JAVA面试题分享五百五十三:SpringBoot 实现动态切换数据源
目录
1 简介
2 代码实现
2.1 实现ThreadLocal
2.2 实现AbstractRoutingDataSource
2.3 配置数据库
2.4 测试
2.5 优化调整
2.5.1 注解切换数据源
2.5.1.1 定义注解
2.5.1.2 实现aop
2.5.1.3 测试
2.5.2 动态添加数据源
2.5.2.1 数据源实体
2.5.2.2 修改DynamicDataSource
2.5.2.3 动态添加数据源
2.5.2.4 测试
1 简介
ThreadLocal:想必大家必不会陌生,全称:thread local variable。主要是为解决多线程时由于并发而产生数据不一致问题。ThreadLocal为每个线程提供变量副本,确保每个线程在某一时间访问到的不是同一个对象,这样做到了隔离性,增加了内存,但大大减少了线程同步时的性能消耗,减少了线程并发控制的复杂程度。
-
ThreadLocal作用:在一个线程中共享,不同线程间隔离
-
ThreadLocal原理:ThreadLocal存入值时,会获取当前线程实例作为key,存入当前线程对象中的Map中。
AbstractRoutingDataSource:根据用户定义的规则选择当前的数据源,
作用:在执行查询之前,设置使用的数据源,实现动态路由的数据源,在每次数据库查询操作前执行它的抽象方法determineCurrentLookupKey(),决定使用哪个数据源。
2 代码实现
程序环境:
SpringBoot2.4.8
Mybatis-plus3.2.0
Druid1.2.6
lombok1.18.20
commons-lang3 3.10
2.1 实现ThreadLocal
创建一个类用于实现ThreadLocal,主要是通过get,set,remove方法来获取、设置、删除当前线程对应的数据源。
/**
* @description:
* @date: 2023/7/27 11:21
**/
public class DataSourceContextHolder {
//此类提供线程局部变量。这些变量不同于它们的正常对应关系是每个线程访问一个线程(通过get、set方法),有自己的独立初始化变量的副本。
private static final ThreadLocal DATASOURCE_HOLDER = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 设置数据源
* @param dataSourceName 数据源名称
*/
public static void setDataSource(String dataSourceName){
DATASOURCE_HOLDER.set(dataSourceName);
}
/**
* 获取当前线程的数据源
* @return 数据源名称
*/
public static String getDataSource(){
return DATASOURCE_HOLDER.get();
}
/**
* 删除当前数据源
*/
public static void removeDataSource(){
DATASOURCE_HOLDER.remove();
}
}
2.2 实现AbstractRoutingDataSource
定义一个动态数据源类实现AbstractRoutingDataSource,通过determineCurrentLookupKey方法与上述实现的ThreadLocal类中的get方法进行关联,实现动态切换数据源。
/**
* @description: 实现动态数据源,根据AbstractRoutingDataSource路由到不同数据源中
* @date: 2023/7/27 11:18
**/
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
public DynamicDataSource(DataSource defaultDataSource,Map targetDataSources){
super.setDefaultTargetDataSource(defaultDataSource);
super.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
}
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DataSourceContextHolder.getDataSource();
}
}
上述代码中,还实现了一个动态数据源类的构造方法,主要是为了设置默认数据源,以及以Map保存的各种目标数据源。其中Map的key是设置的数据源名称,value则是对应的数据源(DataSource)。
2.3 配置数据库
application.yml中配置数据库信息:
#设置数据源
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
master:
url: jdbc:mysql://xxxxxx:3306/test1?characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
slave:
url: jdbc:mysql://xxxxx:3306/test2?characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
initial-size: 15
min-idle: 15
max-active: 200
max-wait: 60000
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
validation-query: ""
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
pool-prepared-statements: false
connection-properties: false
/**
* @description: 设置数据源
* @date: 2023/7/27 11:34
**/
@Configuration
public class DateSourceConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.druid.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource(){
return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.druid.slave")
public DataSource slaveDataSource(){
return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "dynamicDataSource")
@Primary
public DynamicDataSource createDynamicDataSource(){
Map dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>();
DataSource defaultDataSource = masterDataSource();
dataSourceMap.put("master",defaultDataSource);
dataSourceMap.put("slave",slaveDataSource());
return new DynamicDataSource(defaultDataSource,dataSourceMap);
}
}
通过配置类,将配置文件中的配置的数据库信息转换成datasource,并添加到DynamicDataSource中,同时通过@Bean将DynamicDataSource注入Spring中进行管理,后期在进行动态数据源添加时,会用到。
2.4 测试
在主从两个测试库中,分别添加一张表test_user,里面只有一个字段user_name。
create table test_user(
user_name varchar(255) not null comment '用户名'
)
在主库添加信息:
insert into test_user (user_name) value ('master');
从库中添加信息:
insert into test_user (user_name) value ('slave');
我们创建一个getData的方法,参数就是需要查询数据的数据源名称。
@GetMapping("/getData.do/{datasourceName}")
public String getMasterData(@PathVariable("datasourceName") String datasourceName){
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource(datasourceName);
TestUser testUser = testUserMapper.selectOne(null);
DataSourceContextHolder.removeDataSource();
return testUser.getUserName();
}
其他的Mapper和实体类大家自行实现。
执行结果:
1、传递master时:
2、传递slave时:
通过执行结果,我们看到传递不同的数据源名称,查询对应的数据库是不一样的,返回结果也不一样。
在上述代码中,我们看到DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource(datasourceName); 来设置了当前线程需要查询的数据库,通过DataSourceContextHolder.removeDataSource(); 来移除当前线程已设置的数据源。使用过Mybatis-plus动态数据源的小伙伴,应该还记得我们在使用切换数据源时会使用到DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.push(String ds); 和DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.poll(); 这两个方法,翻看源码我们会发现其实就是在使用ThreadLocal时使用了栈,这样的好处就是能使用多数据源嵌套,这里就不带大家实现了,有兴趣的小伙伴可以看看Mybatis-plus中动态数据源的源码。
注:启动程序时,小伙伴不要忘记将SpringBoot自动添加数据源进行排除哦,否则会报循环依赖问题。
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
2.5 优化调整
2.5.1 注解切换数据源
在上述中,虽然已经实现了动态切换数据源,但是我们会发现如果涉及到多个业务进行切换数据源的话,我们就需要在每一个实现类中添加这一段代码。
说到这有小伙伴应该就会想到使用注解来进行优化,接下来我们来实现一下。
2.5.1.1 定义注解
我们就用mybatis动态数据源切换的注解:DS,代码如下:
/**
* @description:
* @date: 2023/7/27 14:39
**/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface DS {
String value() default "master";
}
2.5.1.2 实现aop
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DSAspect {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.jiashn.dynamic_datasource.dynamic.aop.DS)")
public void dynamicDataSource(){}
@Around("dynamicDataSource()")
public Object datasourceAround(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature)point.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
DS ds = method.getAnnotation(DS.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(ds)){
DataSourceContextHolder.setDataSource(ds.value());
}
try {
return point.proceed();
} finally {
DataSourceContextHolder.removeDataSource();
}
}
}
代码使用了@Around,通过ProceedingJoinPoint获取注解信息,拿到注解传递值,然后设置当前线程的数据源。对aop不了解的小伙伴可以自行google或百度。
2.5.1.3 测试
添加两个测试方法:
@GetMapping("/getMasterData.do")
public String getMasterData(){
TestUser testUser = testUserMapper.selectOne(null);
return testUser.getUserName();
}
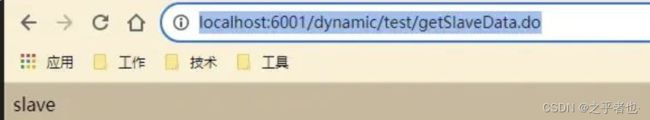
@GetMapping("/getSlaveData.do")
@DS("slave")
public String getSlaveData(){
TestUser testUser = testUserMapper.selectOne(null);
return testUser.getUserName();
}
由于@DS中设置的默认值是:master,因此在调用主数据源时,可以不用进行添加。
执行结果:
1、调用getMasterData.do方法:
2、调用getSlaveData.do方法:
通过执行结果,我们通过@DS也进行了数据源的切换,实现了Mybatis-plus动态切换数据源中的通过注解切换数据源的方式。
2.5.2 动态添加数据源
业务场景 :有时候我们的业务会要求我们从保存有其他数据源的数据库表中添加这些数据源,然后再根据不同的情况切换这些数据源。
因此我们需要改造下DynamicDataSource来实现动态加载数据源。
2.5.2.1 数据源实体
/**
* @description: 数据源实体
* @date: 2023/7/27 15:55
**/
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class DataSourceEntity {
/**
* 数据库地址
*/
private String url;
/**
* 数据库用户名
*/
private String userName;
/**
* 密码
*/
private String passWord;
/**
* 数据库驱动
*/
private String driverClassName;
/**
* 数据库key,即保存Map中的key
*/
private String key;
}
实体中定义数据源的一般信息,同时定义一个key用于作为DynamicDataSource中Map中的key。
2.5.2.2 修改DynamicDataSource
/**
* @description: 实现动态数据源,根据AbstractRoutingDataSource路由到不同数据源中
* @date: 2023/7/27 11:18
**/
@Slf4j
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
private final Map targetDataSourceMap;
public DynamicDataSource(DataSource defaultDataSource,Map targetDataSources){
super.setDefaultTargetDataSource(defaultDataSource);
super.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
this.targetDataSourceMap = targetDataSources;
}
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DataSourceContextHolder.getDataSource();
}
/**
* 添加数据源信息
* @param dataSources 数据源实体集合
* @return 返回添加结果
*/
public void createDataSource(List dataSources){
try {
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(dataSources)){
for (DataSourceEntity ds : dataSources) {
//校验数据库是否可以连接
Class.forName(ds.getDriverClassName());
DriverManager.getConnection(ds.getUrl(),ds.getUserName(),ds.getPassWord());
//定义数据源
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(ds,dataSource);
//申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,这里建议配置为TRUE,防止取到的连接不可用
dataSource.setTestOnBorrow(true);
//建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。
//申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
dataSource.setTestWhileIdle(true);
//用来检测连接是否有效的sql,要求是一个查询语句。
dataSource.setValidationQuery("select 1 ");
dataSource.init();
this.targetDataSourceMap.put(ds.getKey(),dataSource);
}
super.setTargetDataSources(this.targetDataSourceMap);
// 将TargetDataSources中的连接信息放入resolvedDataSources管理
super.afterPropertiesSet();
return Boolean.TRUE;
}
}catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
log.error("---程序报错---:{}", e.getMessage());
}
return Boolean.FALSE;
}
/**
* 校验数据源是否存在
* @param key 数据源保存的key
* @return 返回结果,true:存在,false:不存在
*/
public boolean existsDataSource(String key){
return Objects.nonNull(this.targetDataSourceMap.get(key));
}
}
在改造后的DynamicDataSource中,我们添加可以一个 private final Map,这个map会在添加数据源的配置文件时将创建的Map数据源信息通过DynamicDataSource构造方法进行初始赋值,即:DateSourceConfig类中的createDynamicDataSource()方法中。
同时我们在该类中添加了一个createDataSource方法,进行数据源的创建,并添加到map中,再通过super.setTargetDataSources(this.targetDataSourceMap) ;进行目标数据源的重新赋值。
2.5.2.3 动态添加数据源
上述代码已经实现了添加数据源的方法,那么我们来模拟通过从数据库表中添加数据源,然后我们通过调用加载数据源的方法将数据源添加进数据源Map中。
在主数据库中定义一个数据库表,用于保存数据库信息。
create table test_db_info(
id int auto_increment primary key not null comment '主键Id',
url varchar(255) not null comment '数据库URL',
username varchar(255) not null comment '用户名',
password varchar(255) not null comment '密码',
driver_class_name varchar(255) not null comment '数据库驱动'
name varchar(255) not null comment '数据库名称'
)
为了方便,我们将之前的从库录入到数据库中,修改数据库名称。
insert into test_db_info(url, username, password,driver_class_name, name)
value ('jdbc:mysql://xxxxx:3306/test2?characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=false',
'root','123456','com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver','add_slave')
数据库表对应的实体、mapper,小伙伴们自行添加。
启动SpringBoot时添加数据源:
/**
* @description:
* @date: 2023/7/27 16:56
**/
@Component
public class LoadDataSourceRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Resource
private DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource;
@Resource
private TestDbInfoMapper testDbInfoMapper;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
List testDbInfos = testDbInfoMapper.selectList(null);
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(testDbInfos)) {
List ds = new ArrayList<>();
for (TestDbInfo testDbInfo : testDbInfos) {
DataSourceEntity sourceEntity = new DataSourceEntity();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(testDbInfo,sourceEntity);
sourceEntity.setKey(testDbInfo.getName());
ds.add(sourceEntity);
}
dynamicDataSource.createDataSource(ds);
}
}
}
经过上述SpringBoot启动后,已经将数据库表中的数据添加到动态数据源中,我们调用之前的测试方法,将数据源名称作为参数传入看看执行结果。
2.5.2.4 测试
通过测试我们发现数据库表中的数据库被动态加入了数据源中,小伙伴可以愉快地随意添加数据源了。