Path Sum (路径和)----(LeetCode112+LeetCode113+LeetCode437)
文章目录
-
-
- (一) Leetcode 112 Path Sum
-
-
- 1.题意
- 2.示例
- 3.解题思路及代码实现
-
- (二) Leetcode 113 Path Sum II
-
-
- 1.题意
- 2.示例
- 3.解题思路及代码实现
-
- (三) Leetcode 437 Path Sum III
-
-
- 1.题意
- 2.示例
- 3.解题思路及代码实现(python)
-
-
(一) Leetcode 112 Path Sum
1.题意
给定一个二叉树,找一条从根节点到叶子结点的路径,使得这条路径的和等于给定的sum。最终返回的是否存在一条路径?
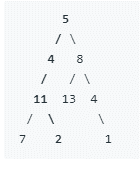
2.示例
3.解题思路及代码实现
如示例所示的树,询问是否有一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径,使得路径上的和等于输入值,当sum==22时,存在一条路径 5 -> 4 -> 11 -> 2 使得 5+4+11+2 == 22。
因此既可以用深度优先搜索来解题,也可以用先序遍历来做,两者效果相当。
DFS实现的java代码如下所示:
其实也是递归操作:
关键在函数定义!定义!根据定义写推导式和终止条件,写完就直接结束,千万别一个一个拿数据再去代。
public class Path_Sum_112 {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root==null) return false;
if(root.left==null && root.right==null) return root.val==sum;
return dfs(root,root.val,sum)>0; //rec初始化为根节点的值
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root,int rec,int sum){ //通过flag的值来判断只要有一条路径成立就可以了
if(root.left==null && root.right==null) //到达叶子节点,判断这条路径之和是否等于输入值sum
return rec-sum==0?1:0; //三目运算符,当rec-sum=0时返回1,不等于0时返回0
int flag=0;
if(root.left!=null) //向左子树搜
flag += dfs(root.left,rec+root.left.val,sum);
if(root.right!=null)
flag += dfs(root.right,rec+root.right.val,sum);
return flag;
}
}
class Solution(object):
def hasPathSum(self, root, sum):
if not root: return False
def dfs(root, target): # 在以root为根结点的树中,能否找到一条从根结点到叶子结点的路径,使得路径和等于target
# 第三步,要是到达叶子节点后的空节点还是没有返回值,则返回False
if not root: return False
# 第一步,递归出来的条件,到达了叶子节点并且叶子节点值刚好等于target,说明这条路径到了!
if not root.left and not root.right and root.val == target:
return True
# 第二步,子问题分解为
# 以root.left为根节点时是否有路径之和为target-root.val 或者
# 以root.right为根节点时是否有路径之和为target-root.val
return dfs(root.left, target-root.val) or dfs(root.right, target-root.val)
return dfs(root, sum)
(二) Leetcode 113 Path Sum II
1.题意
给定一个二叉树,找一条从根节点到叶子结点的路径,使得这条路径的和等于给定的sum。最终返回的是多条存在的路径,用数组存储路径。
2.示例
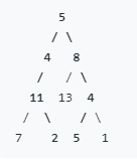
输入:sum = 22
输出:
[
[5,4,11,2],
[5,8,4,5]
]
3.解题思路及代码实现
这道题与上一道LeetCode112很类似,都是使用深度优先遍历或先序遍历来做,不过这道题需要在遍历时保存路径,当路径满足求和等于Sum时把这条路径加入到二维数组之中,最后整棵树都遍历结束之后再返回二维数组。
此外,记录路径需要用到栈。
DFS实现的java代码如下所示:
public class Path_Sum_II_113 {
private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root==null) return ans;
Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<>(); //用来保存一条路径
dfs(root,sum,path);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int sum,Stack<Integer> path){
path.push(root.val);
if(root.left==null && root.right==null) //到达叶子节点
if(root.val==sum) ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
if(root.left!=null) //向左子树搜
dfs(root.left,sum-root.val,path);
if(root.right!=null)
dfs(root.right,sum-root.val,path);
path.pop();//感觉这就是回溯
}
}
python实现:
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
self.res = []
if not root: return []
def dfs(root, Sum, path):
if not root: return
path.append(root.val)
if not root.left and not root.right and root.val==Sum: # 找到一条路径
self.res.append(path[:])
dfs(root.left, Sum-root.val, path)
dfs(root.right, Sum-root.val, path)
path.pop()
dfs(root, sum, [])
return self.res
(三) Leetcode 437 Path Sum III
1.题意
给定一个二叉树,找一条从节点1到叶子2的路径(自顶向下,无需是从根节点到叶子节点),使得这条路径的和等于给定的sum。最终返回的是路径的个数。
2.示例
3.解题思路及代码实现(python)
递归来做,对于当前节点node,计算以自己为开始的路径数(这条路径和等于sum),再分别计算以自己的左儿子,右儿子为开始的路径数!
对于每一个节点都是这么计算,递归下去就行了!!!
- 自顶向下,时间复杂度为O(N^2),还能优化
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
def count(node, sum): # 自己为开头的路径数,不需要到达叶子节点
if not node: return 0
isMe = 1 if node.val == sum else 0
leftBrother = count(node.left, sum - node.val)
rightBrother = count(node.right, sum - node.val)
return isMe + leftBrother + rightBrother
# 递归版的先序遍历
if not root: return 0
pathInLeading = count(root, sum) # 自己为开头的路径数
leftPathSum = self.pathSum(root.left, sum) # 左边路径总数(中间节点路径)
rightPathSum = self.pathSum(root.right, sum) # 右边路径总数
return leftPathSum + rightPathSum + pathInLeading # 以自己,再以左儿子,右儿子为开始的路径总数
- 时间复杂度为O(N)的方法:以空间换时间,缓存中间结果

参考:https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-iii/discuss/141424/Python-step-by-step-walk-through.-Easy-to-understand.-Two-solutions-comparison.-%3A-)
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
def preOrder(root, sum, curPathSum, cache):
if not root: return
# 访问根节点
curPathSum += root.val # 从root到当前结点的路径和
oldPathSum = curPathSum - sum # 剩余还需要的路径和
self.res += cache[oldPathSum] # 看看缓存中有没有还需要的路径和
cache[curPathSum] += 1
preOrder(root.left, sum, curPathSum, cache)
preOrder(root.right, sum, curPathSum, cache)
# 回溯时到其他路径后需要减一
cache[curPathSum] -= 1
self.res = 0
cache = collections.defaultdict(int)
cache[0] = 1 # 初始化时root==sum时也是一条路径
preOrder(root, sum, 0, cache)
return self.res