华为机考108题(c++)(91-100)
HJ91 走方格的方案数
描述
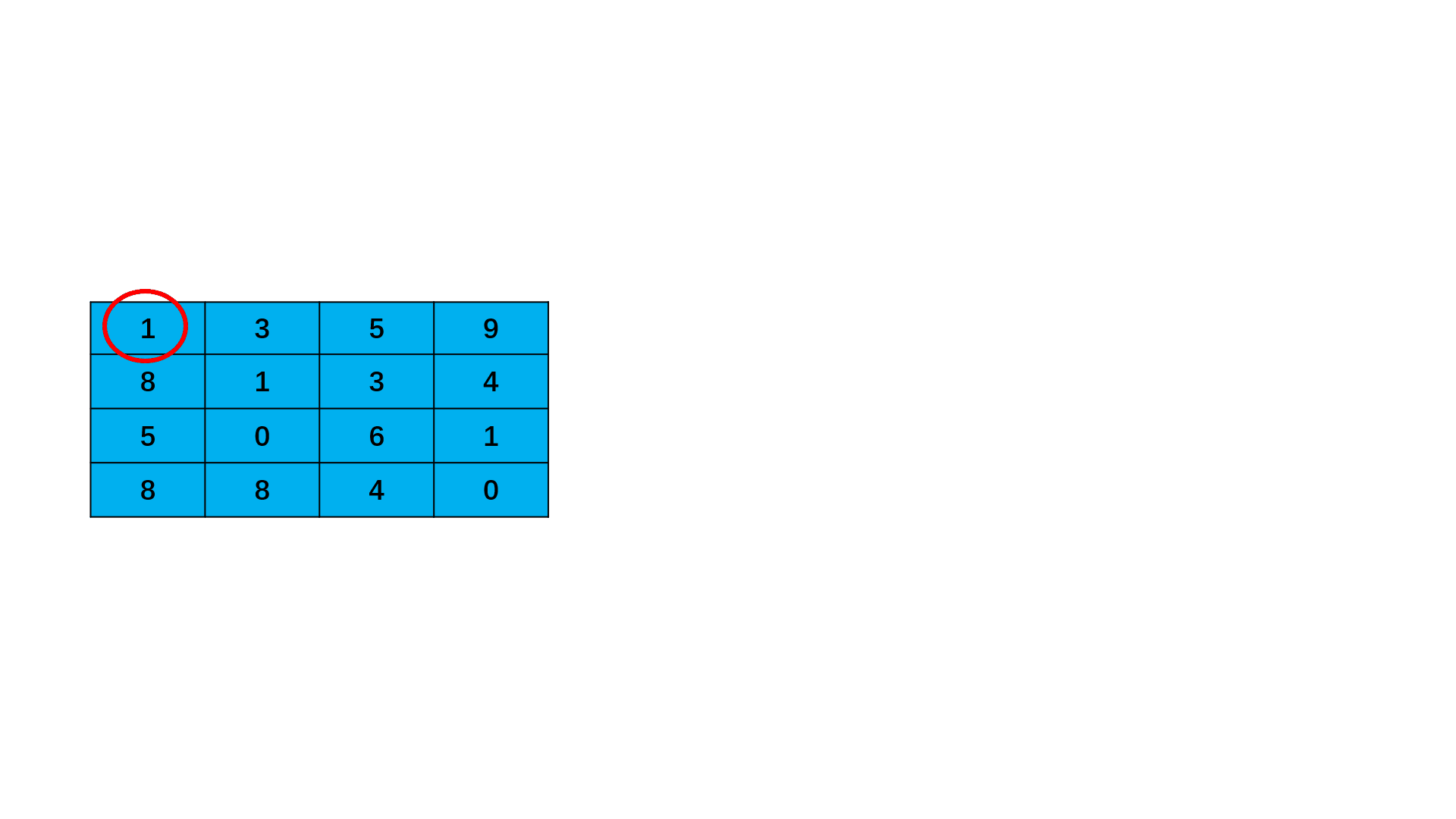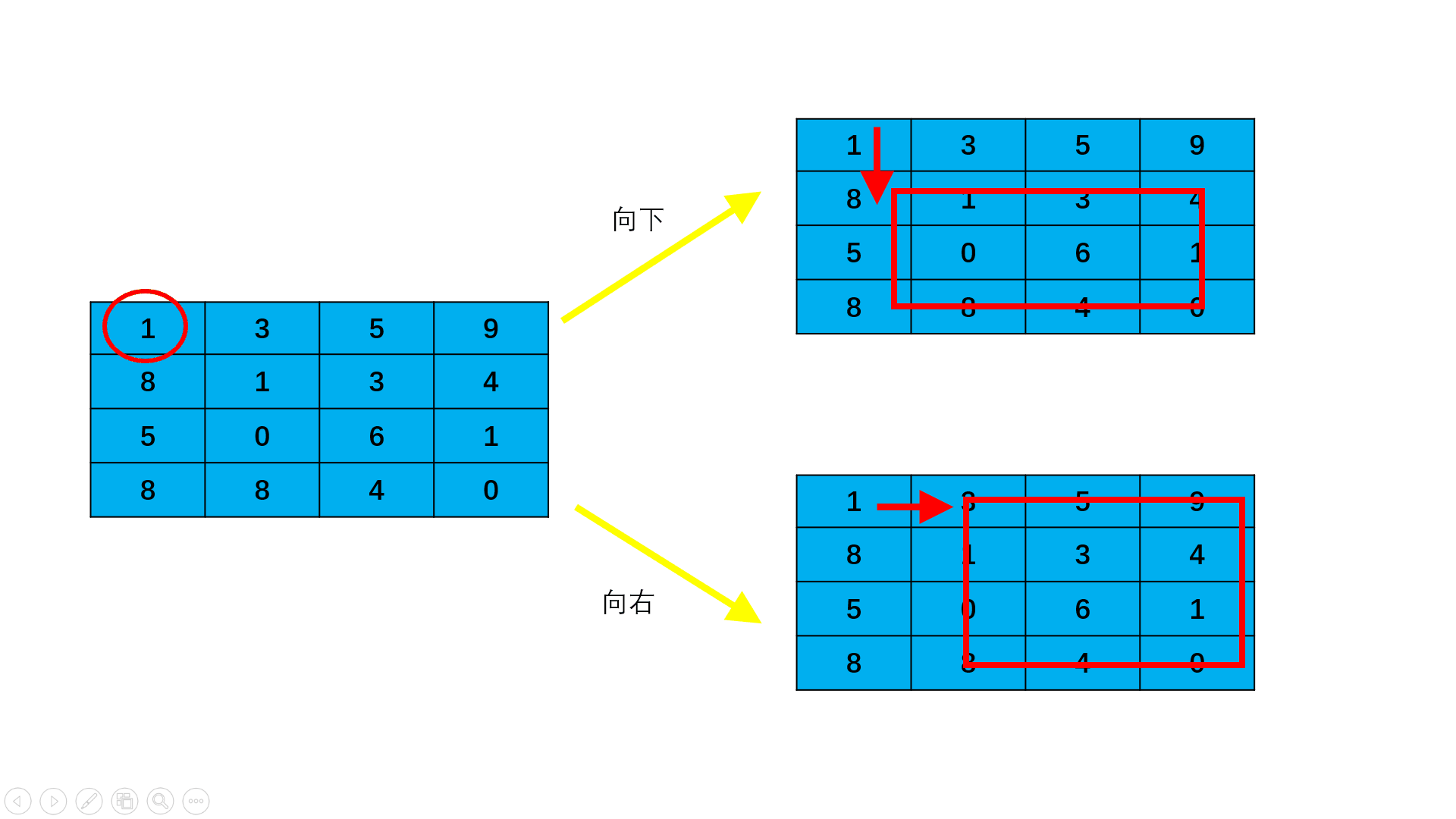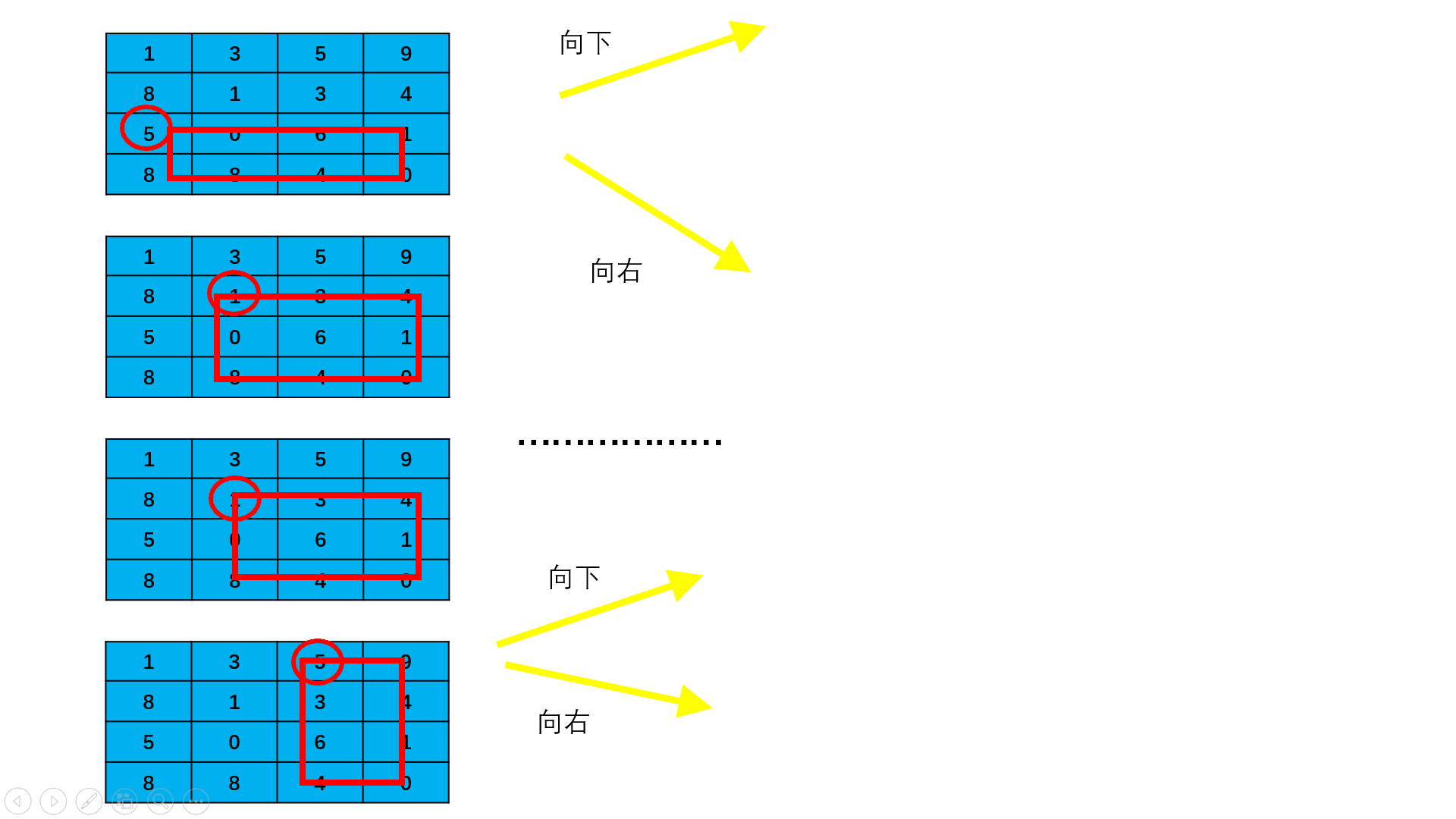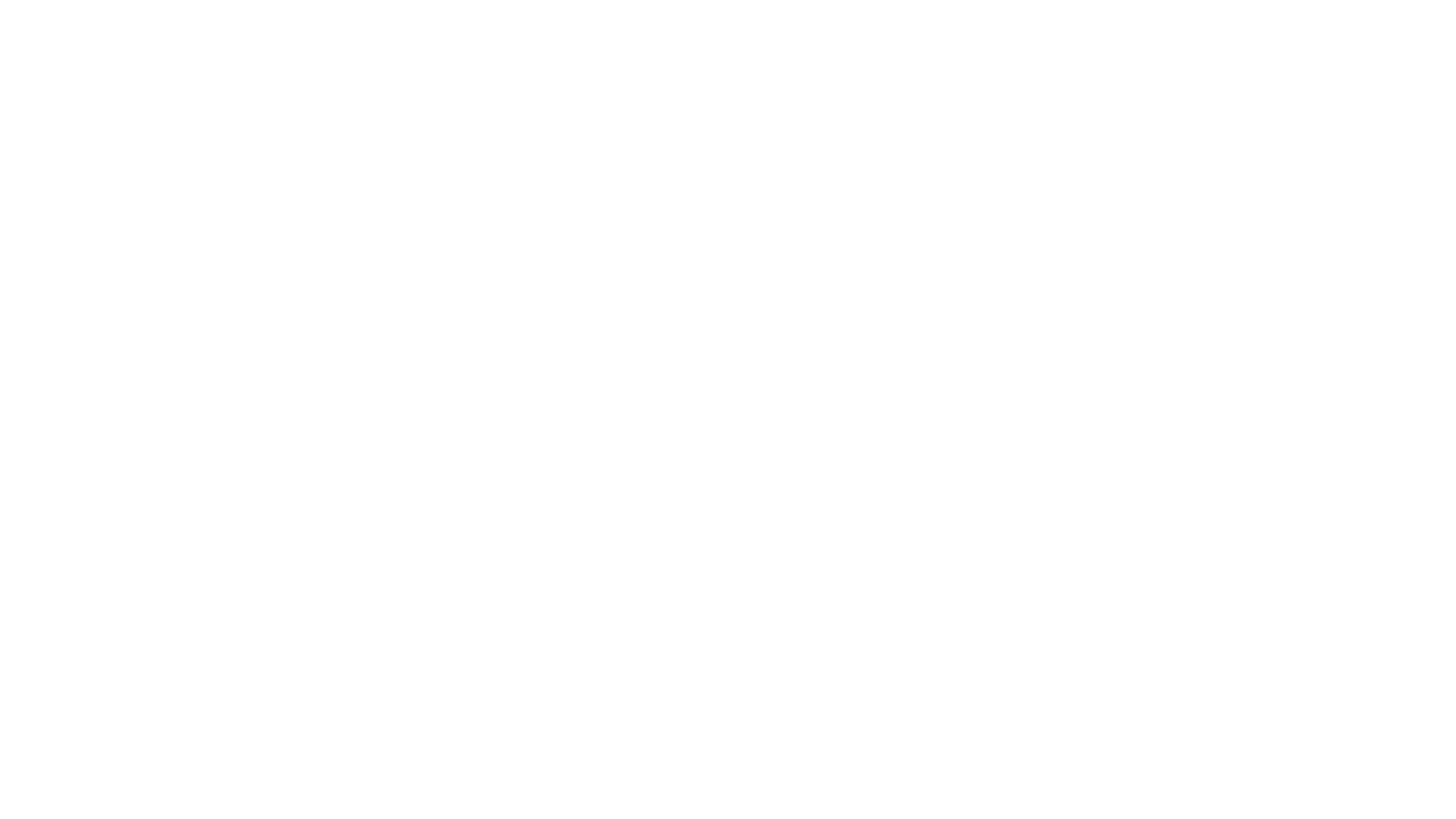
请计算n*m的棋盘格子(n为横向的格子数,m为竖向的格子数)从棋盘左上角出发沿着边缘线从左上角走到右下角,总共有多少种走法,要求不能走回头路,即:只能往右和往下走,不能往左和往上走。
注:沿棋盘格之间的边缘线行走
数据范围: 1≤n,m≤8
输入描述:
输入两个正整数n和m,用空格隔开。(1≤n,m≤8)
输出描述:
输出一行结果
方法一:递归
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int recursion(int i, int j, int m, int n){ //递归计算方案数
if(n == i || m == j) //到边界只有一种走法
return 1;
return recursion(i + 1, j, m, n) + recursion(i, j + 1, m, n); //进入子问题
}
int main(){
int m, n;
while(cin >> n >> m){
cout << recursion(0, 0, m, n) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法二:动态规划
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m, n;
while(cin >> n >> m){
vector > dp(n + 1, vector(m + 1, 0)); //dp[i][j]表示到第i行j列为止的方案数
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j <= m; j++){
if(i == 0 && j == 0) //最开始,一种方法
dp[i][j] = 1;
else if(i == 0) //行数到顶,等于旁边列的方法
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1];
else if(j == 0) //列数到左边,等于旁边行的方法
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
else //等于左边加上边的方法
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j];
}
cout << dp[n][m] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法三:组合数学
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m, n;
while(cin >> n >> m){
int x = 1;
int y = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
x *= m + i; //获取分子
y *= i; //获取分母
}
cout << x / y << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HJ92 在字符串中找出连续最长的数字串
描述
输入一个字符串,返回其最长的数字子串,以及其长度。若有多个最长的数字子串,则将它们全部输出(按原字符串的相对位置)
本题含有多组样例输入。
数据范围:字符串长度 1≤n≤200 , 保证每组输入都至少含有一个数字
输入描述:
输入一个字符串。1<=len(字符串)<=200
输出描述:
输出字符串中最长的数字字符串和它的长度,中间用逗号间隔。如果有相同长度的串,则要一块儿输出(中间不要输出空格)。
方法一:双指针
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
while (cin>>s)
{
int i=0;
int maxm = 0;
//记录最长数字子串的起始位置
vector index;
while (imaxm)
{
maxm = j - i;
index.clear();
index.push_back(i);
}
i = j + 1;
}
else i++;
}
for (int h=0;h 方法二:遍历
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char s[200];
vector num;
while (cin>>s)
{
//替换
for (int i=0;imaxm)
{
maxm = strlen(split);
num.clear();
num.push_back(string(split));
}
split = strtok(NULL, p);
}
for (int i=0;i HJ93 数组分组
描述
输入int型数组,询问该数组能否分成两组,使得两组中各元素加起来的和相等,并且,所有5的倍数必须在其中一个组中,所有3的倍数在另一个组中(不包括5的倍数),不是5的倍数也不是3的倍数能放在任意一组,可以将数组分为空数组,能满足以上条件,输出true;不满足时输出false。
数据范围:每个数组大小满足1≤n≤50 ,输入的数据大小满足 ∣val∣≤500
输入描述:
第一行是数据个数,第二行是输入的数据
输出描述:
返回true或者false
方法一:深度优先搜索
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool dp(vector &num, int t,int k)
{
if (t==0 && k==num.size()) return true;
if (k==num.size()) return false;
//如果只是3的倍数,不能加到该集合中。
if (!(num[k]%3)) return(dp(num,t,k+1));
if (num[k]==t) return true;
//对于一个数有两种选择,加或者不加到该集合中
return(dp(num,t-num[k],k+1)|dp(num,t,k+1));
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(cin>>n)
{
vector num;
int x,sum=0,part=0;//只要找到总和的一半即可,剩下的数字之和自然为总和的一半。
for (int i=0;i>x;
//如果是5的倍数,不放入数组num
if (x%5)
num.push_back(x);
else
part += x;
sum += x;
}
//如果所有数之和不是偶数,则肯定是false
if (sum%2)
{
cout<<"false"< 方法二:动态规划
#include
#include
#include HJ94 记票统计
描述
请实现一个计票统计系统。你会收到很多投票,其中有合法的也有不合法的,请统计每个候选人得票的数量以及不合法的票数。
(注:不合法的投票指的是投票的名字不存在n个候选人的名字中!!)
数据范围:每组输入中候选人数量满足 1≤n≤100 ,总票数量满足 1≤n≤100
输入描述:
第一行输入候选人的人数n,第二行输入n个候选人的名字(均为大写字母的字符串),第三行输入投票人的人数,第四行输入投票。
输出描述:
按照输入的顺序,每行输出候选人的名字和得票数量(以" : "隔开,注:英文冒号左右两边都有一个空格!),最后一行输出不合法的票数,格式为"Invalid : "+不合法的票数。
方法一:暴力查找
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
vector > name(n);
string s;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> s;
name[i] = make_pair(s, 0); //记录候选人的名字,初始票数为0
}
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> s;
for(int i = 0; i < name.size(); i++) //只查找到有这个候选人的再计票
if(s == name[i].first)
name[i].second++;
}
int valid = 0; //统计合法票数
for(int i = 0; i < name.size(); i++){ //遍历候选人的名字,输出其票数
cout << name[i].first << " : " << name[i].second << endl;
valid += name[i].second;
}
cout << "Invalid : " << n - valid << endl; //总票数减去合法票数就是非法票数
}
}
方法二:哈希表
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
unordered_map mp;
vector name(n);
string s;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> s;
mp[s] = 0; //在map中记录候选人,设置票数为0
name[i] = s; //记录候选人的名字
}
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> s;
if(mp.find(s) != mp.end()) //只对map中有的候选人计票
mp[s]++;
}
int valid = 0; //统计合法票数
for(int i = 0; i < name.size(); i++){ //遍历候选人的名字,输出其票数
cout << name[i] << " : " << mp[name[i]] << endl;
valid += mp[name[i]];
}
cout << "Invalid : " << n - valid << endl; //总票数减去合法票数就是非法票数
}
}
HJ95 人民币转换
描述
考试题目和要点:
1、中文大写金额数字前应标明“人民币”字样。中文大写金额数字应用壹、贰、叁、肆、伍、陆、柒、捌、玖、拾、佰、仟、万、亿、元、角、分、零、整等字样填写。
2、中文大写金额数字到“元”为止的,在“元”之后,应写“整字,如532.00应写成“人民币伍佰叁拾贰元整”。在”角“和”分“后面不写”整字。
3、阿拉伯数字中间有“0”时,中文大写要写“零”字,阿拉伯数字中间连续有几个“0”时,中文大写金额中间只写一个“零”字,如6007.14,应写成“人民币陆仟零柒元壹角肆分“。
4、10应写作“拾”,100应写作“壹佰”。例如,1010.00应写作“人民币壹仟零拾元整”,110.00应写作“人民币壹佰拾元整”
5、十万以上的数字接千不用加“零”,例如,30105000.00应写作“人民币叁仟零拾万伍仟元整”
输入描述:
输入一个double数
输出描述:
输出人民币格式
方法一:
#include
using namespace std;
string gewei[10] = {"", "壹", "贰", "叁", "肆", "伍", "陆", "柒", "捌", "玖"};
string res;
void calPart1(string str){
for(int i = str.size() - 1, j = 0; i >= 0; i--, j++){ //i表示这是数字的第几位,j表示字符串下标
if(str[j] != '0'){//将当前位置的数字转为中文
if(!(str[j] == '1' && i % 4 == 1)) //10应写作“拾”
res += gewei[str[j] - '0'];
}
if(i != 0){//当前不是个位
if(i % 8 == 0 && i >= 8){ //亿位
res += "亿";
}
if(i % 4 == 0 && i % 8 != 0){ //万位
res += "万";
if(str[j + 1] == '0') //如果千位为0
res += "零";
}
if(i % 4 == 3 && str[j] != '0'){ //千
res += "仟";
if(str[j + 1] == '0' && str[j + 2] != '0') //百位为0
res += "零";
}
if(i % 4 == 2 && str[j] != '0'){ //百
res += "佰";
if(str[j + 1] == '0' && str[j + 2] != '0') //十位为0
res += "零";
}
if(i % 4 == 1 && str[j] != '0') //十位
res += "拾";
}
}
}
//小数点之后的部分转换
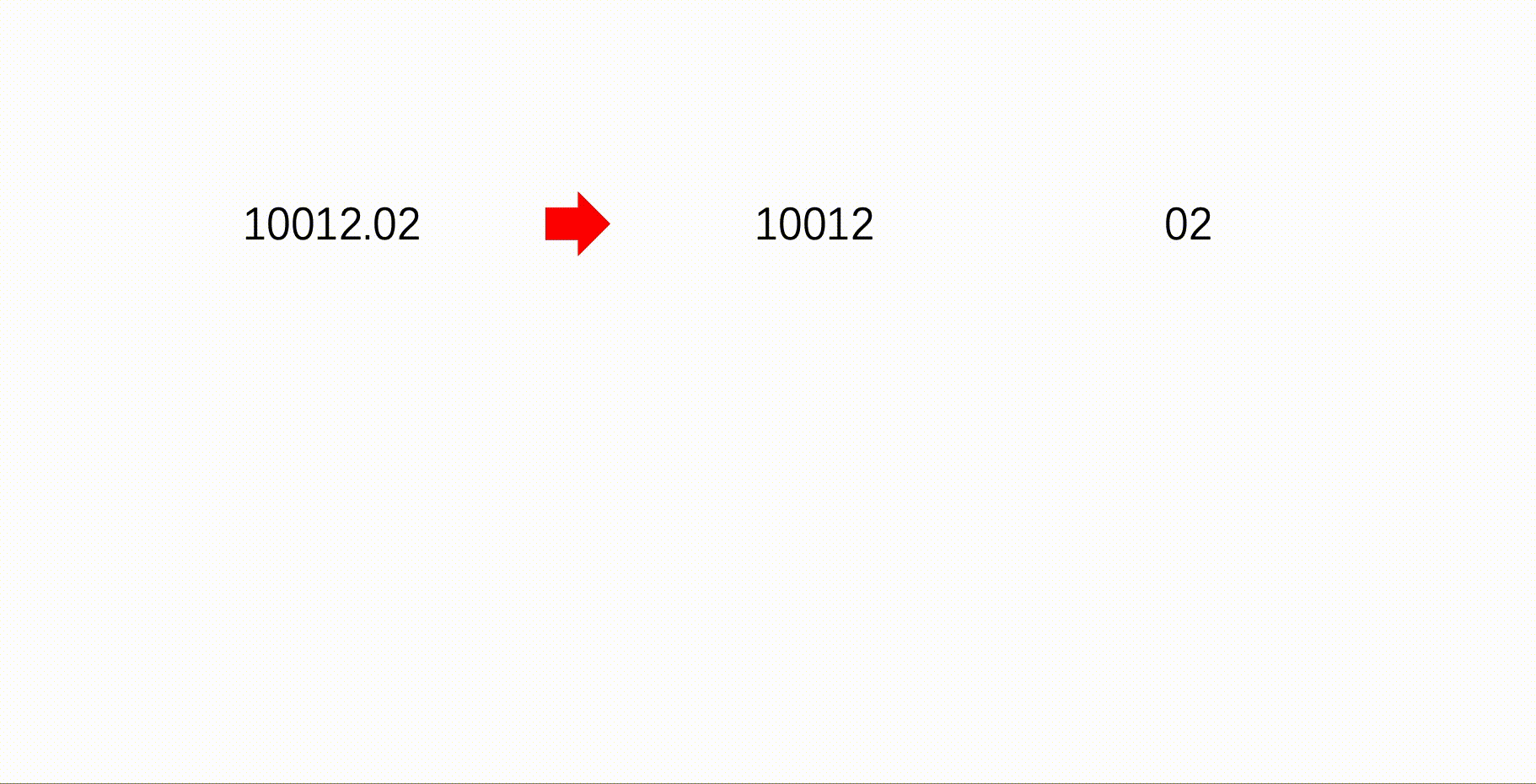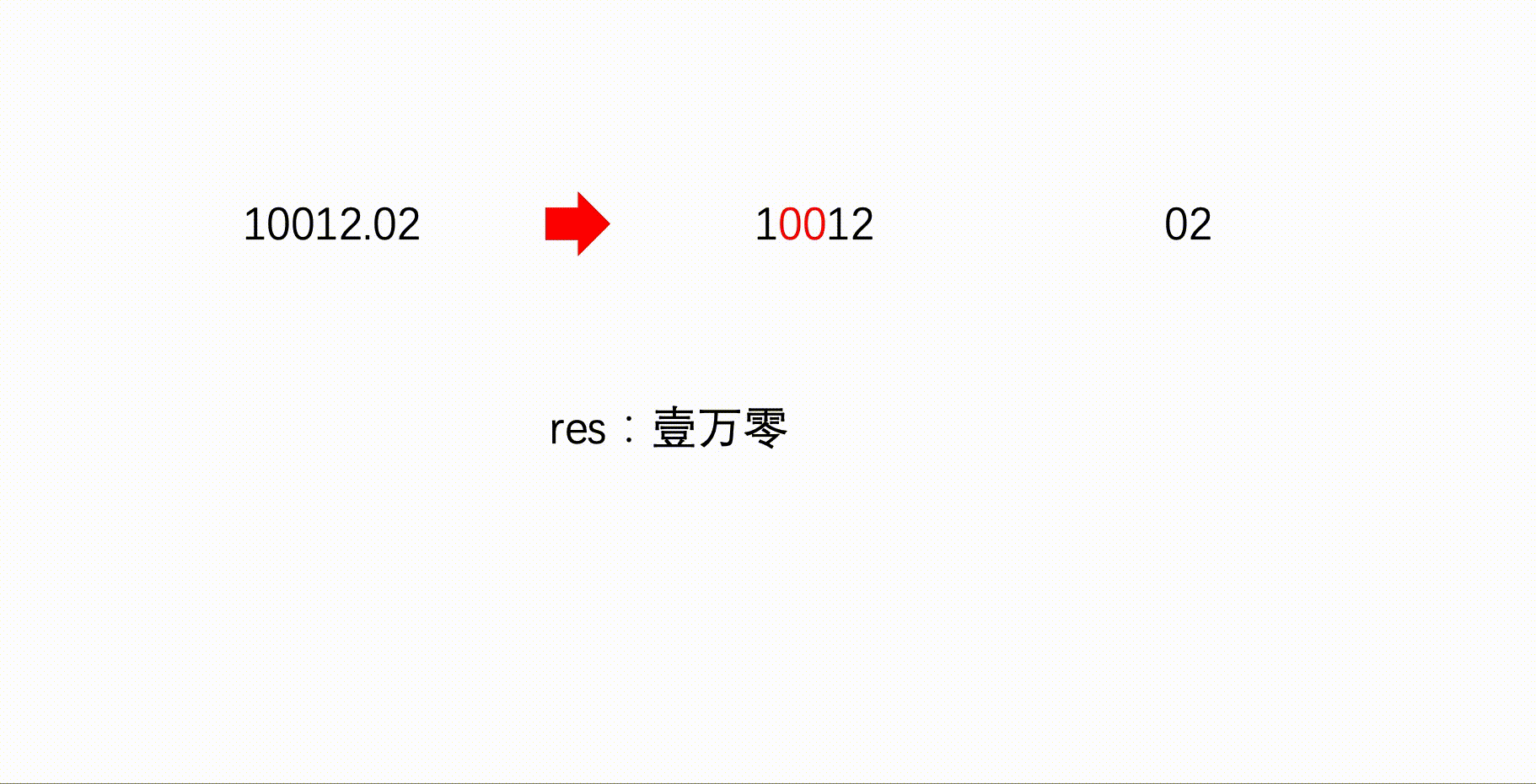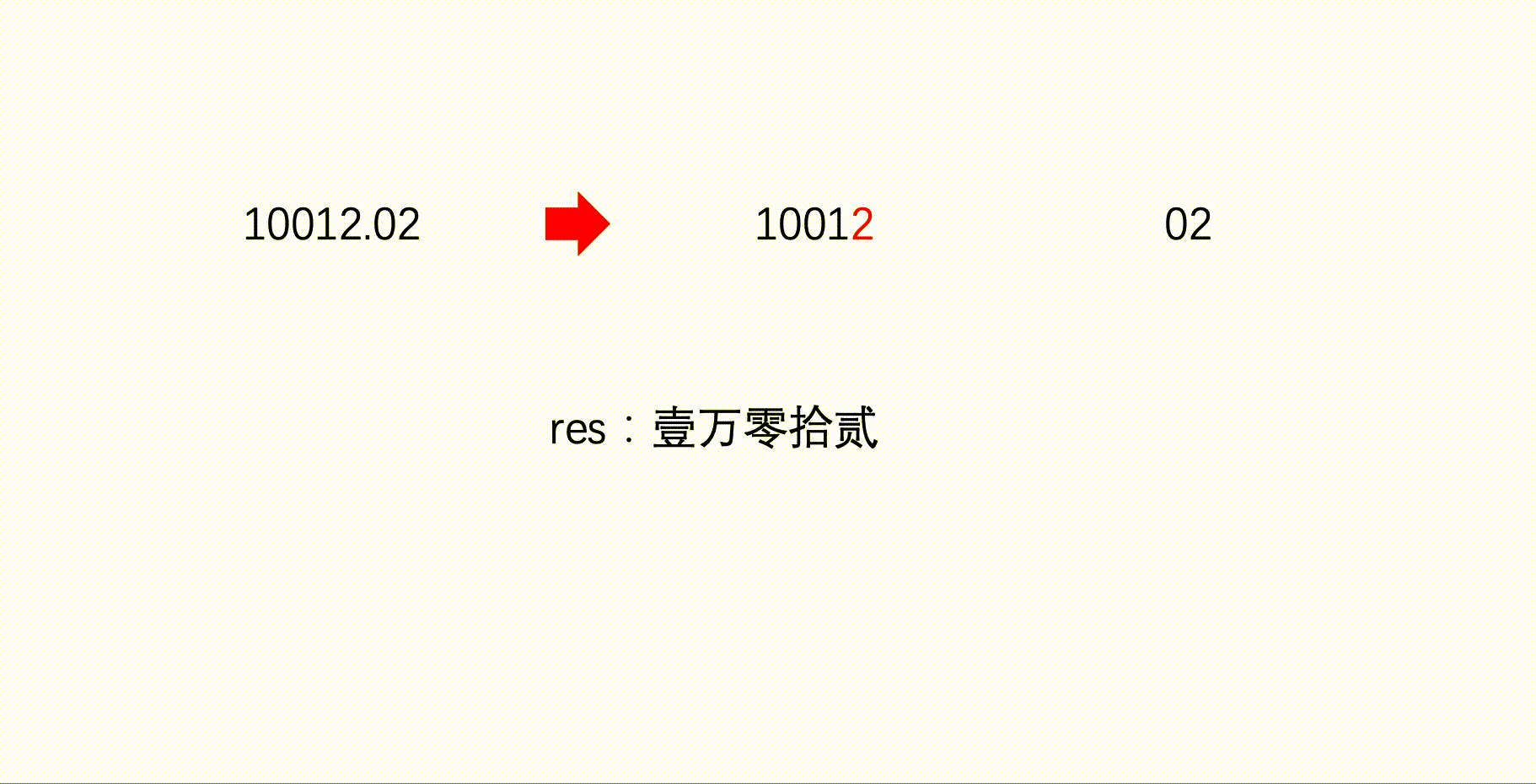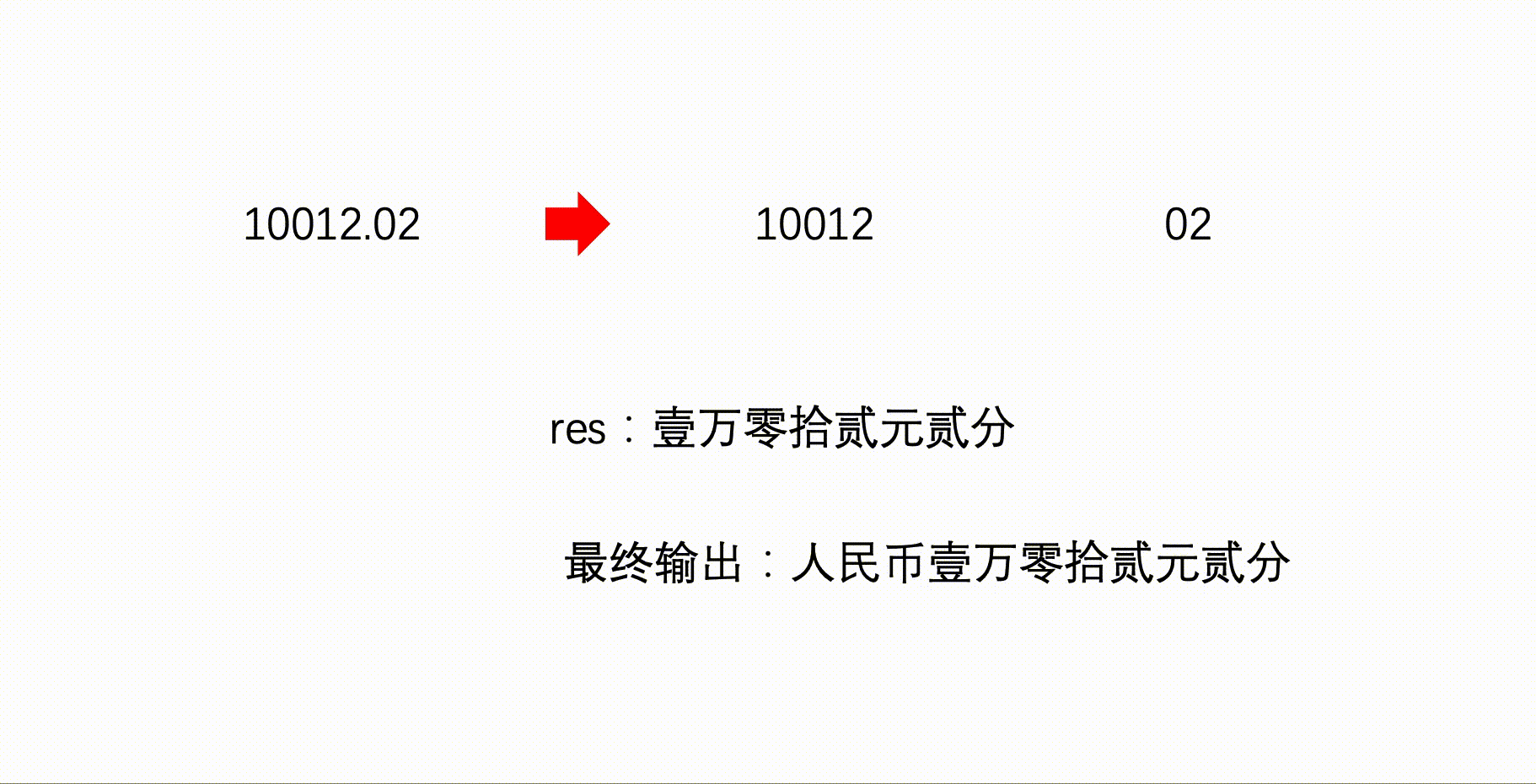
void calPart2(string str){
if(str == "00")
{
res += "整";
return;
}
if (str[0] > '0')
{
res += gewei[str[0]-'0'] + "角";
}
if (str[1] > '0')
{
res += gewei[str[1]-'0'] + "分";
}
return;
}
//主函数
int main()
{
string str;
while(getline(cin, str))
{
//获取小数点的位置
int index = str.find('.');
//获取小数点前的子字符串
string str1 = str.substr(0, index);
//获取小数点后的子字符串
string str2 = str.substr(index + 1);
//输出人民币
cout << "人民币";
//输出元钱
calPart1(str1);
//输出角分零钱
if(str1!="0"){
res += "元";
}
calPart2(str2);
//换行
cout << res << endl;
res.clear();
}
return 0;
}
方法二:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const vector helper1 = {"零","壹","贰","叁","肆","伍","陆","柒","捌","玖"};
const vector helper2 = {"元", "万", "亿"};
const vector helper3 = {"", "拾", "佰", "仟"};
string parts(int num)
{
string str;
if(num > 0 && num <= 9)
str += helper1[num];
else if(num >= 10 && num <= 19)
{
if(num % 10 == 0)
str += helper3[1];
else
str += helper3[1] + helper1[num%10];
}
else if(num >= 20 && num <= 99)
{
if(num % 10 == 0)
str += helper1[num/10] + helper3[1];
else
str += helper1[num/10] + helper3[1] + helper1[num%10];
}
else if(num >= 100 && num <= 999)
{
if(num % 100 == 0)
str += helper1[num/100] + helper3[2];
else if(num % 100 <= 9)
str += helper1[num/100] + helper1[0] + helper1[num%100];
else
str += helper1[num/100] + helper3[2] + parts(num % 100);
}
else if(num >= 1000 && num <= 9999)
{
if(num % 1000 == 0)
str += helper1[num/1000] + helper3[3];
else if(num % 1000 <= 99)
str += helper1[num/1000] + helper3[3] + helper1[0] + parts(num % 1000);
else
str += helper1[num/1000] + helper3[3] + parts(num % 1000);
}
return str;
}
int main(){
double money;
while (cin >> money)
{
money += 0.0001; // 此处+0.0001防止double转换int产生误差
// 分两步,第一步处理整数
int data = static_cast(money);//强制转换,用来强迫隐式转换
vector vec;
string res = "人民币";
while (data)
{
vec.push_back(data % 10000);
data /= 10000;
}
for (int i = vec.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
res += parts(vec[i]);
res += helper2[i];
if (i != 0 && i - 1 >= 0 && vec[i - 1] <= 999 && vec[i - 1] != 0)
res += helper1[0];
}
// 第二步处理小数
int deci = static_cast((money - static_cast(money)) * 100);
if (deci == 0)
res += "整";
else if (deci < 10)
res += helper1[deci] + "分";
else if (deci % 10 == 0)
res += helper1[deci / 10] + "角";
else
res += helper1[deci / 10] + "角" + helper1[deci % 10] + "分";
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HJ96 表示数字
描述
将一个字符中所有的整数前后加上符号“*”,其他字符保持不变。连续的数字视为一个整数。
数据范围:字符串长度满足 1≤n≤100
输入描述:
输入一个字符串
输出描述:
字符中所有出现的数字前后加上符号“*”,其他字符保持不变
方法一:遍历添加
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
while(cin >> s){
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if(isdigit(s[i])){ // 每次第一个遇到的数字前加*
s.insert(i, "*");
i++;
while(isdigit(s[i])) //遍历连续的数字找到这一段的最后一个数字
i++;
s.insert(i, "*"); //最后加*
}
}
cout << s << endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法二:正则表达式
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
while(cin >> s){
regex patten("(\\d+)"); //正则表达式匹配数字
s = regex_replace(s, patten, "\*$1\*"); //将数字的地方替换成前后有*
cout << s << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HJ97 记负均正
描述
首先输入要输入的整数个数n,然后输入n个整数。输出为n个整数中负数的个数,和所有正整数的平均值,结果保留一位小数。
0即不是正整数,也不是负数,不计入计算。如果没有正数,则平均值为0。
数据范围:1≤n ≤2000 ,输入的整数都满足 ∣val∣≤1000
输入描述:
首先输入一个正整数n,
然后输入n个整数。
输出描述:
输出负数的个数,和所有正整数的平均值。
方法一:
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
while(cin>>n){
int ans1=0;
int ans2=0,cnt2=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int x;
cin>>x;
if(x<0){
ans1++;//负数
}else if(x>0){
ans2+=x;//正数
cnt2++;
}
}
cout< HJ98 自动售货系统
描述
1 总体说明
考生需要模拟实现一个简单的自动售货系统,实现投币、购买商品、退币、查询库存商品及存钱盒信息的功能。
系统初始化时自动售货机中商品为6种商品,商品的单价参见1.1规格说明,存钱盒内放置1元、2元、5元、10元钱币,商品数量和钱币张数通过初始化命令设置,参见2.1 系统初始化。
1.1规格说明
1. 商品:每种商品包含商品名称、单价、数量三种属性,其中商品名不重复。考生不能修改商品名称和单价,初始化命令设置商品数量。这些信息在考试框架中进行定义,考生在实现功能代码时可直接使用。
| 商品 名称 |
单价 |
数量 |
| A1 | 2 | X |
| A2 | 3 | X |
| A3 | 4 | X |
| A4 | 5 | X |
| A5 | 8 | X |
| A6 | 6 | X |
2. 存钱盒信息:钱币面额、张数两种属性。初始化命令设置各种面额钱币张数。这些信息在考试框架中进行定义,考生在实现功能代码时可直接使用。
| 钱币面额 |
张数 |
| 10元 |
X |
| 5元 |
X |
| 2元 | X |
| 1元 | X |
3. 退币原则 :
1) 根据系统存钱盒内钱币的 信息 ,按钱币总张数最少的原则进行退币。
2) 如果因零钱不足导致不能退币,则尽最大可能退币,以减少用户损失。
例如:假设存钱盒内只有4张2元,无其它面额钱币。如果需要退币7元,系统因零钱不足无法退币,则继续尝试退币6元,最终系统成功退币3张2元,用户损失1元钱币。
4. 投币操作说明:每次投币成功,投入的钱币面额累加到投币余额;同时,本次投入的钱币放入存钱盒中,存钱盒相应面额钱币增加。
5. 投币余额:指当前自动售货机中用户剩余的可购买商品的钱币总额;例如:投入2元面额的钱币,投币余额增加2元;购买一件价格2元的商品,投币余额减少2元;
6. 退币操作说明:退币操作需要遵守 退币原则 ;退币成功后,投币余额清零,同时扣除存钱盒相应的金额。
7. 购买商品操作说明:一次仅允许购买一件商品;购买商品成功后,自动售货机中对应商品数量减1,投币余额扣除本次购买商品的价格。
2 操作说明
命令字与第一个参数间使用一个空格分隔,多条命令采用分号隔开。考试系统会对输入命令格式进行处理,考生不需要关注输入命令格式的合法性,只需要实现命令处理函数。
2.1 系统初始化
命令格式:
r A1 数量 -A2 数量 -A3 数量 -A4 数量 -A5 数量 -A6 数量 1 元张数 -2 元张数 -5 元张数 -10 元张数
| 参数名称 |
参数说明 |
类型 |
取值范围 |
| A1数量 |
商品A1数量 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
| A2数量 |
商品A2数量 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
| A3数量 |
商品A3数量 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
| A4数量 |
商品A4数量 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
| A5数量 |
商品A5数量 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
| A6数量 |
商品A6数量 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
| 1元张数 |
面额1元钱币张数 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
| 2元张数 |
面额2元钱币张数 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
| 5元张数 |
面额5元钱币张数 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
| 10元张数 |
面额10元钱币张数 |
整数 |
[0,30] |
商品和各种面额钱币取值范围只是作为初始化命令的限制,其它场景下不限制取值范围;考试框架已经实现取值范围的检查,考生不需要关注。
功能说明:设置自动售货机中商品数量和存钱盒各种面额的钱币张数;
约束说明:系统在任意阶段均可执行r初始化系统;考生不需要关注参数的合法性,不需要关注增加或缺少参数的场景;
输出说明:输出操作成功提示(执行完r命令后系统会自动输出操作结果,考生不需要再次调用输出函数),例:
| 命令 | 输出 | 含义 |
| r 6-5-4-3-2-1 4-3-2-1; | S001:Initialization is successful | 初始化成功 |
2.2 投币
命令格式:p 钱币面额
功能说明:
(1) 如果投入非1元、2元、5元、10元的钱币面额(钱币面额不考虑负数、字符等非正整数的情况),输出“E002:Denomination error”;
(2) 如果存钱盒中1元和2元面额钱币总额小于本次投入的钱币面额,输出“E003:Change is not enough, pay fail”,但投入1元和2元面额钱币不受此限制。
(3) 如果自动售货机中商品全部销售完毕,投币失败。输出“E005:All the goods sold out”;
(4) 如果投币成功,输出“S002:Pay success,balance=X”;
约束说明:
(1) 系统在任意阶段都可以投币;
(2) 一次投币只能投一张钱币;
(3) 同等条件下,错误码的优先级:E002 > E003 > E005;
输出说明:如果投币成功,输出“S002:Pay success,balance=X”。
例:
| 命令 |
输出 |
| p 10; |
S002:Pay success,balance=10 |
2.3 购买商品
命令格式:b 商品名称
功能说明:
(1) 如果购买的商品不在商品列表中,输出“E006:Goods does not exist”;
(2) 如果所购买的商品的数量为0,输出“E007:The goods sold out”;
(3) 如果投币余额小于待购买商品价格,输出“E008:Lack of balance”;
(4) 如果购买成功,输出“S003:Buy success,balance=X”;
约束说明:
(1) 一次购买操作仅能购买一件商品,可以多次购买;
(2) 同等条件下,错误码的优先级:E006 > E007 > E008;
输出说明:
如果购买成功,输出“S003:Buy success,balance=X”。
例:
| 命令 |
输出 |
| b A1; |
S003:Buy success,balance=8 |
2.4 退币
命令格式:c
功能说明:
(1) 如果投币余额等于0的情况下,输出“E009:Work failure”;
(2) 如果投币余额大于0的情况下,按照 退币原则 进行“找零”,输出退币信息;
约束说明:
(1) 系统在任意阶段都可以退币;
(2) 退币方式必须按照 退币原则 进行退币;
输出说明:如果退币成功,按照 退币原则 输出退币信息。
例,退5元钱币:
| 命令 |
输出 |
| c; |
1 yuan coin number=0 2 yuan coin number=0 5 yuan coin number=1 10 yuan coin number=0 |
2.5 查询
命令格式:q 查询类别
功能说明:
(1) 查询自动售货机中商品信息,包含商品名称、单价、数量。 根据商品数量从大到小进行排序;商品数量相同时,按照商品名称的先后顺序进行排序 。
例如:A1的商品名称先于A2的商品名称,A2的商品名称先于A3的商品名称。
(2) 查询存钱盒信息,包含各种面额钱币的张数;
(3) 查询类别如下表所示:
| 查询类别 |
查询内容 |
| 0 |
查询商品信息 |
| 1 | 查询存钱盒信息 |
如果“查询类别”参数错误,输出“E010:Parameter error”。“查询类别”参数错误时,不进行下面的处理;
输出说明:
“查询类别”为0时,输出自动售货机中所有商品信息(商品名称单价数量)例:
| 命令 |
输出 |
| q 0; |
A1 2 6 A2 3 5 A3 4 4 A4 5 3 A5 8 2 A6 6 0 |
“查询类别”为1时,输出存钱盒信息(各种面额钱币的张数),格式固定。例:
| 命令 |
输出 |
|
| q 1; |
1 yuan coin number=4 2 yuan coin number=3 5 yuan coin number=2 10 yuan coin number=1 |
|
输入描述:
依照说明中的命令码格式输入命令。
输出描述:
输出执行结果
方法一:直接判断
具体做法:
需要实现5个功能,我们分成5个函数,输入的命令之间通过分号连接,我们可以通过字符串流输入获取分号间的子串,组成一个数组,然后遍历子串数组就是遍历每条命令,命令开头字母对应相应的功能及函数。
- money表示投入的币有多少钱
- goods表示商品数量
- price表示每件商品价格
- coins表示零钱盒中各类零钱的数量
第一个功能,初始化
命令后面两串数字表示分别初始化商品数量和零钱数量,数字之间用-间隔,商品和零钱之间用空格间隔。我们可以截取去掉前两位,遍历后续数字,遇到到数字字符就转化为数字加入数字中,遇到-符号就进入下一个商品,遇到空格则变成开始初始化零钱数量,和前面商品类似,我们可以用一个bool型flag变量来区分。
同时初始化的时候要把money投入的钱置为0,初始化成功之后输出。
第二个功能,投币
只能投入1元、2元、5元、10元四种币种,一次只能投一张钱币,因此截取数字后先检查是否是这四种,然后检查存钱盒中1元和2元面额钱币总额小于本次投入的钱币面额,再检查自动售货机中商品全部销售完毕,最后才是投币成功,零钱盒中数量增加,已投币数量money也增加。优先级的顺序已经用判断语句的先后顺序考虑了,下同
第三个功能,购买
根据输入的命令,检查商品名称是否在A1到A6这个范围内,再检查所购买的商品是否数量为0,再检查已投币money是否小于商品价格,最后才能购买成功,一条命令只能买一条,购买成功需要将money和库存一起减少。
第四个功能,退币
退币有两个条件:
| 1 2 |
|
因此我们准备abcd代表要退的四种面额的数量,应该先从10元的开始退,尽可能多的拿高面值的币,然后剩余的钱要么是零碎的要么是高面值不够了剩余的才开始用低面值的钱,退钱后需要减少已投币money的数量,同时减少零钱盒中相应钱币的数量。
第五个功能,查询
输入命令查询0,是查询商品信息,查询1是查询零钱盒信息,其余的都是非法命令。
对于商品信息,我们使用vector数组来记录商品名称、价格及数量,然后重载比较信息,在数量不同时以数量降序,在数量相同时以名称升序来排序,最后输出。
对于零钱信息就直接输出这四项即可。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int price[6] = {2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6}; // 商品价格
int money = 0; //投入的钱
vector split(string str, const char c){ //通过字符c分割字符串
vector res;
istringstream iss(str); // 字符串流输入
string temp = "";
while(getline(iss, temp, c)) //根据流输入分割
res.push_back(temp);
return res;
}
void init(vector& a, vector& b, string& s){ //初始化函数
money = 0; //初始化投入的钱
s = s.substr(2, s.length() - 2); //去掉前面的r和空格
a[0] = a[1] = a[2] = a[3] = a[4] = a[5] = 0;
b[0] = b[1] = b[2] = b[3] = 0;
int i = 0;
bool flag = false; //判别是前面部分商品价格还是后面部分零钱盒
for(auto c: s){
if(isdigit(c) && !flag) //数字且是价格
a[i] = a[i] * 10 + (c -' 0'); //根据字符计算数字
else if(isdigit(c) && flag) //数字且是零钱
b[i] = b[i] * 10 + (c - '0'); //根据字符计算数字
else if(c == ' '){ //遇到空格换成零钱
flag = true;
i = 0;
}
else if(c == '-') //遇到-后移一位商品或零钱
i++;
}
cout << "S001:Initialization is successful" << endl;
}
void pay(vector& a, vector& b, string& s){ //投币函数
int num = 0;
for(auto &c: s)
if(isdigit(c)) //只计算数字部分
num = num * 10 + (c - '0'); //一次只投一张
if(num == 1 || num == 2 || num == 5 || num == 10){ //投入合法的币种
if(num > 2 && num > (b[0] + b[1] * 2)) //存钱盒中1元和2元面额钱币总额小于本次投入的钱币面额
cout << "E003:Change is not enough, pay fail" << endl;
else if((a[0] || a[1] || a[2] || a[3] || a[4] || a[5]) == 0) //商品全部为0
cout << "E005:All the goods sold out" << endl;
else{ //零钱盒中钱数增加
if(num == 1 || num == 2)
b[num-1]++;
else if(num == 5)
b[2]++;
else b[3]++;
money += num; //投入的总钱数增加
cout << "S002:Pay success,balance=" << money << endl;
}
}
else //不合法币种
cout << "E002:Denomination error" << endl;
}
void buy(vector& a, vector& b, string& s){ //购买函数
//检查命令是否是4位,第三位是否为A,第四位是否数字1-6
if(s.length() == 4 && (s[2] == 'A') && (s[3] - '0' < 7) && isdigit(s[3]) && (s[3] != '0')){
if(a[s[3] - '1'] == 0) //该商品的售罄
cout << "E007:The goods sold out" << endl;
else if(price[s[3] - '1'] > money) //该商品价格大于投入的钱
cout << "E008:Lack of balance" << endl;
else{ //成功购买
money -= price[s[3] - '1']; //投入的钱要减去买的商品
a[s[3] - '1']--;
cout << "S003:Buy success,balance=" << money << endl;
}
}
else //输入命令不合法,商品不存在
cout << "E006:Goods does not exist" << endl;
}
void back(vector& coins){//退币函数
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0, d = 0; //四个币种
if(money == 0) //投入的没有钱了,不用退
cout << "E009:Work failure" << endl;
else{
d = money / 10; //优先退大币额的数量
if(d <= coins[3]){ //10块的钱够退
money = money % 10;
coins[3] -= d;
}
else{ //10块的钱不够退
d = coins[3]; //全部退完
coins[3] = 0;
money -= d * 10; //剩余要退的
}
c = money / 5; //再计算要退的5块钱的数量
if(c <= coins[2]){ //5块的钱够退
money = money % 5;
coins[2] -= c;
}
else{ //5块的钱不够退
c = coins[2]; //全部退完
coins[2] = 0;
money -= d * 5; //剩余要退的
}
b = money / 2; //再计算要退的2块钱的数量
if(b <= coins[1]){ //2块的钱够退
money = money % 2;
coins[1] -= b;
}
else{ //2块的钱不够退
b = coins[1]; //全部退完
coins[1] = 0;
money -= d * 2; //剩余要退的
}
a = money; //再计算要退的1块钱的数量
if(a <= coins[0]){ //1块的钱够退
coins[0] -= a;
money = 0;
}
else{ //1块的钱不够退
coins[0] = 0;
money -= a;
}
cout << "1 yuan coin number=" << a << endl << "2 yuan coin number=" << b << endl << "5 yuan coin number=" << c << endl << "10 yuan coin number=" << d << endl;
}
}
bool cmp(pair, int>& a, pair, int>& b){ //重载比较
if(a.second != a.second) //优先比较商品数量
return a.second > b.second;
else //再比较商品名字
return a.first.first < b.first.first;
}
void query(vector& a, vector& b, string& s){ //查询函数
if(s[1] == ' ' && s.length() == 3){ //检查查询命令的合法性
if(s[2] == 0){ //类别为0
vector, int> > temp;
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) //商品信息入vector方便排序输出
temp.push_back(make_pair(make_pair("A" + char(i + 1), price[i]), a[i]));
sort(temp.begin(), temp.end(), cmp); //按照重载后的比较排序
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) //输出
cout << temp[i].first.first << " " << temp[i].first.second << " " << temp[i].second << endl;
}
else if(s[2] == 1){ //类别为1
cout << "1 yuan coin number=" << b[0] << endl
<< "2 yuan coin number=" << b[1] << endl
<< "5 yuan coin number=" << b[2] << endl
<< "10 yuan coin number=" << b[3] << endl;
}
else
cout << "E010:Parameter error" << endl;
}
else
cout << "E010:Parameter error" << endl;
}
int main(){
string s;
vector goods(6, 0);
vector coins(4, 0);
while(getline(cin, s)){
vector orders = split(s, ';');
for(auto c: orders){
switch(c[0]){
case 'r': //初始化
init(goods, coins, c);
break;
case 'p': //投币
pay(goods, coins, c);
break;
case 'b': //购买商品
buy(goods, coins, c);
break;
case 'c': //退币
back(coins);
break;
case 'q': //查询
query(goods, coins, c);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
方法二:类封装
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool cmp(pair, int>& a, pair, int>& b){ //重载比较
if(a.second != a.second) //优先比较商品数量
return a.second > b.second;
else //再比较商品名字
return a.first.first < b.first.first;
}
class Vending{
private:
vector price = {2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 6}; // 商品价格
int money = 0;
vector goods; //商品数量
vector coins; //零钱数量
public:
void init(string& s){ //初始化函数
money = 0; //初始化投入的钱
s = s.substr(2, s.length() - 2); //去掉前面的r和空格
goods.resize(6);
coins.resize(4);
goods[0] = goods[1] = goods[2] = goods[3] = goods[4] = goods[5] = 0;
coins[0] = coins[1] = coins[2] = coins[3] = 0;
int i = 0;
bool flag = false; //判别是前面部分商品价格还是后面部分零钱盒
for(auto c: s){
if(isdigit(c) && !flag) //数字且是价格
goods[i] = goods[i] * 10 + (c -' 0'); //根据字符计算数字
else if(isdigit(c) && flag) //数字且是零钱
coins[i] = coins[i] * 10 + (c - '0'); //根据字符计算数字
else if(c == ' '){ //遇到空格换成零钱
flag = true;
i = 0;
}
else if(c == '-') //遇到-后移一位商品或零钱
i++;
}
cout << "S001:Initialization is successful" << endl;
}
void pay(string& s){ //投币函数
int num = 0;
for(auto &c: s)
if(isdigit(c)) //只计算数字部分
num = num * 10 + (c - '0'); //一次只投一张
if(num == 1 || num == 2 || num == 5 || num == 10){ //投入合法的币种
if(num > 2 && num > (coins[0] + coins[1] * 2)) //存钱盒中1元和2元面额钱币总额小于本次投入的钱币面额
cout << "E003:Change is not enough, pay fail" << endl;
else if((goods[0] || goods[1] || goods[2] || goods[3] || goods[4] || goods[5]) == 0) //商品全部为0
cout << "E005:All the goods sold out" << endl;
else{ //零钱盒中钱数增加
if(num == 1 || num == 2)
coins[num-1]++;
else if(num == 5)
coins[2]++;
else coins[3]++;
money += num; //投入的总钱数增加
cout << "S002:Pay success,balance=" << money << endl;
}
}
else //不合法币种
cout << "E002:Denomination error" << endl;
}
void buy(string& s){ //购买函数
//检查命令是否是4位,第三位是否为A,第四位是否数字1-6
if(s.length() == 4 && (s[2] == 'A') && (s[3] - '0' < 7) && isdigit(s[3]) && (s[3] != '0')){
if(goods[s[3] - '1'] == 0) //该商品的售罄
cout << "E007:The goods sold out" << endl;
else if(price[s[3] - '1'] > money) //该商品价格大于投入的钱
cout << "E008:Lack of balance" << endl;
else{ //成功购买
money -= price[s[3] - '1']; //投入的钱要减去买的商品
goods[s[3] - '1']--;
cout << "S003:Buy success,balance=" << money << endl;
}
}
else //输入命令不合法,商品不存在
cout << "E006:Goods does not exist" << endl;
}
void back(){//退币函数
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0, d = 0; //四个币种
if(money == 0) //投入的没有钱了,不用退
cout << "E009:Work failure" << endl;
else{
d = money / 10; //优先退大币额的数量
if(d <= coins[3]){ //10块的钱够退
money = money % 10;
coins[3] -= d;
}
else{ //10块的钱不够退
d = coins[3]; //全部退完
coins[3] = 0;
money -= d * 10; //剩余要退的
}
c = money / 5; //再计算要退的5块钱的数量
if(c <= coins[2]){ //5块的钱够退
money = money % 5;
coins[2] -= c;
}
else{ //5块的钱不够退
c = coins[2]; //全部退完
coins[2] = 0;
money -= d * 5; //剩余要退的
}
b = money / 2; //再计算要退的2块钱的数量
if(b <= coins[1]){ //2块的钱够退
money = money % 2;
coins[1] -= b;
}
else{ //2块的钱不够退
b = coins[1]; //全部退完
coins[1] = 0;
money -= d * 2; //剩余要退的
}
a = money; //再计算要退的1块钱的数量
if(a <= coins[0]){ //1块的钱够退
coins[0] -= a;
money = 0;
}
else{ //1块的钱不够退
coins[0] = 0;
money -= a;
}
cout << "1 yuan coin number=" << a << endl << "2 yuan coin number=" << b << endl << "5 yuan coin number=" << c << endl << "10 yuan coin number=" << d << endl;
}
}
void query(string& s){ //查询函数
if(s[1] == ' ' && s.length() == 3){ //检查查询命令的合法性
if(s[2] == 0){ //类别为0
vector, int> > temp;
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) //商品信息入vector方便排序输出
temp.push_back(make_pair(make_pair("A" + char(i + 1), price[i]), goods[i]));
sort(temp.begin(), temp.end(), cmp); //按照重载后的比较排序
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) //输出
cout << temp[i].first.first << " " << temp[i].first.second << " " << temp[i].second << endl;
}
else if(s[2] == 1){ //类别为1
cout << "1 yuan coin number=" << coins[0] << endl
<< "2 yuan coin number=" << coins[1] << endl
<< "5 yuan coin number=" << coins[2] << endl
<< "10 yuan coin number=" << coins[3] << endl;
}
else
cout << "E010:Parameter error" << endl;
}
else
cout << "E010:Parameter error" << endl;
}
};
vector split(string str, const char c){ //通过字符c分割字符串
vector res;
istringstream iss(str); // 字符串流输入
string temp = "";
while(getline(iss, temp, c)) //根据流输入分割
res.push_back(temp);
return res;
}
int main(){
string s;
while(getline(cin, s)){
Vending sale; //实例化类
vector orders = split(s, ';'); //以;分割字符串
for(auto c: orders){
switch(c[0]){
case 'r': //初始化
sale.init(c);
break;
case 'p': //投币
sale.pay(c);
break;
case 'b': //购买商品
sale.buy(c);
break;
case 'c': //退币
sale.back();
break;
case 'q': //查询
sale.query(c);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
HJ99 自守数
描述
自守数是指一个数的平方的尾数等于该数自身的自然数。例如:25^2 = 625,76^2 = 5776,9376^2 = 87909376。请求出n(包括n)以内的自守数的个数
数据范围: 1≤n≤10000
输入描述:
int型整数
输出描述:
n以内自守数的数量。
方法一:取模验证法
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
int count = 1; //0属于自守数
int base = 10; //取余基数
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x = i * i;
if(i == base) //保证每次取余与i的位数相同
base *= 10;
if(x % base == i) //取余后是否等于i
count++;
}
cout << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法二:字符串比较法
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
int count = 1; //0属于自守数
string s;
string pows;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
s = to_string(i); //将数字转成字符串
pows = to_string(i * i);
if(pows.substr(pows.length() - s.length()) == s) //比较平方字符串末尾是否等于i
count++;
}
cout << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}
HJ100 等差数列
描述
等差数列 2,5,8,11,14。。。。
(从 2 开始的 3 为公差的等差数列)
输出求等差数列前n项和
数据范围: 1≤n≤1000
输入描述:
输入一个正整数n。
输出描述:
输出一个相加后的整数。
方法一:累加求和
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
int x = 2; //数组第一个元素
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) //遍历数组前n项
sum += x + 3 * i; //累加
cout << sum << endl;
}
return 0;
}
方法二:求和公式
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
int x = 2; //数组第一个元素
int sum = n * x + n * (n - 1) * 3 / 2; //等差数列求和公式
cout << sum << endl;
}
return 0;
}