tkinter绘制组件(20)——带状等待框
tkinter绘制组件(20)——带状等待框
- 引言
- 布局
-
- 函数结构
- 背景
- 滑块
- 滑块动画
-
- 起始函数
- 运动函数
- 停止函数
- 完整代码函数
- 效果
-
- 测试代码
- 最终效果
- 2022-7-12新样式
- github项目
- pip下载
- 修改开源协议
- 结语
引言
wow,TinUI已经引来了它的第20号组件——带状等待框!
与之前的点状等待框、圆形等待框一样,带状等待框相当于耗时操作中反馈给用户的动画类型组件。相比于它的两个前辈,它与点状等待框类似,占用较小的位置,但是和点状等待框一样,不适合使用为等待窗口的唯一组件。
当相比于点状等待框,它除了样式上的不同外,还具有一个作用:区分加载类耗时操作和程序类耗时操作。也就是说,带状等待框更加符合程序类的暂停或耗时操作,如等待请求、静候某操作完成等情景。而想下载或载入大文件的耗时,就交给点状等待框吧。
其实就是为了有新的样式,而编的以上理由。
实际上是参考了WinUI3的
processbar。
布局
函数结构
def add_waitbar3(self,pos:tuple,width:int=200,fg='#3041d8',bg='#f3f3f3',okcolor='lightgreen'):#绘制带状等待框
'''
pos::起始位置
width::宽度
fg::滑块颜色
bg::背景色
okcolor::完成时的颜色
'''
背景
习以为常:
ifok=TinUINum()#记录是否暂停
ifok.ok=False
bbox=(pos[0],pos[1],pos[0]+width,pos[1]+4)
back=self.create_rectangle(bbox,fill=bg,outline=bg)
uid='waitbar3'+str(back)
self.itemconfig(back,tags=uid)
我们将使用与
waitbar2同样的技术-1:通过
ifok.ok的值判断是否继续动画。
滑块
这里借鉴了waitbar2的另一个技术-2:
通过不断重绘滑块对象,来显示动画效果。
self.itemconfig(back,tags=uid)
maxwidth=width//3
bar=self.create_rectangle((pos[0],pos[1],pos[0],pos[1]),fill=fg,outline=fg,tags=uid)
maxwidth是滑块的最大宽度。
滑块动画
再次借鉴waitbar2的一个技术-3:
由一个起始函数作为动画的开始,并作为动画操作代码的主要控制中心;再在控制之下调用的执行函数继续调用这一个起始函数,循环往复。
之前没有说明为什么需要使用循环调用而不是迭代的代码结构,是为了防止迭代深度超过栈堆。如果TinUI存在这一种情况,请在GitHub上反馈BUG,我会尽快修复。
起始函数
带状等待框分为三种动画形式:
- 持续增长,直到滑块最大宽度
- 保持最大长度,平滑滚动
- 右端到达终点,宽度逐渐减小
接着重新来过。
我们需要判断这三种情况。其中,明显【1】和【3】是比较好判断的,因为我们全部采用整数计数,而除数是“3”:
def start(nowwidth=0):#开始动画
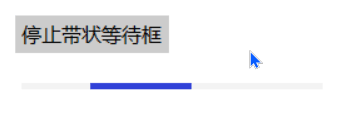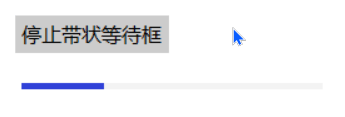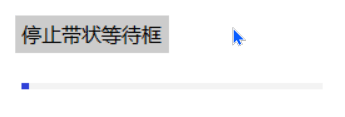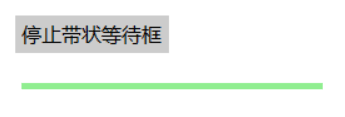
if ifok.ok==True:#已完成
self.itemconfig(bar,fill=okcolor,outline=okcolor)
self.coords(bar,(pos[0],pos[1],pos[0]+width,pos[1]+4))
if nowwidth<=maxwidth:#增长阶段
self.after(50,lambda : move(0,nowwidth,nowwidth))
elif nowwidth>=width:#缩小阶段
self.after(50,lambda : move(nowwidth-maxwidth,width,nowwidth))
else:#平滑阶段。因为我们去整数,所以平滑阶段无法使用断点判断
self.after(50,lambda : move(nowwidth-maxwidth,nowwidth,nowwidth))
运动函数
老生常谈:
def move(startx,endx,nowwidth):
if nowwidth-maxwidth>width:#一轮动画完成
start()
return
self.coords(bar,(pos[0]+startx,pos[1],pos[0]+endx,pos[1]+4))
start(nowwidth+5)
停止函数
def stop():#停止
ifok.ok=True
完整代码函数
def add_waitbar3(self,pos:tuple,width:int=200,fg='#3041d8',bg='#f3f3f3',okcolor='lightgreen'):#绘制带状等待框
def move(startx,endx,nowwidth):
if nowwidth-maxwidth>width:#一轮动画完成
start()
return
self.coords(bar,(pos[0]+startx,pos[1],pos[0]+endx,pos[1]+4))
start(nowwidth+5)
def start(nowwidth=0):#开始动画
if ifok.ok==True:#已完成
self.itemconfig(bar,fill=okcolor,outline=okcolor)
self.coords(bar,(pos[0],pos[1],pos[0]+width,pos[1]+4))
if nowwidth<=maxwidth:#增长阶段
self.after(50,lambda : move(0,nowwidth,nowwidth))
elif nowwidth>=width:#缩小阶段
self.after(50,lambda : move(nowwidth-maxwidth,width,nowwidth))
else:#平滑阶段。因为我们去整数,所以平滑阶段无法使用断点判断
self.after(50,lambda : move(nowwidth-maxwidth,nowwidth,nowwidth))
def stop():#停止
ifok.ok=True
ifok=TinUINum()#记录是否暂停
ifok.ok=False
bbox=(pos[0],pos[1],pos[0]+width,pos[1]+4)
back=self.create_rectangle(bbox,fill=bg,outline=bg)
uid='waitbar3'+str(back)
self.itemconfig(back,tags=uid)
maxwidth=width//3
bar=self.create_rectangle((pos[0],pos[1],pos[0],pos[1]),fill=fg,outline=fg,tags=uid)
start()
return back,bar,stop,uid
效果
测试代码
def test(event):
a.title('TinUI Test')
b.add_paragraph((50,150),'这是TinUI按钮触达的事件函数回显,此外,窗口标题也被改变、首行标题缩进减小')
b.coords(m,100,5)
def test1(word):
print(word)
def test2(event):
ok1()
def test3(event):
ok2()
def test4(event):
from time import sleep
for i in range(1,101):
sleep(0.02)
progressgoto(i)
def test5(result):
b.itemconfig(scale_text,text='当前选值:'+str(result))
if __name__=='__main__':
a=Tk()
a.geometry('700x700+5+5')
b=TinUI(a,bg='white')
b.pack(fill='both',expand=True)
m=b.add_title((600,0),'TinUI is a test project for futher tin using')
m1=b.add_title((0,680),'test TinUI scrolled',size=2,angle=24)
b.add_paragraph((20,290),''' TinUI是基于tkinter画布开发的界面UI布局方案,作为tkinter拓展和TinEngine的拓展而存在。目前,TinUI已可应用于项目。''',
angle=-18)
b.add_paragraph((20,100),'下面的段落是测试画布的非平行字体显示效果,也是TinUI的简单介绍')
b.add_button((250,450),'测试按钮',activefg='white',activebg='red',command=test,anchor='center')
b.add_checkbutton((80,430),'允许TinUI测试',command=test1)
b.add_label((10,220),'这是由画布TinUI绘制的Label组件')
b.add_entry((250,330),350,'这里用来输入')
b.add_separate((20,200),600)
b.add_radiobutton((50,480),300,'sky is blue, water is blue, too. So, what is your heart',('red','blue','black'),command=test1)
b.add_link((400,500),'TinGroup知识库','http://tinhome.baklib-free.com/')
b.add_link((400,530),'执行print函数',print)
_,ok1,_=b.add_waitbar1((500,220),bg='#CCCCCC')
b.add_button((500,270),'停止等待动画',activefg='cyan',activebg='black',command=test2)
bu1=b.add_button((700,200),'停止点状滚动条',activefg='white',activebg='black',command=test3)[1]
bu2=b.add_button((700,250),'nothing button 2')[1]
bu3=b.add_button((700,300),'nothing button 3')[1]
b.add_labelframe((bu1,bu2,bu3),'box buttons')
_,_,ok2,_=b.add_waitbar2((600,400))
b.add_combobox((600,550),text='你有多大可能去珠穆朗玛峰',content=('20%','40%','60%','80%','100%','1000%'))
b.add_button((600,480),text='测试进度条(无事件版本)',command=test4)
_,_,_,progressgoto,_,_=b.add_progressbar((600,510))
b.add_table((180,630),data=(('a','space fans over the\nworld','c'),('you\ncan','2','3'),('I','II','have a dream, then try your best to get it!')))
b.add_paragraph((300,850),text='上面是一个表格')
b.add_onoff((600,100))
b.add_spinbox((680,100))
b.add_scalebar((680,50),command=test5)
scale_text,_=b.add_label((890,50),text='当前选值:2')
b.add_info((680,140),info_text='this is info widget in TinUI')
mtb=b.add_paragraph((0,720),'测试菜单(右键单击)')
b.add_menubar(mtb,cont=(('command',print),('menu',test1),'-',('TinUI文本移动',test)))
ttb=b.add_paragraph((0,800),'TinUI能做些什么?')
b.add_tooltip(ttb,'很多很多')
b.add_back(pos=(0,0),uids=(ttb,),bg='cyan')
_,_,ok3,_=b.add_waitbar3((600,800),width=240)
b.add_button((600,750),text='停止带状等待框',command=lambda event:ok3())
a.mainloop()
最终效果
2022-7-12新样式
github项目
TinUI的github项目地址
pip下载
pip install tinui
修改开源协议
从2022年2月开始,TinUI(包括TinUIXml技术)使用GPLv3开源协议。若要在你的软件或程序中使用TinUI,请遵照TinUI开源协议和开源条款。
开源条款见TinUI的github项目地址。
结语
TinUI推出了最新的现代化xml布局方式——TinUIXml。赶快去使用吧!!!
tkinter创新