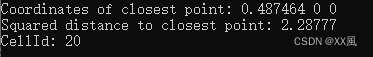
使用 VTK 中的单元定位器来查找最近的点
开发环境:
- Windows 11 家庭中文版
- Microsoft Visual Studio Community 2019
- VTK-9.3.0.rc0
- vtk-example
关键点:
- 创建了一个球体数据源,并使用它构建了一个单元定位器(cell locator)。
- 通过 FindClosestPoint 方法查找了测试点的最近点,并输出了最近点的坐标、到最近点的距离的平方以及包含最近点的单元格的 ID。
- vtkCellTreeLocator vtkCellLocator的区别是什么?
vtkCellLocator 和 vtkCellTreeLocator 都是 VTK 中用于空间搜索的类,但它们之间存在一些区别。
vtkCellLocator 是 VTK 中用于查找单元格的类,它构建了一个内部的空间数据结构,用于高效地定位数据集中的单元格。它提供了多种方法,如查找距离给定点最近的单元格、查找被一条线穿过的所有单元格等。它适用于一般的空间搜索和相交检测。而 vtkCellTreeLocator 是 vtkCellLocator 的一个特定类型,它使用了一种叫做 "cell tree" 的数据结构来组织数据,以提高空间搜索的效率。相比于普通的 vtkCellLocator,vtkCellTreeLocator 在某些情况下可能具有更快的查询速度,特别是对于大型数据集和高维数据。
因此,可以说 vtkCellTreeLocator 是 vtkCellLocator 的一种优化实现,专门用于处理更复杂的空间搜索情况。当使用VTK进行空间搜索时,例如在三维数据集中查找最近的单元格或执行射线投射,您可以选择使用vtkCellLocator或vtkCellTreeLocator。
举个例子,如果您有一个非常大的三维数据集,比如地质模型或医学图像,您想要在其中执行大量的空间查询操作,那么使用vtkCellTreeLocator可能会比vtkCellLocator更有效率。因为vtkCellTreeLocator使用了一种更高效的数据结构,可以在大型和高维数据集中提供更快的查询速度。
另一方面,如果您的数据集相对较小,或者您只需要进行少量的空间查询操作,那么使用普通的vtkCellLocator可能已经足够满足您的需求。
因此,在选择使用哪种空间搜索类时,您可以根据您的具体应用场景和性能需求来决定。
prj name: CellLocator
#include project name: CellTreeLocator
#include