com.haojie.spring
// 4、得到全类名
System.out.println(cls.getName()); // com.haojie.spring.Car
// 5、通过cls来创建对象实例
Car car = (Car) cls.newInstance();
System.out.println(car); // Car{brand='bmw', price=500000, color='red'}
// 6、通过反射获取属性
Field brand = cls.getField("brand");
System.out.println(brand.get(car)); // bmw
// 7、通过反射给属性赋值
brand.set(car, "奔驰");
System.out.println(brand.get(car)); // 奔驰
// 8、得到所有的属性
Field[] fields = cls.getFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field.get(car));
}
}
}
3.2、获取Class对象的六种方式
1、Class.forName
2、类.class
3、对象.getClass()
4、使用ClassLoader
package com.haojie.spring.reflection.class_;
import com.haojie.spring.Car;
/**
* @Author: lihaojie
* @Description: 演示得到Class对象的各种方式
* @DateTime: 2024/1/19 11:14
**/
public class GetClass_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、Class.forName
String classAllPath = "com.haojie.spring.Car"; // 通过读取配置文件获取
Class cls = Class.forName(classAllPath);
System.out.println(cls); // class com.haojie.spring.Car
// 2、通过类名.class 应用场景 多用于参数的传递
System.out.println(Car.class); // class com.haojie.spring.Car
// 3、通过对象名.getClass() 应用场景 已经有了对象实例
Car car = new Car();
Class cls3 = car.getClass();
System.out.println(cls3);
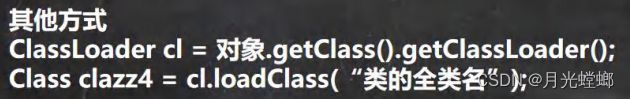
// 4、通过类加载器【4种】获取类的Class对象
// 4.1、先得到类加载器 Car classLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = car.getClass().getClassLoader();
// 4.2、通过类加载器得到Class对象
Class cls4 = classLoader.loadClass("com.haojie.spring.Car");
System.out.println(cls4); // class com.haojie.spring.Car
}
}
3.3、哪些类型有Class对象?
4、类加载
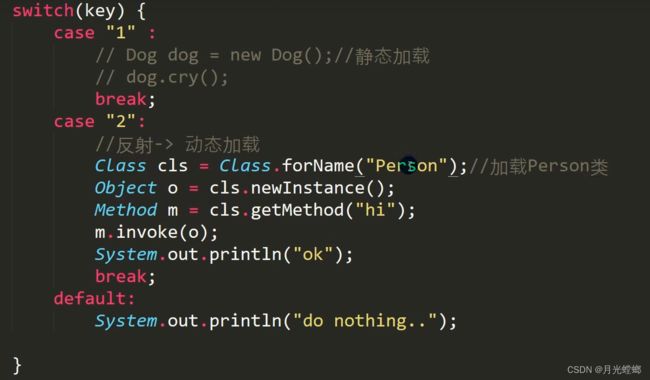
- 静态加载:编译时加载相关的类,如果没有则报错,依赖性太强
- 动态加载:运行时加载需要的类,如果运行时不用该类,则不报错,降低了依赖性 (如果没走到这块代码,就不会真的加载)
因为new Dog()是静态加载,因此必须编写Dog
Person类是动态加载,所以,没有编写Person类也不会报错,只有动态加载到该类时才会报错
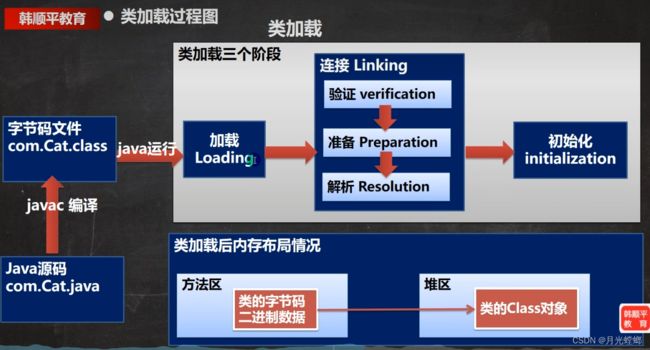
4.1、类加载过程
4.2、类加载各阶段
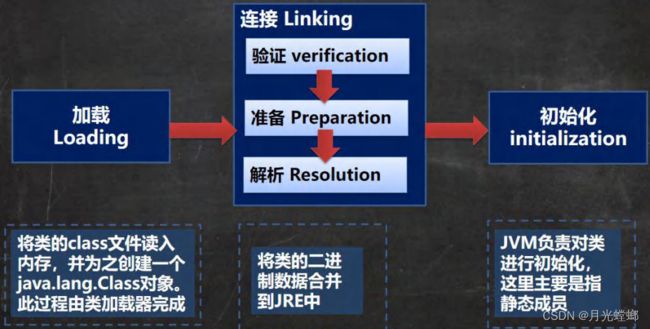
加载阶段
JVM在该阶段的主要目的是将字节码从不同的数据源(可能是class文件、也可能是jar包,甚至网络)转化为二进制字节流加载到内存中,并生成一个代表该类的java.lang.Class 对象
连接阶段-验证
1.目的是为了确保 Class 文件的字节流中包含的信息符合当前虚拟机的要求,并且不会危害虚拟机自身的安全。
2.包括:文件格式验证(是否以魔数oxcafebabe开头)、元数据验证、字节码验证和符号引用验证[举例说明]
3.可以考虑使用-Xverify:none 参数来关闭大部分的类验证措施,缩短虚拟机类加载的时间。
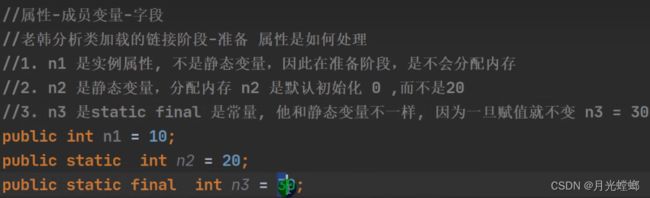
连接阶段-准备
JVM 会在该阶段对静态变量,分配内存并默认初始化(对应数据类型的默认初始值,如0、OL、null、false等)。这些变量所使用的内存都将在方法区中进行分配
连接阶段-解析
1、虚拟机将常量池内的符号引用替换为直接引用的过程
初始化阶段
1.到初始化阶段,才真正开始执行类中定义的Java程序代码,此阶段是执行
2.
ClassLoad03.java]
3.虚拟机会保证一个类的
4.3、通过反射获取类结构信息
package com.haojie.spring.reflection;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @Author: lihaojie
* @Description: 演示如何通过反射获取类的结构信息
* @DateTime: 2024/1/22 10:04
**/
public class ReflectionUtils {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
}
// 第一组方法API
@Test
public void api_01() throws Exception {
// 得到Class对象
Class cls = Class.forName("com.haojie.spring.reflection.Person");
// 获取全类名
System.out.println(cls.getName()); // com.haojie.spring.reflection.Person
// 获取简单类名
System.out.println(cls.getSimpleName()); // Person
// 获取所有public修饰的属性, 包含本类以及父类的
Field[] fields = cls.getFields(); // name hobby
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println("获取本类及父类所有属性=" + field.getName());
}
// 获取本类所有属性 (忽略访问修饰符)
Field[] declaredFields = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
System.out.println("获取本类所有属性(忽略访问修饰符)=" + declaredField.getName()); // name age job sal
}
// 获取所有public修饰的方法 包含本类以及父类的
Method[] methods = cls.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("本类及父类的method" + method.getName());
}
// 只获取本类的method (忽略访问修饰符)
Method[] declaredMethods = cls.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {
System.out.println("本类的method(忽略访问修饰符)" + declaredMethod.getName());
}
// 获取所有public修饰的构造器 包含本类的
Constructor[] constructors = cls.getConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println("本类及父类的构造器" + constructor.getName());
}
// 获取所有本类的构造器
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = cls.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor declaredConstructor : declaredConstructors) {
System.out.println("declaredConstructor" + declaredConstructor.getName());
}
// 以Package形式返回 包信息
System.out.println(cls.getPackage()); // package com.haojie.spring.reflection
// 以Class形式返回父类信息
System.out.println(cls.getSuperclass()); // class com.haojie.spring.reflection.A
// 以Class[]形式返回接口信息
Class[] classes = cls.getInterfaces();
for (Class aClass : classes) {
System.out.println(aClass.getName());
}
// 返回注解信息
Annotation[] annotations = cls.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println("注解信息" + annotation);
}
}
@Test
public void api_02() throws Exception {
// 得到Class对象
Class cls = Class.forName("com.haojie.spring.reflection.Person");
//java.lang.reflect.Field类
// 1、getModifiers :以int形式返回修饰符 默认修饰符-0 public-1 private-2 protected-4 static-8 final-16
// public static final = 1 + 8 + 16 = 25
Field[] declaredFields = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
System.out.println("本类所有属性=" + declaredField +
",该属性的修饰符总值=" + declaredField.getModifiers() +
",该属性的类型=" + declaredField.getType());
}
// method
Method[] declaredMethods = cls.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {
System.out.println("本类的所有方法=" + declaredMethod.getName() +
",该方法的访问修饰符值=" + declaredMethod.getModifiers() +
",该方法返回类型=" + declaredMethod.getReturnType());
// 当前这个方法的形参
Class[] parameterTypes = declaredMethod.getParameterTypes();
for (Class parameterType : parameterTypes) {
System.out.println("该方法的形参类型" + parameterType);
}
}
// constructors
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = cls.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor declaredConstructor : declaredConstructors) {
System.out.println(declaredConstructor);
}
}
}
class A {
public String hobby;
public A() {
}
}
interface IA {
}
interface IB {
}
@Deprecated
class Person extends A implements IA, IB {
// 属性
public String name;
protected int age;
String job;
private double sal;
public static final String gender = "man";
// 构造器
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name) {
}
// 方法
public void m1(String name, int age, double sal) {
}
protected String m2() {
return null;
}
void m3() {
}
private void m4() {
}
}
4.4、通过反射创建对象
方式一:调用类中的public修饰的无参构造器
方式二:调用类中的指定构造器