SpringBean生命周期之初始化篇
文章目录
- 注意事项
- 环境
- 源码解析
-
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
-
- initializeBean
-
- invokeAwareMethods
- invokeInitMethods
-
- invokeCustomInitMethod
- applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
- 总结
注意事项
阅读本文需要有一定的基础,并且要跟着调用链走,不然会很容易懵圈。
环境
Spring Framework Version:5.3.x
Gradle Version:7.5.1
源码解析
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
initializeBean
- 调用Aware方法
- 初始化之前回调BeanPostProcessor
- 初始化Bean
- 初始化之后回调BeanPostProcessor(代理对象也是在此生成)
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
//校验安全管理器,一般没有
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
//如果当前bean实现了BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、BeanFactoryAware这三个Aware接口中的一个或多个,那么会在此方法里调用设置值
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
//包装bean
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//在Bean初始化之前回调各种BeanPostProcessor
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//初始化Bean
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//在Bean初始化之后回调各种BeanPostProcessor(包括动态代理对象生成)
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
BeanPostProcessor是一个扩展点,在bean初始化前后可以对bean进行一些定制操作
invokeAwareMethods
private void invokeAwareMethods(String beanName, Object bean) {
//当前bean是否是Aware类型的,如果是,进行一些列的判断并设置值,如果不是,直接跳过设置
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
invokeInitMethods
- 回调InitializingBean接口中的afterPropertiesSet方法
- 调用自定义初始化方法(init-method属性)
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
//当前bean是否是InitializingBean
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.hasAnyExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
//安全管理器!=null, 一般都是null
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
//回调InitializingBean接口中的afterPropertiesSet方法
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.hasAnyExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
//调用自定义初始化方法(init-method属性)
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
invokeCustomInitMethod
- 获取需要进行调用的自定义初始化方法
- 检查访问权限,如果没有就进行设置
- 通过反射invoke
protected void invokeCustomInitMethod(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
Assert.state(initMethodName != null, "No init method set");
//使用反射获取到需要初始化的方法
Method initMethod = (mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed() ?
BeanUtils.findMethod(bean.getClass(), initMethodName) :
ClassUtils.getMethodIfAvailable(bean.getClass(), initMethodName));
if (initMethod == null) {
if (mbd.isEnforceInitMethod()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionValidationException("Could not find an init method named '" +
initMethodName + "' on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No default init method named '" + initMethodName +
"' found on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
// Ignore non-existent default lifecycle methods.
return;
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking init method '" + initMethodName + "' on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
//看看初始化方法是否是接口方法,如果找到就是调用接口方法,否则调用原来的方法
Method methodToInvoke = ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(initMethod, bean.getClass());
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(methodToInvoke);
return null;
});
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>)
() -> methodToInvoke.invoke(bean), getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
InvocationTargetException ex = (InvocationTargetException) pae.getException();
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
else {
try {
//检查访问权限
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(methodToInvoke);
//通过反射去调用自定义初始化方法
methodToInvoke.invoke(bean);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
//回调处理,我们来看看Spring内置的BeanPostProcessor有几个
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
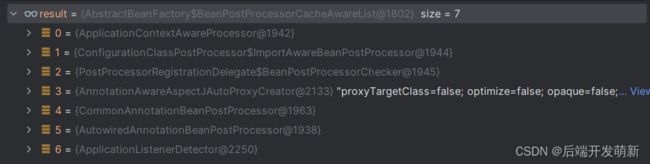
我们可以看到,有7个内置的后处理器,代理是在AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator处理器中处理,不过是由父类实现(AbstractAutoProxyCreator),关于代理对象的创建,后续再单独讲解
至此,Bean的初始化就讲解完毕了,接下来我们进行总结
总结
这块来说相对比较简单,初始化时都做了哪些事?
- 调用Aware方法进行设置值
- 初始化之前回调BeanPostProcessor
- 初始化方法
- 如果实现了InitializingBean接口,那么会进行回调afterPropertiesSet方法
- 通过反射调用自定义初始化方法(init-method属性)
- 初始化之后回调BeanPostProcessor(没有循环依赖情况下,代理对象在此生成)