图(高阶数据结构)
目录
一、图的基本概念
二、图的存储结构
2.1 邻接矩阵
2.2 邻接表
三、图的遍历
3.1 广度优先遍历
3.2 深度优先遍历
四、最小生成树
4.1 Kruskal算法
4.2 Prim算法
五、最短路径
5.1 单源最短路径-Dijkstra算法
5.2 单源最短路径-Bellman-Ford算法
5.3 多源最短路径-Floyd-Warshall算法
一、图的基本概念
图是由顶点集合和边的集合组成的一种数据结构,记作 ![]()
有向图与无向图
- 在有向图中,顶点对
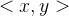 是有序的,顶点对
是有序的,顶点对 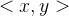 称为顶点
称为顶点  到顶点
到顶点  的一条边,
的一条边, 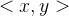 和
和 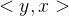 是两条不同的边
是两条不同的边 - 在无向图中,顶点对
 是无序的,顶点对
是无序的,顶点对  称为顶点
称为顶点  和顶点
和顶点  相关联的一条边,这条边没有特定方向,
相关联的一条边,这条边没有特定方向, 和
和 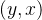 是同一条边
是同一条边
完全图
- 在有
 个顶点的无向图中,若有
个顶点的无向图中,若有 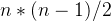 条边,即任意两个顶点之间都有直接相连的边,则称此图为无向完全图
条边,即任意两个顶点之间都有直接相连的边,则称此图为无向完全图 - 在有
 个顶点的有向图中,若有
个顶点的有向图中,若有 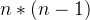 条边,即任意两个顶点之间都有双向的边,则称此图为有向完全图
条边,即任意两个顶点之间都有双向的边,则称此图为有向完全图
邻接顶点
- 在无向图中,若
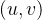 是图中的一条边,则称
是图中的一条边,则称  和
和  互为邻接顶点,并称边
互为邻接顶点,并称边 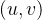 依附于顶点
依附于顶点  和顶点
和顶点 
- 在有向图中,若
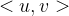 是图中的一条边,则称顶点
是图中的一条边,则称顶点  邻接到顶点
邻接到顶点  ,顶点
,顶点  邻接自顶点
邻接自顶点  ,并称边
,并称边 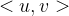 与顶点
与顶点  和顶点
和顶点  相关联
相关联
顶点的度
- 在有向图中,顶点的度等于该顶点的入度与出度之和,顶点的入度是以该顶点为终点的边的条数,顶点的出度是以该顶点为起点的边的条数
- 在无向图中,顶点的度等于与该顶点相关联的边的条数,同时也等于该顶点的入度和出度
路径与路径长度
- 若从顶点
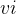 出发有一组边使其可到达顶点
出发有一组边使其可到达顶点 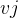 ,则称顶点
,则称顶点 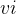 到顶点
到顶点 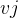 的顶点序列为从顶点
的顶点序列为从顶点 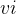 到顶点
到顶点 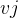 的路径
的路径 - 对于不带权的图,一条路径的长度是指该路径上的边的条数;对于带权的图,一条路径的长度是指该路径上各个边权值的总和
带权图示例:
简单路径与回路
- 若路径上的各个顶点均不相同,则称这样的路径为简单路径
- 若路径上第一个顶点与最后一个顶点相同,则称这样的路径为回路或环
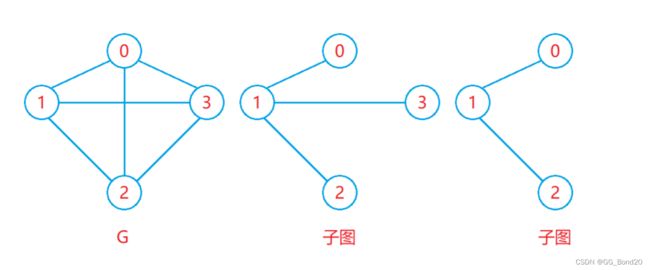
子图
设图 ![]() 和图
和图 ![]() ,若
,若 ![]() 且
且 ![]() ,则称
,则称 ![]() 是
是 ![]() 的子图
的子图
连通图和强连通图
- 在无向图中,若从顶点
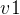 到顶点
到顶点 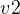 有路径,则称顶点
有路径,则称顶点 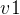 与顶点
与顶点 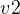 是连通的,若图中任意一对顶点都是连通的,则称此图为连通图
是连通的,若图中任意一对顶点都是连通的,则称此图为连通图 - 在有向图中,若每一对顶点
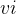 和
和 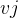 之间都存在一条从
之间都存在一条从 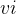 到
到 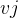 的路径,也存在一条从
的路径,也存在一条从 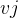 到
到 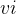 的路,则称此图是强连通图
的路,则称此图是强连通图
生成树与最小生成树
- 一个连通图的最小连通子图称为该图的生成树,有
 个顶点的连通图的生成树有
个顶点的连通图的生成树有  个顶点和
个顶点和 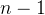 条边
条边 - 最小生成树指的是一个图的生成树中,总权值最小的生成树
图的相关应用场景
图常见的表示场景如下:
- 交通网络:图中的每个顶点表示一个地点,图中的边表示这两个地点之间是否有直接相连的公路,边的权值可以是这两个地点之间的距离、高铁时间等
- 网络设备拓扑:图中的每个顶点表示网络中的一个设备,图中的边表示这两个设备之间是否可以互传数据,边的权值可以是这两个设备之间传输数据所需的时间、丢包的概率等
- 社交网络:图中的每个顶点表示一个人,图中的边表示这两个人是否互相认识,边的权值可以是这两个人之间的亲密度、共同好友个数
关于有向图和无向图:
- 交通网络对应的图可以是有向图,也可以是无向图,无向图对应就是双向车道,有向图对应就是单向车道
- 网络设备拓扑对应的图通常是无向图,两个设备之间有边表示这两个设备之间可以互相收发数据
- 社交网络对应的图可以是有向图,也可以是无向图,无向图通常表示一些强社交关系,比如QQ、微信等(一定互为好友),有向图通常表示一些弱社交关系,比如微博、抖音(不一定互相关注)
图的其他相关作用:
- 在交通网络中,根据最短路径算法计算两个地点之间的最短路径,根据最小生成树算法得到将各个地点连通起来所需的最小成本
- 在社交网络中,根据广度优先搜索得到两个人之间的共同好友进行好友推荐,根据入边表和出边表得知有哪些粉丝以及关注了哪些博主
图与树的联系与区别
- 树是一种有向无环且连通的图(空树除外),但图并不一定是树
- 有
 个结点的树必须有
个结点的树必须有  条边,而图中边的数量不取决于顶点的数量
条边,而图中边的数量不取决于顶点的数量 - 树通常用于存储数据,并快速查找目标数据,而图通常用于表示某种场景
二、图的存储结构
图由顶点和边组成,存储图的本质就是将图中的顶点和边存储起来
2.1 邻接矩阵
邻接矩阵存储图的方式
- 用一个数组存储顶点集合,顶点所在位置的下标作为该顶点的编号(所给顶点可能不是整型)
- 用一个二维数组
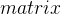 存储边的集合,其中
存储边的集合,其中 ![matrix[i][j]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/51cc0c406ecb4880bae9ecba04357509.png) 表示编号为
表示编号为  和
和  的两个顶点之间的关系
的两个顶点之间的关系
说明:
- 对于不带权的图,两个顶点之间要么相连,要么不相连,可以用0和1表示。
![matrix[i][j]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/51cc0c406ecb4880bae9ecba04357509.png) 为1表示编号为
为1表示编号为  和
和  的两个顶点相连,为0表示不相连
的两个顶点相连,为0表示不相连 - 对于带权的图,连接两个顶点的边会带有一个权值,可以用这个权值来设置对应
![matrix[i][j]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/51cc0c406ecb4880bae9ecba04357509.png) 的值;若两个顶点不相连,则使用不会出现的权值进行设置即可(图中为无穷大)
的值;若两个顶点不相连,则使用不会出现的权值进行设置即可(图中为无穷大) - 对于无向图来说,顶点
 和顶点
和顶点  相连,那么顶点
相连,那么顶点  就和顶点
就和顶点  相连,因此无向图对应的邻接矩阵是一个对称矩阵,即
相连,因此无向图对应的邻接矩阵是一个对称矩阵,即 ![matrix[i][j]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/51cc0c406ecb4880bae9ecba04357509.png) 的值等于
的值等于 ![matrix[j][i]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/66d4b8a773e747d3843f43cdfaa8fb30.png) 的值
的值 - 在邻接矩阵中,第
 行元素中有效权值的个数就是编号为
行元素中有效权值的个数就是编号为  的顶点的出度,第
的顶点的出度,第  列元素中有效元素的个数就是编号为
列元素中有效元素的个数就是编号为  的顶点的入度
的顶点的入度
邻接矩阵的优缺点
优点:
- 邻接矩阵适合存储稠密图,因为存储稠密图和稀疏图时所开辟的二维数组大小是相同的,因此图中的边越多,邻接矩阵的优势就越明显
- 邻接矩阵能够
 的判断两个顶点是否相连,并获得相连边的权值
的判断两个顶点是否相连,并获得相连边的权值
缺点:
- 邻接矩阵不适合查找一个顶点连接出去的所有边,需要遍历矩阵中对应的一行,该过程的时间复杂度是
 ,其中
,其中  表示的是顶点的个数
表示的是顶点的个数
邻接矩阵的实现
成员变量:
- 数组
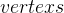 :用于存储顶点集合,顶点所在位置的下标作为该顶点的编号
:用于存储顶点集合,顶点所在位置的下标作为该顶点的编号 - 映射关系
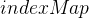 :用于建立顶点与其下标的映射关系,便于根据顶点找到其对应的下标编号(无需遍历
:用于建立顶点与其下标的映射关系,便于根据顶点找到其对应的下标编号(无需遍历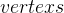 数组)
数组) - 邻接矩阵
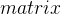 :用于存储边的集合,
:用于存储边的集合,![matrix[i][j]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/51cc0c406ecb4880bae9ecba04357509.png) 表示编号为
表示编号为  和
和  的两个顶点之间的关系
的两个顶点之间的关系
实现原理:
- 为了支持任意类型的顶点类型以及权值,可以将图定义为模板类。其中
 和
和  分别表示顶点和权值的类型,
分别表示顶点和权值的类型,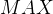 _
_ 表示两个顶点没有连接时邻接矩阵中存储的值,将
表示两个顶点没有连接时邻接矩阵中存储的值,将 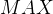 _
_ 的缺省值设置为
的缺省值设置为 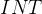 _
_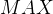 (权值一般为整型)。
(权值一般为整型)。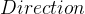 表示图是否为有向图,将
表示图是否为有向图,将 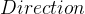 的缺省值设置为
的缺省值设置为 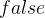 (无向图居多)
(无向图居多) - 在构造函数中完成顶点集合的设置,并建立各个顶点与其对应下标的映射关系,同时为邻接矩阵开辟空间,将矩阵中的值初始化为
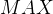 _
_ ,表示刚开始时各个顶点之间均不相连
,表示刚开始时各个顶点之间均不相连 - 提供一个接口用于添加边,在添加边时先分别获取源顶点和目标顶点对应的下标编号,然后再将邻接矩阵中对应位置设置为边的权值,若为无向图,则还需要在邻接矩阵中添加目标顶点到源顶点的边
- 在获取顶点对应的下标时,先在
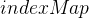 中进行查找,若找到了对应的顶点,则返回该顶点对应的下标编号;若没有找到对应的顶点,则说明所给顶点不存在,此时可以抛出异常
中进行查找,若找到了对应的顶点,则返回该顶点对应的下标编号;若没有找到对应的顶点,则说明所给顶点不存在,此时可以抛出异常
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace matrix
{
template
class Graph
{
public:
Graph() = default;
Graph(const V* vertex, size_t size)
:_vertexs(vertex, vertex + size), _matrix(size, vector(size, MAX_W))
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
_indexMap[vertex[i]] = i;
}
//获取顶点对应的下标
int GetVertexIndex(const V& v)
{
auto it = _indexMap.find(v);
if (it != _indexMap.end()) //顶点存在
return it->second;
else { //顶点不存在
throw invalid_argument("顶点不存在");
return -1;
}
}
//添加边
void AddEdge(const V& source, const V& destion, const W& weight)
{
int sourceIndex = GetVertexIndex(source), destionIndex = GetVertexIndex(destion);
_matrix[sourceIndex][destionIndex] = weight;
if (Direction == false)
_matrix[destionIndex][sourceIndex] = weight;
}
//打印顶点集合和邻接矩阵
void Print()
{
int size = _vertexs.size();
//打印顶点集合
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << "[" << i << "]->" << _vertexs[i] << endl;
cout << endl;
//打印邻接矩阵
cout << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%4d", i);
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
cout << i << " "; //竖下标
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
if (_matrix[i][j] == MAX_W) printf("%4c", '*');
else printf("%4d", _matrix[i][j]);
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
vector _vertexs; //顶点集合
unordered_map _indexMap; //顶点映射下标
vector> _matrix; //邻接矩阵
};
} - 为了方便观察,可以在类中增加一个
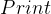 接口,用于打印顶点集合和邻接矩阵
接口,用于打印顶点集合和邻接矩阵 - 后续图的相关算法都会以邻接矩阵为例进行讲解,因为一般只有比较稠密的图才会存在最小生成树和最短路径的问题
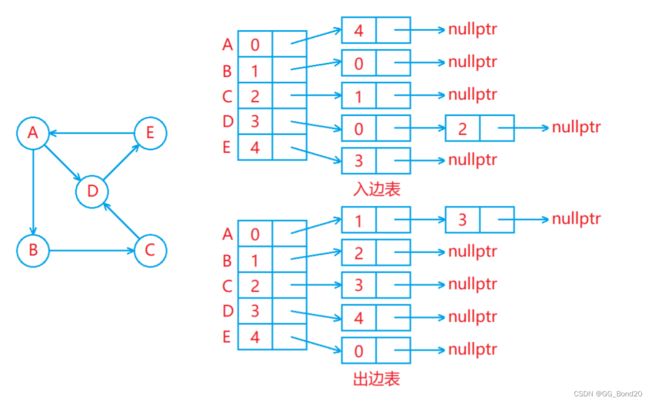
2.2 邻接表
邻接表存储图的方式
- 用一个数组存储顶点集合,顶点所在的位置的下标作为该顶点的编号(顶点可能不是整型)
- 出边表存储从各个顶点连接出去的边,出边表中下标为
 的位置存储的是从编号为
的位置存储的是从编号为  的顶点连接出去的边
的顶点连接出去的边 - 入边表存储连接到各个顶点的边,入边表中下标为
 的位置存储的是连接到编号为
的位置存储的是连接到编号为  的顶点的边
的顶点的边
说明:
- 出边表和入边表类似于哈希桶,其中每个位置存储的都是一个链表,出边表中下标为
 的位置的链表中存储的都是从编号为
的位置的链表中存储的都是从编号为  的顶点连接出去的边,入边表中下标为
的顶点连接出去的边,入边表中下标为  的位置的链表中存储的都是连接到编号为
的位置的链表中存储的都是连接到编号为  的顶点的边
的顶点的边 - 在邻接表中,出边表中下标为
 的位置的链表中元素的个数就是编号为
的位置的链表中元素的个数就是编号为  的顶点的出度,入边表中下标为
的顶点的出度,入边表中下标为  的的位置的链表中元素的个数就是编号为
的的位置的链表中元素的个数就是编号为  的顶点的入度
的顶点的入度 - 在实现邻接表时,一般只需要用一个出边表来存储从各个顶点连接出去的边即可,因为大多数情况下都是需要从一个顶点出发找与其相连的其他顶点,所以一般不需要存储入边表
邻接表的优缺点
优点:
- 邻接表适合存储稀疏图,因为邻接表存储图时开辟的空间大小取决于边的数量,图中边的数量越少,邻接表存储边时所需的内存空间就越少
- 邻接表适合查找一个顶点连接出去的所有边,出边表中下标为
 的位置的链表中存储的就是从顶点
的位置的链表中存储的就是从顶点  连接出去的所有边
连接出去的所有边
缺点:
- 邻接表不适合确定两个顶点是否相连,需要遍历出边表中源顶点对应位置的链表,该过程的时间复杂度是
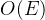 ,其中
,其中  表示从源顶点连接出去的边的数量
表示从源顶点连接出去的边的数量
邻接表的实现
链表结点成员变量:
- 源顶点下标
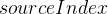 :表示边的源顶点
:表示边的源顶点 - 目标顶点下标
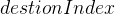 :表示边的目标顶点
:表示边的目标顶点 - 权值
 :表示边的权值
:表示边的权值 - 指针
 :连接下一个结点
:连接下一个结点
namespace link_table
{
//链表结点
template
struct Edge
{
Edge(int dstI, const W& w) : _destionIndex(dstI), _weight(w), _next(nullptr) {}
//int _sourceIndex; //可选
int _destionIndex;
W _weight;
Edge* _next;
};
}
- 对于出边表来说,下标为
 的位置的链表中存储的边的源顶点都是顶点
的位置的链表中存储的边的源顶点都是顶点  ,所以链表结点中的源顶点成员可以不用存储
,所以链表结点中的源顶点成员可以不用存储 - 对于入边表来说,下标为
 的位置的链表中存储的边的目标顶点都是顶点
的位置的链表中存储的边的目标顶点都是顶点  ,所以链表结点中的目标顶点成员可以不用存储
,所以链表结点中的目标顶点成员可以不用存储
邻接表成员变量:
- 数组
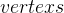 :用于存储顶点集合,顶点所在位置的下标作为该顶点的编号
:用于存储顶点集合,顶点所在位置的下标作为该顶点的编号 - 映射关系
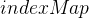 :用于建立顶点与其下标的映射关系,便于根据顶点找到其对应的下标编号
:用于建立顶点与其下标的映射关系,便于根据顶点找到其对应的下标编号 - 邻接表(出边表)
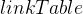 :用于存储边的集合,
:用于存储边的集合,![linkTable[i]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/7cae56b761d74ad4bd42dee3b89a64cd.png) 链表中存储的边的源顶点都是顶点
链表中存储的边的源顶点都是顶点 
实现原理:
- 为了支持任意类型的顶点类型以及权值,可以将图定义为模板,其中
 和
和  分别表示顶点和权值的类型,
分别表示顶点和权值的类型,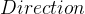 表示图是否为有向图,将
表示图是否为有向图,将 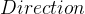 的缺省值设置为
的缺省值设置为 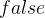
- 在构造函数中完成顶点集合的设置,并建立各个顶点与其对应下标的映射关系,同时为邻接表开辟空间,将邻接表中的值初始化为空指针,表示刚开始时各个顶点之间均不相连
- 提供一个接口用于添加边,在添加边时先分别获取源顶点和目标顶点对应的下标编号,然后在源顶点对应的链表中头插一个边结点,若图为无向图,则还需要在目标顶点对应的链表中头插一个边结点
namespace link_table
{
template
class Graph
{
typedef Edge Edge;
public:
Graph() = default;
Graph(const V* vertexs, size_t size)
:_vertexs(vertexs, vertexs + size), _linkTable(size, nullptr)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
_indexMap[vertexs[i]] = i;
}
int GetVertexIndex(const V& vertex)
{
auto it = _indexMap.find(vertex);
if (it != _indexMap.end()) return it->second;
else {
throw invalid_argument("不存在的顶点");
return -1;
}
}
void AddEdge(const V& src, const V& dst, const W& w)
{
int srcIndex = GetVertexIndex(src), dstIndex = GetVertexIndex(dst);
Edge* newEdge = new Edge(dstIndex, w);
newEdge->_next = _linkTable[srcIndex];
_linkTable[srcIndex] = newEdge;
if (Direction == false)
{
Edge* newEdge = new Edge(srcIndex, w);
newEdge->_next = _linkTable[dstIndex];
_linkTable[dstIndex] = newEdge;
}
}
void Print()
{
int size = _vertexs.size();
//打印顶点集合
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << "[" << i << "]->" << _vertexs[i] << " ";
cout << endl << endl;
//打印邻接表
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
Edge* cur = _linkTable[i];
cout << "[" << i << ":" << _vertexs[i] << "]->";
while (cur) {
cout << "[" << cur->_destionIndex << ":" << _vertexs[cur->_destionIndex] << ":" << cur->_weight << "]->";
cur = cur->_next;
}
cout << "nullptr" << endl;
}
}
private:
vector _vertexs; //顶点集合
unordered_map _indexMap; //映射关系
vector _linkTable; //出边表
};
} 三、图的遍历
图的遍历指的是遍历图中的顶点,主要有广度优先遍历和深度优先遍历两种方式
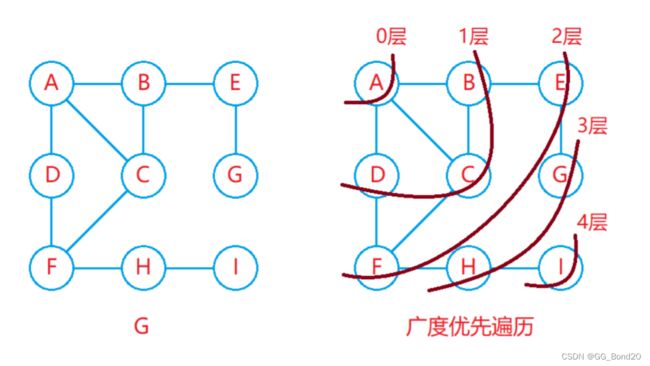
3.1 广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历又称BFS,类似于二叉树的层序遍历,从起始顶点开始一层一层向外进行遍历
实现原理:
- 广度优先遍历需借助一个队列和一个标记数组,利用队列先进先出的特点实现一层一层向外遍历,利用标记数组来记录各个顶点是否被访问过
- 刚开始时将起始顶点入队列,并将起始顶点标记为访问过,然后不断从队列中取出顶点进行访问,并判断该顶点是否有邻接顶点。若有邻接顶点并且该邻接顶点没有被访问过,则将该邻接顶点入队列,并在入队列后立即将该邻接顶点标记为访问过
void BFS(const V& source)
{
int sourceIndex = GetVertexIndex(source);
queue qe;
vector visited(_vertexs.size(), false);
qe.push(sourceIndex);
visited[sourceIndex] = true;
while (!qe.empty())
{
int front = qe.front();
qe.pop();
cout << _vertexs[front] << " ";
for (int j = 0; j < _vertexs.size(); ++j)
{
if (_matrix[front][j] != MAX_W && visited[j] == false)
{
qe.push(j);
visited[j] = true;
}
}
}
cout << endl;
} 说明:
- 为了防止顶点被重复加入队列导致死循环,因此需要一个标记数组,当一个顶点被访问过后就不应该再将其加入队列了
- 若当一个顶点从队列中取出访问时才再将其标记为访问过,也可能会存在顶点被重复加入队列的情况。比如当图中的顶点B出队列时,顶点C作为顶点B的邻接顶点并且还没有被访问过(顶点C还在队列中),此时顶点C就会再次被加入队列,因此最好在一个顶点被入队列时就将其标记为访问过
- 若所给图不是一个连通图,那么从一个顶点开始进行广度优先遍历,无法遍历完图中的所有顶点,这时可以遍历标记数组,查看哪些顶点还没有被访问过,对于没有被访问过的顶点,则从该顶点处继续进行广度优先遍历,直到图中所有的顶点都被访问过
3.2 深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历又称DFS,类似于二叉树的先序遍历,从起始顶点开始不断对顶点进行深入遍历
实现原理:
- 深度优先遍历可以通过递归实现,也要借助一个标记数组来记录各个顶点是否被访问过
- 从起始顶点处开始进行递归遍历,在遍历过程中先对当前顶点进行访问,并将其标记为访问过,然后判断该顶点是否有邻接顶点。若有邻接顶点并且该邻接顶点没有被访问过,则递归遍历该邻接顶点
void _DFS(int srcIndex, vector& visvited)
{
cout << _vertexs[srcIndex] << " "; // 访问
visvited[srcIndex] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < _vertexs.size(); ++j)
if (_matrix[srcIndex][j] != MAX_W && visvited[j] == false)
_DFS(j, visvited);
}
void DFS(const V& source)
{
int sourceIndex = GetVertexIndex(source);
vector visvited(_vertexs.size(), false);
_DFS(sourceIndex, visvited);
cout << endl;
} 若所给图不是一个连通图,那么从一个顶点开始进行深度优先遍历,无法遍历完图中的所有顶点。这时可以遍历标记数组,查看哪些顶点还没有被访问过,对于没有被访问过的顶点,则从该顶点处继续进行深度优先遍历,直到图中所有的顶点都被访问过
四、最小生成树
认识最小生成树
- 一个连通图的最小连通子图称为该图的生成树,若连通图由
 个顶点组成,则其生成树必含
个顶点组成,则其生成树必含  个顶点和
个顶点和  条边,最小生成树指的是一个图的生成树中,总权值最小的生成树
条边,最小生成树指的是一个图的生成树中,总权值最小的生成树 - 连通图中的每一棵生成树都是原图的一个极大无环子图,从其中删去任何一条边,生成树就不再连通,在其中引入任何一条新边,都会形成一条回路
说明:
- 对于各个顶点来说,除了第一个顶点之外,其他每个顶点想要连接到图中,至少需要一条边使其连接进来,所以由
 个顶点的连通图的生成树有
个顶点的连通图的生成树有  个顶点和
个顶点和  条边
条边 - 对于生成树来说,图中的每个顶点已经连通了,若再引入一条新边,那么必然会使得被新边相连的两个顶点之间存在一条直接路径和一条间接路径,即形成回路。
- 最小生成树是图的生成树中总权值最小的生成树,生成树是图的最小连通子图,而连通图是无向图的概念,有向图对应的是强连通图,所以最小生成树算法的处理对象都是无向图
构成最小生成树的准则
- 只能使用图中的边来构造最小生成树
- 只能使用恰好
 条边来连接图中的
条边来连接图中的  个顶点
个顶点 - 选用的
 条边不能构成回路
条边不能构成回路
构造最小生成树的算法有 Kruskal(克鲁斯卡尔)算法和 Prim(普里姆)算法,这两个算法都采用了逐步求解的贪心策略
4.1 Kruskal算法
基本思想
- 首先构造一个含
 个顶点、不含任何边的图作为最小生成树,对原图中的各个边按权值进行排序
个顶点、不含任何边的图作为最小生成树,对原图中的各个边按权值进行排序 - 每次从原图中选出一条最小权值的边,将其加入到最小生成树中,若加入这条边会使得最小生成树中构成回路,则重新选择一条边
- 按照上述规则不断选边,当选出
 条合法的边时,则说明最小生成树构造完毕,若无法选出
条合法的边时,则说明最小生成树构造完毕,若无法选出  条合法的边,则说明原图不存在最小生成树
条合法的边,则说明原图不存在最小生成树
具体实现
- 根据原图设置最小生成树的顶点集合,以及顶点与下标的映射关系,开辟最小生成树的邻接矩阵空间,并将矩阵中的值初始化为 ,表示刚开始时最小生成树中不含任何边
- 遍历原图的邻接矩阵,按权值将原图中的所有边添加到优先级队列(小堆)中,为了避免重复添加相同的边,在遍历原图的邻接矩阵时只应该遍历矩阵的一半
- 使用一个并查集来辅助判环操作,刚开始时图中的顶点各自为一个集合,当两个顶点相连时将这两个顶点对应的集合进行合并,使得连通的顶点在同一个集合,这样通过并查集就能判断所选的边是否会使得最小生成树中构成回路,若所选边连接的两个顶点本就在同一个集合,那么加入这条边就会构成回路
- 使用
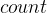 和
和  分别记录所选边的数量和最小生成树的总权值,当
分别记录所选边的数量和最小生成树的总权值,当 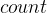 的值等于
的值等于  时则停止选边,此时可以将最小生成树的总权值作为返回值进行返回
时则停止选边,此时可以将最小生成树的总权值作为返回值进行返回 - 每次选边时从优先级队列中获取一个权值最小的边,并通过并查集判断这条边连接的两个顶点是否在同一个集合,如果在则重新选边,如果不在则将这条边添加到最小生成树中,并将这条边连接的两个顶点对应的集合进行合并,同时更新
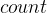 和
和  的值
的值 - 当选边结束时,若
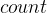
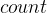 的值等于
的值等于  ,则说明最小生成树构造成功,否则说明原图无法构造出最小生成树
,则说明最小生成树构造成功,否则说明原图无法构造出最小生成树
//添加边
void _AddEdge(int& srcIndex, int& dstIndex, const W& weight)
{
_matrix[srcIndex][dstIndex] = weight;
if (Direction == false)
_matrix[dstIndex][srcIndex] = weight;
}
void AddEdge(const V& source, const V& destion, const W& weight)
{
int sourceIndex = GetVertexIndex(source), destionIndex = GetVertexIndex(destion);
_AddEdge(sourceIndex, destionIndex, weight);
}
struct Edge
{
Edge(int srcIndex, int dstIndex, const W& weight)
:_sourceIndex(srcIndex), _destionIndex(dstIndex), _weight(weight) {}
bool operator>(const Edge& edge)const {
return _weight > edge._weight;
}
int _sourceIndex;
int _destionIndex;
W _weight;
};
W Kruskal(Graph& minTree)
{
int size = _vertexs.size();
//最小生成树初始化
minTree._vertexs = _vertexs;
minTree._indexMap = _indexMap;
minTree._matrix.resize(size, vector (size, MAX_W));
priority_queue, greater> minHeap;//小堆
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)//只遍历矩阵一半,避免添加重复的边
if (_matrix[i][j] != MAX_W)
minHeap.push(Edge(i, j, _matrix[i][j]));
UnionFindSet ufs(size); //size个顶点的并查集, 用于判环
int count = 0; //已选边的数量
W totalWeight = W(); //最小生成树的总权值
while (!minHeap.empty() && count < size - 1)
{
//获取此时最小的边
Edge minEdge = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
int srcI = minEdge._sourceIndex, dstI = minEdge._destionIndex;
W weight = minEdge._weight;
if (!ufs.IsInSet(srcI, dstI)) //边的源顶点和目标顶点不在同一个集合, 即无环
{
minTree._AddEdge(srcI, dstI, weight);
ufs.Union(srcI, dstI);
++count;
totalWeight += weight;
cout << "选边: " << _vertexs[srcI] << "->" << _vertexs[dstI] << ":" << weight << endl;
}
}
if (count == size - 1) {
cout << "构建最小生成树成功" << endl;
return totalWeight;
}
else {
cout << "无法构成最小生成树" << endl;
return W();
}
} 4.2 Prim算法
基本思想
- 首先构造一个含
 个顶点、不含任何边的图作为最小生成树。将图中的顶点分为两个集合,
个顶点、不含任何边的图作为最小生成树。将图中的顶点分为两个集合,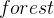 集合中的顶点是已经连接到最小生成树中的顶点,
集合中的顶点是已经连接到最小生成树中的顶点,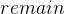 集合中的顶点是还没有连接到最小生成树中的顶点,刚开始时
集合中的顶点是还没有连接到最小生成树中的顶点,刚开始时 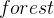 集合中只包含给定的起始顶点
集合中只包含给定的起始顶点 - 每次从连接
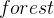 集合与
集合与 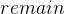 集合的所有边中选出一条权值最小的边,将其加入到最小生成树中,由于选出来的边对应的两个顶点一个属于
集合的所有边中选出一条权值最小的边,将其加入到最小生成树中,由于选出来的边对应的两个顶点一个属于 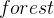 集合,另一个属于
集合,另一个属于 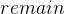 集合,因此是不会构成回路的
集合,因此是不会构成回路的 - 按照上述规则不断选边,当选出
 条边时,所有的顶点都已经加入到了
条边时,所有的顶点都已经加入到了 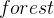 集合,此时最小生成树构造完毕,若无法选出
集合,此时最小生成树构造完毕,若无法选出  条边,则说明原图不存在最小生成树
条边,则说明原图不存在最小生成树
具体实现
- 根据原图设置最小生成树的顶点集合,以及顶点与下标的映射关系,开辟最小生成树的邻接矩阵空间,并将矩阵中的值初始化为
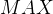 _
_ ,表示刚开始时最小生成树中不含任何边
,表示刚开始时最小生成树中不含任何边 - 使用一个
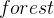 数组来表示各个顶点是否在
数组来表示各个顶点是否在 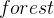 集合中,刚开始时只有起始顶点在
集合中,刚开始时只有起始顶点在 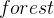 集合中,并将所有从起始顶点连接出去的边加入优先级队列(小堆),这些边就是刚开始时连接
集合中,并将所有从起始顶点连接出去的边加入优先级队列(小堆),这些边就是刚开始时连接 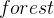 集合与
集合与 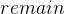 集合的边
集合的边 - 使用
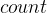 和
和  分别记录所选边的数量和最小生成树的总权值,当
分别记录所选边的数量和最小生成树的总权值,当 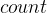 的值等于
的值等于  时则停止选边,此时将最小生成树的总权值作为返回值进行返回
时则停止选边,此时将最小生成树的总权值作为返回值进行返回 - 每次选边时从优先级队列中获取一个权值最小的边,将这条边添加到最小生成树中,并将这条边的目标顶点加入
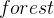 集合中,同时更新
集合中,同时更新 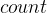 和
和  的值。还需将从这条边的目标顶点连接出去的边加入优先级队列,但是需要保证加入的边的目标顶点不能在
的值。还需将从这条边的目标顶点连接出去的边加入优先级队列,但是需要保证加入的边的目标顶点不能在 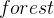 集合,否则后续选出源顶点和目标顶点都在
集合,否则后续选出源顶点和目标顶点都在 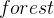 集合的边就会构成回路
集合的边就会构成回路 - 每次从优先级队列中选出一个权值最小的边时,还需要保证选出的这条边的目标顶点不在
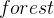 集合中,避免构成回路。虽然向优先级队列中加入边时保证了加入的边的目标顶点不在
集合中,避免构成回路。虽然向优先级队列中加入边时保证了加入的边的目标顶点不在 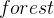 集合中,但经过后续不断的选边,可能会导致之前加入优先级队列中的某些边的目标顶点也被加入到了
集合中,但经过后续不断的选边,可能会导致之前加入优先级队列中的某些边的目标顶点也被加入到了 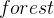 集合中
集合中 - 当选边结束时,若
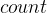 的值等于
的值等于  ,则说明最小生成树构造成功,否则说明原图无法构造出最小生成树
,则说明最小生成树构造成功,否则说明原图无法构造出最小生成树
W Prim(Graph& minTree, const V& start)
{
int size = _vertexs.size();
//最小生成树初始化
minTree._vertexs = _vertexs;
minTree._indexMap = _indexMap;
minTree._matrix.resize(size, vector(size, MAX_W));
int startIndex = GetVertexIndex(start);
vector forest(size, false);
forest[startIndex] = true;
priority_queue, greater> minHeap;
//将初始顶点连接的边加入堆中
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j)
if (_matrix[startIndex][j] != MAX_W)
minHeap.push(Edge(startIndex, j, _matrix[startIndex][j]));
int count = 0;
W totalWeight = W();
while (!minHeap.empty() && count < size - 1)
{
Edge minEdge = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
int srcIndex = minEdge._sourceIndex, dstIndex = minEdge._destionIndex;
W weight = minEdge._weight;
if (forest[dstIndex] == false) // 边的目标顶点还没有被加入到forest集合中
{
//将目标顶点连接出去的边加入到优先级队列中
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j)
if (_matrix[dstIndex][j] != MAX_W)
minHeap.push(Edge(dstIndex, j, _matrix[dstIndex][j]));
minTree._AddEdge(srcIndex, dstIndex, weight);
forest[dstIndex] = true;
++count;
totalWeight += weight;
cout << "选边: " << _vertexs[srcIndex] << "->" << _vertexs[dstIndex] << ":" << weight << endl;
}
}
if (count == size - 1) {
cout << "构建最小生成树成功" << endl;
return totalWeight;
}
else {
cout << "无法构成最小生成树" << endl;
return W();
}
} - Prim算法构造最小生成树的思想在选边时是不需要判环,但上述利用优先级队列实现的过程中仍需判环,若在每次选边的时候能够通过某种方式,从连接
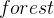 集合和
集合和 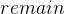 集合的所有边中选出权值最小的边,那么就无需判环,但这两个集合中的顶点是不断在变化的,每次选边时都遍历连接两个集合的所有边,该过程的时间复杂度较高
集合的所有边中选出权值最小的边,那么就无需判环,但这两个集合中的顶点是不断在变化的,每次选边时都遍历连接两个集合的所有边,该过程的时间复杂度较高 - Kruskal算法本质是一种全局的贪心,每次选边时都是在所有边中选出权值最小的边,而Prim算法本质是一种局部的贪心,每次选边时是从连接
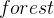 集合和
集合和 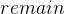 集合的所有边中选出权值最小的边
集合的所有边中选出权值最小的边
五、最短路径
- 最短路径问题:从带权有向图中的某一顶点出发,找出一条通往另一顶点的最短路径,最短指的是路径各边的权值总和达到最小,最短路径可分为单源最短路径和多源最短路径
- 单源最短路径指的是从图中某一顶点出发,找出通往其他所有顶点的最短路径,而多源最短路径指的是,找出图中任意两个顶点之间的最短路径
5.1 单源最短路径-Dijkstra算法
注意:使用前提,图中所有边的权值非负
迪杰斯特拉算法基本思想
- 将图中的顶点分为两个集合,集合
 中的顶点是已经确定从源顶点到该顶点的最短路径的顶点,集合
中的顶点是已经确定从源顶点到该顶点的最短路径的顶点,集合  中的顶点是尚未确定从源顶点到该顶点的最短路径的顶点
中的顶点是尚未确定从源顶点到该顶点的最短路径的顶点 - 每个顶点都有一个估计值,表示从源顶点到该顶点的可能最短路径长度,每次从集合
 中选出一个估计值最小的顶点,将其加入到集合
中选出一个估计值最小的顶点,将其加入到集合  中,并对该顶点连接出去的顶点的估计值和前驱顶点进行松弛更新
中,并对该顶点连接出去的顶点的估计值和前驱顶点进行松弛更新 - 按照上述步骤不断从集合
 中选取估计值最小的顶点到集合
中选取估计值最小的顶点到集合  中,直到所有的顶点都被加入到集合
中,直到所有的顶点都被加入到集合  中,此时通过各个顶点的估计值就可以得知源顶点到该顶点的最短路径长度,通过各个顶点的前驱顶点就可以得知最短路径的走向
中,此时通过各个顶点的估计值就可以得知源顶点到该顶点的最短路径长度,通过各个顶点的前驱顶点就可以得知最短路径的走向
具体实现
- 使用一个
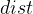 数组来记录从源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径长度估计值,初始时将源顶点的估计值设置为权值的缺省值,表示从源顶点到源顶点的路径长度为0,将其余顶点的估计值设置为
数组来记录从源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径长度估计值,初始时将源顶点的估计值设置为权值的缺省值,表示从源顶点到源顶点的路径长度为0,将其余顶点的估计值设置为 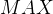 _
_ ,表示从源顶点暂时无法到达其他顶点
,表示从源顶点暂时无法到达其他顶点 - 使用一个
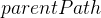 数组来记录到达各个顶点路径的前驱顶点,初始时将各个顶点的前驱顶点初始化为-1,表示各个顶点暂时只能自己到达自己,没有前驱顶点
数组来记录到达各个顶点路径的前驱顶点,初始时将各个顶点的前驱顶点初始化为-1,表示各个顶点暂时只能自己到达自己,没有前驱顶点 - 使用一个
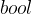 数组来记录各个顶点是否在
数组来记录各个顶点是否在  集合中,初始时所有顶点均不在
集合中,初始时所有顶点均不在  集合,表示各个顶点都还没有确定最短路径
集合,表示各个顶点都还没有确定最短路径 - 每次从
 集合中选出一个估计值最小的顶点
集合中选出一个估计值最小的顶点  ,将其加入到
,将其加入到  集合,并对顶点
集合,并对顶点  连接出去的各个顶点
连接出去的各个顶点  进行松弛更新。若能够将顶点
进行松弛更新。若能够将顶点  更新出更小的估计值,则更新其估计值,并将被更新的顶点
更新出更小的估计值,则更新其估计值,并将被更新的顶点  的前驱顶点改为顶点
的前驱顶点改为顶点  ,因为从顶点
,因为从顶点  到顶点
到顶点  能够得到更小的估计值,所以在当前看来(后续可能还会更新)到达顶点
能够得到更小的估计值,所以在当前看来(后续可能还会更新)到达顶点  的最短路径的前驱顶点就应该是顶点
的最短路径的前驱顶点就应该是顶点  ,若不能将顶点
,若不能将顶点  更新出更小的估计值,则维持原样
更新出更小的估计值,则维持原样 - 当所有的顶点都加入集合
 后,
后,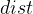 数组中存储的就是从源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径长度,
数组中存储的就是从源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径长度,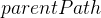 数组中存储的就是从源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径的前驱顶点,通过不断查找各个顶点的前驱顶点,最终就能得到从源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径
数组中存储的就是从源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径的前驱顶点,通过不断查找各个顶点的前驱顶点,最终就能得到从源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径
void Dijkstra(const V& source, vector& dist, vector& parentPath)
{
int size = _vertexs.size();
int srcIndex = GetVertexIndex(source);
dist.resize(size, MAX_W);
dist[srcIndex] = W();
parentPath.resize(size, -1);
vector S(size, false);//已确定最短路径的顶点的集合
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)//目标是将Q集合中的所有顶点都加入S集合
{
//从集合Q中选出一个估计值最小的顶点
W minW = MAX_W; //记录最小估计值
int u = -1; //记录拥有最小估计值的顶点
for(int j = 0; j < size; ++j)
if (S[j] == false && dist[j] < minW) {
minW = dist[j];
u = j;
}
//将选出的顶点加入S集合
S[u] = true;
//对u连接出去的顶点进行松弛更新
for (int v = 0; v < size; ++v)
{
if (S[v] == false && _matrix[u][v] != MAX_W && dist[u] + _matrix[u][v] < dist[v])
{
dist[v] = dist[u] + _matrix[u][v];
parentPath[v] = u;
}
}
}
}
//打印最短路径及路径权值
void PrintShortPath(const V& src, const vector& dist, const vector& parentPath)
{
int n = _vertexs.size();
int srci = GetVertexIndex(src); //获取源顶点的下标
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
vector path;
int cur = i;
while (cur != -1) { //源顶点的前驱顶点为-1
path.push_back(cur);
cur = parentPath[cur];
}
reverse(path.begin(), path.end()); //逆置
for (int j = 0; j < path.size(); j++) {
cout << _vertexs[path[j]] << "->";
}
cout << "路径权值: " << dist[i] << "" << endl;
}
} 算法原理
- Dijkstra算法每次从集合
 中选出一个估计值最小的顶点
中选出一个估计值最小的顶点  ,将该顶点加入到集合
,将该顶点加入到集合  中,表示确定了从源顶点到顶点
中,表示确定了从源顶点到顶点  的最短路径
的最短路径 - 因为图中所有边的权值非负(使用Dijkstra算法的前提),所以对于估计值最小的顶点
 来说,其估计值不可能再被其他比它估计值更大的顶点松弛更新得更小,因此顶点
来说,其估计值不可能再被其他比它估计值更大的顶点松弛更新得更小,因此顶点  的最短路径就是当前的估计值
的最短路径就是当前的估计值 - 对于集合
 中的其他顶点来说,这些顶点的估计值比顶点
中的其他顶点来说,这些顶点的估计值比顶点  的估计值大,因此顶点
的估计值大,因此顶点  可能将它们的估计值松弛更新得更小,所以顶点
可能将它们的估计值松弛更新得更小,所以顶点  在加入集合
在加入集合  后还需要尝试对其连接出去的顶点进行松弛更新
后还需要尝试对其连接出去的顶点进行松弛更新 - Dijkstra算法每次需要选出一个顶点,并对其连接出去的顶点进行松弛更新,因此其时间复杂度是
 ,空间复杂度是
,空间复杂度是 
5.2 单源最短路径-Bellman-Ford算法
贝尔曼福特算法基本思想
- Bellman-Ford算法本质是暴力求解,对于从源顶点
 到目标顶点
到目标顶点  的路径来说,若存在从源顶点
的路径来说,若存在从源顶点  到顶点
到顶点  的路径,还存在一条从顶点
的路径,还存在一条从顶点  到顶点
到顶点  的边,并且其权值之和小于当前从源顶点
的边,并且其权值之和小于当前从源顶点  到目标顶点
到目标顶点  的路径长度,则可以对顶点
的路径长度,则可以对顶点  的估计值和前驱顶点进行松弛更新
的估计值和前驱顶点进行松弛更新 - Bellman-Ford算法根据路径的终边来进行松弛更新,但是仅对图中的边进行一次遍历可能并不能正确更新出最短路径,最坏的情况下需要对图中的边进行
 轮遍历(
轮遍历(  表示图中的顶点个数)
表示图中的顶点个数)
具体实现
- 使用一个 dist 数组来记录从源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径长度估计值,初始时将源顶点的估计值设置为权值的缺省值,表示从源顶点到源顶点的路径长度为0,将其余顶点的估计值设置为MAX_W,表示从源顶点暂时无法到达其他顶点
- 使用一个
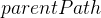 数组来记录到达各个顶点路径的前驱顶点,初始时将各个顶点的前驱顶点初始化为-1,表示各个顶点暂时只能自己到达自己,没有前驱顶点
数组来记录到达各个顶点路径的前驱顶点,初始时将各个顶点的前驱顶点初始化为-1,表示各个顶点暂时只能自己到达自己,没有前驱顶点 - 对图中的边进行
 轮遍历,对于
轮遍历,对于 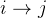 的边来说,若存在
的边来说,若存在 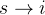 的路径,并且
的路径,并且 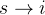 的路径权值与边
的路径权值与边  的权值之和小于当前
的权值之和小于当前 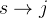 的路径长度,则将顶点
的路径长度,则将顶点  的估计值进行更新,并将顶点
的估计值进行更新,并将顶点  的前驱顶点改为顶点
的前驱顶点改为顶点  ,因为
,因为  是图中的一条直接相连的边,在这条路径中顶点
是图中的一条直接相连的边,在这条路径中顶点  的上一个顶点就是顶点
的上一个顶点就是顶点 
- 再对图中的边进行一次遍历,尝试进行松弛更新,若还能更新则说明图中带有负权回路,无法找到最短路径
bool BellmanFord(const V& source, vector& dist, vector& parentPath)
{
int size = _vertexs.size();
int srcIndex = GetVertexIndex(source);
dist.resize(size, MAX_W);
dist[srcIndex] = W();
parentPath.resize(size, -1);
for (int k = 0; k < size - 1; ++k) // 最多更新size - 1轮
{
bool update = false;//记录本轮是否更新过
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j)
{
if (_matrix[i][j] != MAX_W && dist[i] != MAX_W && dist[i] + _matrix[i][j] < dist[j])
{
dist[j] = dist[i] + _matrix[i][j];
parentPath[j] = i;
update = true;
}
}
}
if (update == false) break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j)
if (_matrix[i][j] != MAX_W && dist[i] + _matrix[i][j] < dist[j])
return false; //带有负权回路的图无法求出最短路径
return true;
} - Bellman-Ford算法是暴力求解,可以解决带有负权边的单源最短路径问题
- 负权回路指的是在图中形成回路的各个边的权值之和为负数,路径每绕一圈回路其权值都会减少,导致无法找到最短路径,由于最多需要进行
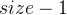 轮松弛更新,因此可以在
轮松弛更新,因此可以在 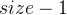 轮松弛更新后再进行一轮松弛更新,若还能进行更新则说明带有负权回路
轮松弛更新后再进行一轮松弛更新,若还能进行更新则说明带有负权回路 - Bellman-Ford算法需要对图中的边进行
 轮遍历,因此其时间复杂度是
轮遍历,因此其时间复杂度是 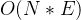 ,由于这里是用邻接矩阵实现的,遍历图中的所有边的时间复杂度是
,由于这里是用邻接矩阵实现的,遍历图中的所有边的时间复杂度是  ,所以上述代码的时间复杂度是
,所以上述代码的时间复杂度是 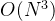 ,空间复杂度是
,空间复杂度是 
为什么最多进行 n-1 轮松弛更新?
从一个顶点到另一个顶点的最短路径中不能包含回路:
- 若形成回路的各个边的权值之和为负数,则该回路为负权回路,找不到最短路径
- 若形成回路的各个边的权值之和为非负数,则多走这个回路是"徒劳"的,可能会使得路径长度变长
在每一轮松弛过程中,后面路径的更新可能会影响到前面已经更新过的路径,比如使得前面已经更新过的路径的长度可以变得更短,或者使得某些源顶点之前不可达的顶点变得可达,但每一轮松弛至少能确定最短路径中的一条边,若图中有 ![]() 个顶点,那么两个顶点之间的最短路径最多有
个顶点,那么两个顶点之间的最短路径最多有 ![]() 条边,因此最多需要进行
条边,因此最多需要进行 ![]() 次松弛更新。
次松弛更新。
下图中,顶点 ![]() 、
、![]() 、
、![]() 、
、![]() 、
、![]() 的下标分别是0、1、2、3、4,现在要计算以顶点
的下标分别是0、1、2、3、4,现在要计算以顶点 ![]() 为源顶点的单源最短路径
为源顶点的单源最短路径
对于上述图来说,Bellman-Ford算法在第一轮松弛的时候只能更新出![]() 这条边,在第二轮的时候只能更新出
这条边,在第二轮的时候只能更新出 ![]() ,以此类推,最终就会进行4轮松弛更新
,以此类推,最终就会进行4轮松弛更新
- 由于只有当前轮次进行过更新,才有可能会影响其他路径,因此在代码中使用
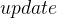 标记每轮松弛算法是否进行过更新,若没有进行过更新,则无需进行后面轮次的更新
标记每轮松弛算法是否进行过更新,若没有进行过更新,则无需进行后面轮次的更新 - Bellman-Ford算法还有一个优化方案叫做SPFA(Shortest Path Faster Algorithm),其用一个队列来维护可能需要松弛更新的顶点,避免了不必要的冗余计算
5.3 多源最短路径-Floyd-Warshall算法
弗洛伊德算法基本思想
- Floyd-Warshall算法解决的是任意两点间的最短路径的算法,其考虑的是路径的中间顶点,对于从顶点
 到顶点
到顶点  的路径来说,若存在从顶点
的路径来说,若存在从顶点  到顶点
到顶点  的路径,还存在从顶点
的路径,还存在从顶点  到顶点
到顶点  的路径,并且这两条路径的权值之和小于当前从顶点
的路径,并且这两条路径的权值之和小于当前从顶点  到顶点
到顶点  的路径长度,则可以对顶点
的路径长度,则可以对顶点  的估计值和前驱顶点进行松弛更新
的估计值和前驱顶点进行松弛更新 - Floyd-Warshall算法本质是一个简单的动态规划,就是判断从顶点
 到顶点
到顶点  的这条路径是否经过顶点
的这条路径是否经过顶点  ,若经过顶点
,若经过顶点  可以让这条路径的权值变得更小,则经过,否则则不经过
可以让这条路径的权值变得更小,则经过,否则则不经过
具体实现
- 使用一个
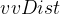 二维数组来记录从各个源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径长度的估计值,
二维数组来记录从各个源顶点到各个顶点的最短路径长度的估计值,![vvDist[i][j]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/136e859913a947e7bf08348bbcf3b91a.png) 表示从顶点
表示从顶点  到顶点
到顶点  的最短路径长度的估计值,初始时将二维数组中的值全部初始化为MAX_W,表示各个顶点之间暂时无法互通
的最短路径长度的估计值,初始时将二维数组中的值全部初始化为MAX_W,表示各个顶点之间暂时无法互通 - 使用一个
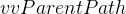 二维数组来记录从各个源顶点到达各个顶点路径的前驱顶点,初始时将二维数组中的值全部初始化为-1,表示各个顶点暂时只能自己到自己,没有前驱顶点
二维数组来记录从各个源顶点到达各个顶点路径的前驱顶点,初始时将二维数组中的值全部初始化为-1,表示各个顶点暂时只能自己到自己,没有前驱顶点 - 根据邻接矩阵对
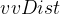 和
和 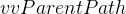 进行初始化,若从顶点
进行初始化,若从顶点  到顶点
到顶点  有直接相连的边,则将
有直接相连的边,则将 ![vvDist[i][j]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/136e859913a947e7bf08348bbcf3b91a.png) 初始化为这条边的权值,并将
初始化为这条边的权值,并将 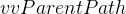 初始化为
初始化为  ,表示在
,表示在  这条路径中顶点
这条路径中顶点  前驱顶点是
前驱顶点是  ,将
,将 ![vvDist[i][i]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c652e90ced224751ab8ed47a1fa4b3ce.png) 的值设置为权值的缺省值,表示自己到自己的路径长度为0
的值设置为权值的缺省值,表示自己到自己的路径长度为0 - 依次取各个顶点
 作为
作为  路径的中间顶点,若同时存在
路径的中间顶点,若同时存在 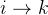 的路径和
的路径和 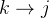 的路径,并且这两条路径的权值之和小于当前
的路径,并且这两条路径的权值之和小于当前  路径的权值,则更新
路径的权值,则更新 ![vvDist[i][j]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/136e859913a947e7bf08348bbcf3b91a.png) 的值,并将
的值,并将 ![vvParentPath[i][j]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f8353c502a704397ada33e4809ca5b28.png) 的值更新为
的值更新为 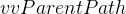 的值
的值
void FloydWarshall(vector>& vvDist, vector>& vvParentPath)
{
int size = _vertexs.size();
vvDist.resize(size, vector(size, MAX_W));
vvParentPath.resize(size, vector(size, -1));
//根据邻接矩阵初始化直接相连的顶点
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j)
{
if (_matrix[i][j] != MAX_W)//i -> j 有边
{
vvDist[i][j] = _matrix[i][j];
vvParentPath[i][j] = i;
}
if (i == j) vvDist[i][j] = W();
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < size; ++k)//依次选取各个顶点作为i->j路径的中间顶点
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j)
if (vvDist[i][k] != MAX_W && vvDist[k][j] != MAX_W &&
vvDist[i][k] + vvDist[k][j] < vvDist[i][j])
{
vvDist[i][j] = vvDist[i][k] + vvDist[k][j];
vvParentPath[i][j] = vvParentPath[k][j];
}
} - Bellman-Ford算法是根据路径的终边来进行松弛更新的,而Floyd-Warshall算法是根据路径经过的中间顶点来进行松弛更新的,因为根据Bellman-Ford算法中的
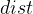 只能得知从指定源顶点到某一顶点的路径权值,而根据Floyd-Warshall算法中的
只能得知从指定源顶点到某一顶点的路径权值,而根据Floyd-Warshall算法中的 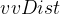 可以得知任意两个顶点之间的路径权值
可以得知任意两个顶点之间的路径权值 - Floyd-Warshall算法的时间复杂度是
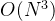 ,空间复杂度是
,空间复杂度是  。虽然求解多源最短路径也可以以图中不同的顶点作为源顶点,去调用Dijkstra算法或Bellman-Ford算法,但Dijkstra算法不能解决带负权的图,Bellman-Ford算法调用
。虽然求解多源最短路径也可以以图中不同的顶点作为源顶点,去调用Dijkstra算法或Bellman-Ford算法,但Dijkstra算法不能解决带负权的图,Bellman-Ford算法调用  次的时间复杂度又太高
次的时间复杂度又太高