【Leetcode】优先队列(PriorityQueue)问题解析
优先队列PriorityQueue对应的堆是一种常用的数据结构。
文章目录
-
-
- 优先队列PriorityQueue
-
- 1. 简介
- 2. java内置优先队列的API
- 23. 合并K个升序链表
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 参考代码
- 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 参考代码
- 1753. 移除石子的最大得分
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 参考代码
- LCP 30. 魔塔游戏
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 参考代码
- 1705. 吃苹果的最大数目
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 参考代码
- 778. 水位上升的泳池中游泳
-
- 1. 题目描述
- 2. 思路分析
- 3. 参考代码
-
优先队列PriorityQueue
1. 简介
Java PriorityQueue 实现了 Queue 接口,不允许放入 null 元素;其通过堆实现,具体说是通过完全二叉树(complete binary tree)实现的小顶堆(任意一个非叶子节点的权值,都不大于其左右子节点的权值),也就意味着可以通过数组来作为PriorityQueue 的底层实现,数组初始大小为11;也可以用一棵完全二叉树表示。
2. java内置优先队列的API
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
});
Lambda表达式写法(推荐使用)
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1 , o2) -> o1 - o2); // 小根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1 , o2) -> o2 - o1); // 大根堆
23. 合并K个升序链表
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
将链表存入优先队列中,使用优先队列来选择最小元素,先把k个链表加入到优先队列中,然后依次从队列中取出链表,把链表的节点插入小根堆中。
3. 参考代码
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
// 小根堆
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> (o1.val - o2.val));
for (ListNode list : lists) {
if (list != null) {
queue.offer(list);
}
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1); // 头结点
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ListNode head = queue.poll();
cur.next = head;
if (head.next != null) {
queue.offer(head.next);
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
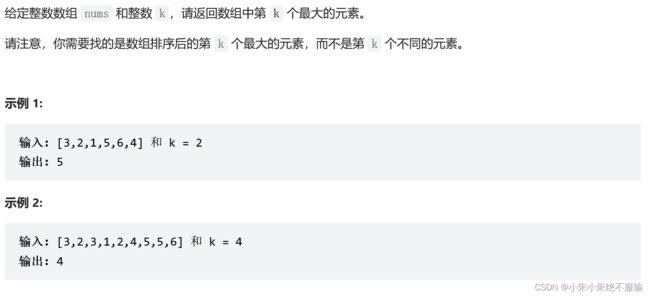
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
优先队列:小根堆存储元素,判断当堆中元素多于k个时,删除堆顶元素。 最后堆顶元素即为第k个最大元素。
3. 参考代码
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
// 小根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int num : nums) {
queue.offer(num);
// 堆中元素多于k个时,删除堆顶元素
if (queue.size() > k) {
queue.poll();
}
}
return queue.peek(); // 堆顶元素即为第k个最大元素
}
}
1753. 移除石子的最大得分
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
方法一:排序
当排序后的第一个数或者第二个数大于0的时候,将第一个数和第二个数分别减1,得分加1,重新对数组进行排序。
方法二:优先队列
大根堆,第一个poll()就是最大的,第二个poll()的就是中间的,判断当中间的值不等于0,分数加1,再把最大值和中间值各自减一加入大根堆。
3. 参考代码
方法一:排序
class Solution {
public int maximumScore(int a, int b, int c) {
// 排序
int[] nums = new int[]{a, b, c};
Arrays.sort(nums);
int res = 0;
while (nums[0] > 0 || nums[1] > 0) {
nums[1]--;
nums[2]--;
res++;
Arrays.sort(nums);
}
return res;
}
}
方法二:优先队列
class Solution {
public int maximumScore(int a, int b, int c) {
// 大根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);
queue.offer(a);
queue.offer(b);
queue.offer(c);
int res = 0;
while(true) {
int max = queue.poll();
int mid = queue.poll();
if (mid == 0) break;
res++;
queue.offer(mid - 1);
queue.offer(max - 1);
}
return res;
}
}
LCP 30. 魔塔游戏
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
贪心算法加优先队列,当血不够减时,把扣的最多的血加回来,再把扣的最多的血调整数组末尾。优先队列用来存储扣的血,小根堆,每次输出的都是扣的最多的血。
3. 参考代码
class Solution {
public int magicTower(int[] nums) {
// 贪心算法加优先队列,每次不够用的时候,将负的最小值调整到序列末尾
int sum = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();
sum = sum + 1;
if (sum < 1) return -1;
long blood = 1; // 防止溢出
int count = 0;
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int num : nums) {
blood += num;
if (num < 0) queue.offer(num);
if (blood < 1) {
while (blood < 1 && !queue.isEmpty()) {
blood -= queue.poll(); // 加上减去的最小值,将最小值调整到末尾
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
1705. 吃苹果的最大数目
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
优先队列,按第i天的苹果可以存储到的天数和第i天长出的苹果个数,构建小根堆。如果时间到了,且没有处在保质期的苹果,则break。然后移除超过保质期的苹果,最后吃苹果。
3. 参考代码
class Solution {
public int eatenApples(int[] apples, int[] days) {
// 优先队列,按第i天的苹果可以存储到的天数和第i天长出的苹果个数,构建小根堆
PriorityQueue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1[0] - o2[0]);
int count = 0, day = 0;
while (true) {
if (day < apples.length) {
queue.offer(new int[]{days[day] + day, apples[day]});
} else if (day >= apples.length && queue.isEmpty()) {
break; // 时间到了,且没有处在保质期的苹果
}
// 移除腐烂苹果
while (!queue.isEmpty() && (queue.peek()[0] <= day || queue.peek()[1] == 0)) {
queue.poll();
}
// 吃苹果
if (!queue.isEmpty()) {
count++;
queue.peek()[1]--;
}
// 天数+1
day++;
}
return count;
}
}
778. 水位上升的泳池中游泳
1. 题目描述
2. 思路分析
优先队列+BFS,从起点开始bfs扩散,看需要几步到达终点,使用优先队列选择最小的高度,res = Math.max(res, 路径中每个位置的高度)。
3. 参考代码
class Solution {
public int swimInWater(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
int res = 0;
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
// 优先队列每次拿出高度最小的元素
PriorityQueue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> grid[a[0]][a[1]] - grid[b[0]][b[1]]);
queue.offer(new int[]{0, 0}); // 存储索引
visited[0][0] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] index = queue.poll();
res = Math.max(res, grid[index[0]][index[1]]);
if (index[0] == m - 1 && index[1] == n - 1) {
return res;
}
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int x = index[0] + dir[0];
int y = index[1] + dir[1];
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= m || y >= n || visited[x][y]) {
continue;
}
queue.offer(new int[]{x, y});
visited[x][y] = true;
}
}
return -1;
}
}