【C++第二阶段】封装之类访问权限 & struct class区别&成员设置私有&案例
内容包括 : 访问权限,class,struct区别,成员属性设置为私有,设计案例。
访问权限
C++中的访问权限有3种,对于成员属性/变量及成员函数/方法,都一样。
①public的成员属性/变量及成员函数/方法,无论是在类内还是在类外(main()函数或其他函数中),都可以访问(我理解为更改==编辑==赋值)。
②protected的成员属性/变量及成员函数/方法,类内可以访问,类外不可以访问。
③private的成员属性/变量及成员函数/方法,类内可以访问,类外不可以访问。
protected和private都是类内可以访问,类外不可以访问,区别是什么?前者在继承时,可以被子类访问(更改==编辑==赋值),而后者不可以。
设计实验,说明以上的语法。
①所有成员属性和成员函数都设置为public,进行类内和类外的访问。
#include此时没有报错,运行结果为:
D:\Program\C++\BlackHorse\Clion\cmake-build-debug\BlackHorse.exe
父类名字为:Washton。进程已结束,退出代码0
实验设计②
所有成员属性及成员函数设置为protected,在类外访问。
#include结果为:
但若仅将成员变量设置为私有,可以运行:
class Father{
protected:
string class_father_name;
public:
void set_class_father_name(string name){
class_father_name = name;
}
void print(){
cout<<"父类名字为:"<<class_father_name<<"。"<<endl;
}
};
int main(){
Father washton;
washton.set_class_father_name("Washton");
washton.print();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
D:\Program\C++\BlackHorse\Clion\cmake-build-debug\BlackHorse.exe
父类名字为:Washton。进程已结束,退出代码0
说明可以通过public权限的成员函数将值传递给成员变量。
③将成员属性设置为private,但成员函数仍然是public。
运行结果仍然如上。
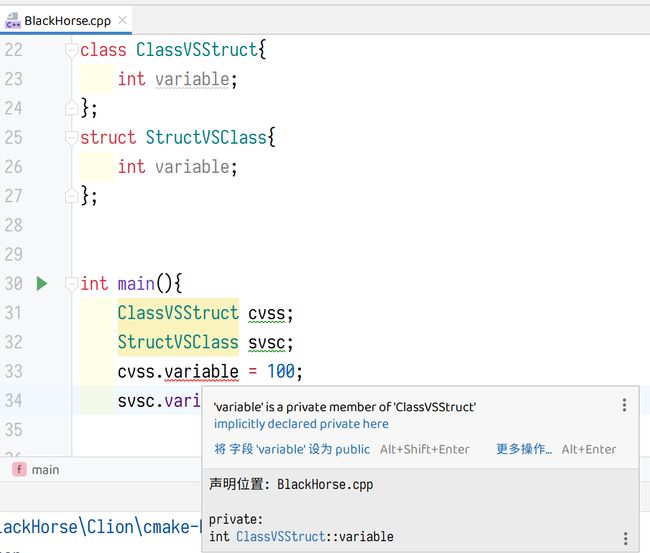
C++中,struct和class有什么区别?
①前者默认权限为public,后者默认权限是private。
②前者能定义方法吗?我不知道。后者可以定义方法。
以实验代码说明两者权限。分别创建结构体和类,及成员变量,并在主函数中访问。看是否会报错。
#include可以看到编译器提示,类的默认权限为private。
说明类的默认权限是私有。
成员属性设置为私有
优点①:将所有成员属性设置为私有,可以控制读写权限。
优点②:对于写权限,可以检测数据的有效性。
对于优点①,拿实验来说明,对于一个人,希望昵称是可以读,也可以写的,因为不同平台的昵称可能不同;对于年龄,希望是可以读的,因为短期内不会突然长老;对于idol,希望只是可以写的,因为是独属于自己的idol。
对于优点②,进行年龄的验证,如果年龄输入的有点离谱,返回默认年龄。
根据这个思路,来进行代码编写。
//对于优点①,拿实验来说明,对于一个人,希望昵称是可以读,也可以写的,因为不同平台的昵称可能不同;
// 对于年龄,希望是可以读的,因为短期内不会突然长老;
// 对于idol,希望只是可以写的,因为是独属于自己的idol。
class Person{
string person_name;
short int person_age = 18;
string person_idol;
public:
void setName(string name){
person_name = name;
}
string getName(){
return person_name;
}
int getAge(){
return person_age;
}
// 年龄验证
void setAge(short int age){
if (age < 0 || age > 150){
cout<<"年龄为:"<<age<<",是修仙了吗?"<<endl;
return;
}
person_age = age;
}
void setIdol(string idol){
person_idol = idol;
}
};
int main(){
Person jack;
string jack_name;
short int jack_age;
string jack_idol;
jack_name = "Jack.Smith";
jack.setName(jack_name);
cout<<"获取Jack名称为:"<<jack.getName()<<endl;
jack_age = 1000;
jack.setAge(jack_age);
cout<<"获取jack年龄为;"<<jack.getAge()<<endl;
jack_idol = "张艺兴";
jack.setIdol(jack_idol);
return 0;
}
两个案例
案例①
设计立方体类Cube,求出立方体的面积和体积,分别用全局函数和成员函数判断两个立方体是否相等。
我的思路:首先面积和体积是由长宽高算出来的,这个长宽高是私有的,所以只能写入,不能得到。接着就是计算它的表面积和体积。
代码:
#include
res_array = Sort(get_length(),get_width(),get_depth() , res_array );
// for (int i = 0 ; i< res_array.len;i++){
// cout<<"res_array中第"<
// }
// cout<<"ult数组排序"<
ult_array = Sort(cube.get_length() ,cube.get_width() , cube.get_depth() , ult_array );
// for (int i = 0 ; i< res_array.len;i++){
// cout<<"ult_array中第"<
// }
for(int i = 0 ; i<res_array.len; i++){
if(res_array.Array[i] != ult_array.Array[i]){
// cout<<"此时res_array值为:"<
// cout<<"此时ult_array值为:"<
cout<<"两者不一致了。"<<endl;
break;
}else{
}
if(i == 2){
cout<<"两者一致。"<<endl;
}
}
}
};
double Calculate_Superficial_Area(double &length , double &width , double &depth){
return 2*(length * width + length*depth + width*depth);
}
double Calculate_Bulk(double &length , double &width , double &depth){
return length*width*depth;
}
void Distinguish(Cube &res , Cube &ult){
CubeArray res_array , ult_array;
// cout<<"res数组排序"<
res_array = Sort(res.get_length(),res.get_width(),res.get_depth() , res_array );
// for (int i = 0 ; i< res_array.len;i++){
// cout<<"res_array中第"<
// }
// cout<<"ult数组排序"<
ult_array = Sort(ult.get_length() ,ult.get_width() , ult.get_depth() , ult_array );
// for (int i = 0 ; i< res_array.len;i++){
// cout<<"ult_array中第"<
// }
for(int i = 0 ; i<res_array.len; i++){
if(res_array.Array[i] != ult_array.Array[i]){
// cout<<"此时res_array值为:"<
// cout<<"此时ult_array值为:"<
cout<<"两者不一致了。"<<endl;
break;
}else{
}
if(i == 2){
cout<<"两者一致。"<<endl;
}
}
}
int main(){
Cube cu,be;
double cu_length = 2.3;
double cu_width = 2.2;
double cu_depth = 1.1;
cu.set_length(cu_length);
cu.set_width(cu_width);
cu.set_depth(cu_depth);
double be_length = 2.2;
double be_width = 1.1;
double be_depth = 2.3;
be.set_length(be_length);
be.set_width(be_width);
be.set_depth(be_depth);
double cube_superficial_area = cu.get_superficial_area();
double cube_bulk = cu.get_bulk();
double global_superficial_area = Calculate_Superficial_Area(cu_length , cu_width , cu_depth);
double global_bulk = Calculate_Bulk(cu_length , cu_width , cu_depth);
cu.distinguish(be);
Distinguish(cu , be);
}
因为长宽高可能是翻转的关系,所以没有挨个对比,用了排序,来看三者关系。
案例②
点和圆的关系,有3种关系,但是重点在于类内包含类。在这个案例中,就是圆里面要有圆心,这个圆心是一个点,可以作为一个类。
另外一个要掌握的知识点就是分文件编写。
头文件中包括函数和类(成员属性和成员函数)的声明
头文件有两个circle.h和point.h,对应的两个源文件里要有声明,声明时要写输入输出流以及命名空间吗?实现要写输入输出流以及命名空间吗?
问题①:先写#pragma once,要写输入输出流以及命名空间。
问题②:需要写,并且还要写对应的头文件。
在实现源文件中,首先删除class以及大括号以及成员变量。然后,可能会报错,因为写在源文件中编译器会认为这是全局函数,但实际上是成员函数这时需要在 前面写类名::,这样编译器就认为这是某个类名的作用域下的成员函数。
point.h
#pragma once
#includecircle.h
#pragma once
#includePoint.cpp
#includeCircle.cpp
#includesection-2.cpp
#include运行结果: