Spring用法学习总结(一)
Spring学习
- 1 Spring框架概述
- 2 Spring容器
- 3 基于XML方式创建对象
- 4 基于XML方式注入属性
-
- 4.1 通过set方法注入属性
- 4.2 通过构造器注入属性
- 4.3 使用p命名空间注入属性
- 4.4 注入bean与自动装配
- 4.5 注入集合
- 4.6 注入外部属性文件
- 4.7 注入属性的全部代码
1 Spring框架概述
- Spring是轻量级的开源的JavaEE框架,提供了多个模块
- Spring可以解决企业应用开发的复杂性
- Spring有两个核心部分:IOC和Aop
(1)IOC:控制反转,把创建对象过程交给Spring进行管理
(2)Aop:面向切面,不修改源代码进行功能增强 - Spring特点
(1)方便解耦,简化开发
(2)Aop编程支持
(3)方便程序测试
(4)方便和其他框架进行整合
(5)方便进行事务操作
(6)降低API开发难度

2 Spring容器
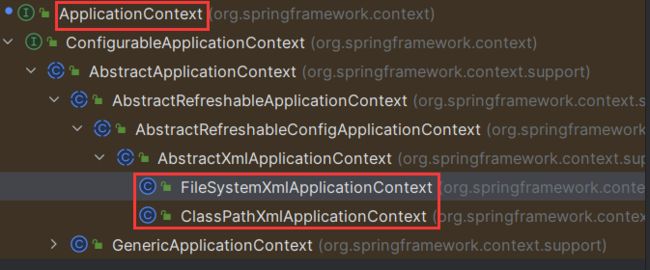
Spring提供了两种容器,分别是BeanFactory和ApplicationConetxt
BeanFactory
BeanFactory是bean的实例化工厂,主要负责bean的解析、实现和保存化操作,不提供给开发人员使用
ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext继承于BeanFactory,提供更多更强大的功能,一般由开发人员进行使用
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xml路径");
或
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("xml路径");
3 基于XML方式创建对象
定义一个User类
package springstudy;//自己的包名
public class User {
public void add() {
System.out.println("add...");
}
}
创建一个XML文件,注意XML文件路径
其中
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="springstudy.User">bean>
beans>
在Test类使用User类,注意ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“bean1.xml”)的路径是./src/bean1.xml,其他位置需要使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“file:xml文件绝对路径”)
package springstudy;//自己的包名
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
user.add();
}
}
设置单实例还是多实例
bean 标签里面有属性(scope)用于设置单实例还是多实例
设置 scope 值是 singleton 时,加载 spring 配置文件时就会创建单实例对象;设置 scope 值是 prototype 时,不是在加载 spring 配置文件时创建对象,而是在调用getBean 方法时候创建多实例对象
4 基于XML方式注入属性
DI(Dependency Injection):依赖注入,就是注入属性
4.1 通过set方法注入属性
在User类中定义set方法
//属性
private String name;
private int age;
private String address;
private String degree;
public User(int height, int weight) {
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
//set方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public void setDegree(String degree) {
this.degree = degree;
}
在bean1.xml中使用 property 完成属性注入,name:类里面属性名称, value:向属性注入的值,property标签可以加
<property name="name" value="西施">property>
<property name="age"><value>18value>property>
<property name="address"><null/>property>
4.2 通过构造器注入属性
在User类中定义构造器
//属性
private int height;
private int weight;
//构造器
public User(int height, int weight) {
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
在bean1.xml中使用constructor-arg标签注入属性
<constructor-arg name="height" value="168">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="weight" value="90">constructor-arg>
4.3 使用p命名空间注入属性
注:使用p命名空间注入属性,该属性必须定义set方法
在bean1.xml文件中添加p命名空间,在bean标签中添加p:属性名=“属性值”
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
<bean id="user" class="springstudy.User" p:degree="本科">
4.4 注入bean与自动装配
创建Card类
package springstudy;
public class Card {
private int id;
private double money;
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
}
在User类定义Card属性
private Card card;
public void setCard(Card card) {
this.card = card;
}
public Card getCard() {
return card;
}
在bean1.xml添加如下代码,如果通过
<bean id="user" class="springstudy.User" p:degree="本科">
<property name="card">
<bean id="card" class="springstudy.Card">
<property name="id" value="1">property>
<property name="money" value="1000">property>
bean>
property>
<property name="card" ref="card">property>
<property name="card.money" value="999">property>
bean>
<bean id="card" class="springstudy.Card">
<property name="id" value="1">property>
<property name="money" value="1000">property>
bean>
自动装配
自动装配是自动注入相关联的bean到另一个bean,通过bean标签的autowire属性实现
autowire=“byType”根据class类型自动装配
修改注入Bean方式1,设置autowire=“byType”,在byType(类型模式中)Spring容器会基于反射查看bean定义的类,然后找到依赖类型相同的bean注入到另外的bean中,这个过程需要set方法来完成(需要在User类中定义setCard方法),如果存在多个类型相同的bean,会注入失败,这时需要通过在不需要注入的bean中添加autowire-candidate=“false”来解决,id的属性值可以不和类中定义的属性相同(如User类中定义private Card card,但是在bean中id可以为card1)
<bean id="user" class="springstudy.User" p:degree="本科" autowrite="byType">
bean>
<bean id="card" class="springstudy.Card">
<property name="id" value="1">property>
<property name="money" value="1000">property>
bean>
<bean id="card1" class="springstudy.Card" autowire-candidate=“false”>
<property name="id" value="1">property>
<property name="money" value="10000">property>
bean>
autowire=“byName”根据id属性值自动装配
设置autowire=“byName”,Spring会尝试将属性名和bean中的id进行匹配,如果找到的话就注入依赖中,没有找到该属性就为null(如User类中定义private Card card,需要bean中的id为card才能注入)
<bean id="user" class="springstudy.User" p:degree="本科" autowire="byName">
bean>
<bean id="card" class="springstudy.Card">
<property name="id" value="1">property>
<property name="money" value="1000">property>
bean>
除了通过xml方式自动装配外还可以通过注解自动装配
4.5 注入集合
在User类中定义集合的set方法
//数组
private String[] costumes;
//list集合
private List<String> list;
private List<String> testlist;
//map集合
private Map<String,String> maps;
//set集合
private Set<String> sets;
public void setSets(Set<String> sets) {
this.sets = sets;
}
public void setCostumes(String[] costumes) {
this.costumes = costumes;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setTestlist(List<String> testlist) {
this.testlist = testlist;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
在bean1.xml注入集合属性,除了通过
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="springstudy.User" p:degree="本科">
<property name="costumes">
<array>
<value>裙子value>
<value>汉服value>
array>
property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>张三value>
<value>小三value>
list>
property>
<property name="testlist" ref="bookList">property>
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="JAVA" value="java">entry>
<entry key="PHP" value="php">entry>
map>
property>
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>MySQLvalue>
<value>Redisvalue>
set>
property>
bean>
<util:list id="bookList">
<value>易筋经value>
<value>九阴真经value>
<value>九阳神功value>
util:list>
beans>
4.6 注入外部属性文件
Spring提供了读取外部properties文件的机制,可以将读到数据为bean的属性赋值
在src目录下创建user.properties配置文件
test.name=小乔
user.age=21
age=18
在bean1.xml文件中加入content命名空间及其xsd文件,通过property-placeholder加载properties文件(放在bean标签的外面),其中location=“classpath:user.properties” 的地址实际为 ./src/user.properties,file-encoding设置文件编码格式,避免中文乱码。如果设置file-encoding="UTF-8"出现中文为问号,请在编辑器中设置properties配置文件的格式
在IDEA打开Settings–>Editor–>File Encodings

<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:user.properties" file-encoding="UTF-8"/>
<beans>
在bean中添加属性
<property name="name" value="${test.name}">property>
<property name="age" value="${user.age}">property>
发现个有意思的东西,设置value=“${user.name}”,user.name是电脑的用户名,不知道其他人会不会这样
4.7 注入属性的全部代码
User类
package springstudy;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class User {
//属性
private String name;
private int age;
private int height;
private int weight;
private String address;
private String degree;
private Card card;
//数组
private String[] costumes;
//list集合
private List<String> list;
private List<String> testlist;
//map集合
private Map<String,String> maps;
//set集合
private Set<String> sets;
public User(int height, int weight) {
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
//set方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public void setDegree(String degree) {
this.degree = degree;
}
public void setCard(Card card) {
this.card = card;
}
public Card getCard() {
return card;
}
public void setSets(Set<String> sets) {
this.sets = sets;
}
public void setCostumes(String[] costumes) {
this.costumes = costumes;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setTestlist(List<String> testlist) {
this.testlist = testlist;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public void add() {
System.out.println("add...");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", height=" + height +
", weight=" + weight +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
", degree='" + degree + '\'' +
", card.money='" + card.getMoney() + '\'' +
'}';
}
//集合输出
public void print() {
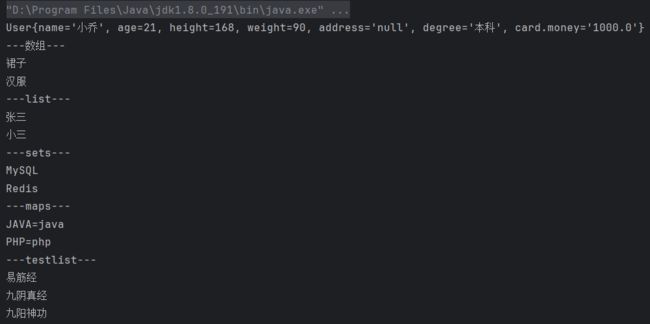
System.out.println("---数组---");
for (String i : costumes) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("---list---");
for (String i : list) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("---sets---");
for (String i : sets) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("---maps---");
for (String key : maps.keySet()){
String value = (String) maps.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
System.out.println("---testlist---");
for (String i : testlist) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
bean1.xml文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:user.properties" file-encoding="UTF-8"/>
<bean id="user" class="springstudy.User" p:degree="本科" autowire="byName">
<property name="address"><null/>property>
<constructor-arg name="height" value="168">constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="weight" value="90">constructor-arg>
<property name="costumes">
<array>
<value>裙子value>
<value>汉服value>
array>
property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>张三value>
<value>小三value>
list>
property>
<property name="testlist" ref="bookList">property>
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="JAVA" value="java">entry>
<entry key="PHP" value="php">entry>
map>
property>
<property name="sets">
<set>
<value>MySQLvalue>
<value>Redisvalue>
set>
property>
<property name="name" value="${test.name}">property>
<property name="age" value="${user.age}">property>
bean>
<bean id="card" class="springstudy.Card" autowire-candidate="false">
<property name="id" value="1">property>
<property name="money" value="1000">property>
bean>
<bean id="card1" class="springstudy.Card">
<property name="id" value="1">property>
<property name="money" value="10000">property>
bean>
<util:list id="bookList">
<value>易筋经value>
<value>九阴真经value>
<value>九阳神功value>
util:list>
beans>
Card类
package springstudy;
public class Card {
private int id;
private double money;
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
}
Test类,其中System.out.println(user);会自动调用User类的toString方法
package springstudy; //自己的包
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
user.print();
}
}
user.properties文件
test.name=小乔
user.age=21
age=18
不想创建那么多文件,看起来太乱。。。