【C++航海王:追寻罗杰的编程之路】类与对象你学会了吗?(上)
目录
1 -> 面向过程与面向对象的初步认识
2 -> 类的引入
3 -> 类的定义
4 -> 类的访问限定符及封装
4.1 -> 访问限定符
4.2 -> 封装
5 -> 类的作用域
6 -> 类的实例化
7 -> 类对象模型
7.1 -> 如何计算类对象的大小
7.2 -> 类对象存储方式的猜测
7.3 -> 结构体内存对齐规则
8 -> this指针
8.1 -> this指针的引出
8.2 -> this指针的特性
8.3 -> C语言和C++实现Stack的对比
1 -> 面向过程与面向对象的初步认识
- C语言是面向过程的,关注的是过程,分析出求解问题的步骤,通过函数调用逐步解决问题。
- C++是基于面向对象的,关注的是对象,将一件事拆分成不同的,靠对象之间的交互完成。
模拟一个做饭的场景:
在C语言中,我们可以定义一个主函数,然后按照面向过程的思路,将做饭的各个步骤拆分成不同的函数,每个函数负责一个特定的任务,比如洗菜、切菜、烧火、炒菜等。在主函数中按照顺序调用这些函数来完成整个做饭过程。在这种方式下,我们需要手动管理各个步骤之间的数据传递和调用顺序。
在C++中,我们可以定义一个名为"Chef"的类,这个类可以包含一些属性和方法,比如"洗菜"、"切菜"、"烧火"、"炒菜"等。每个方法可以用来执行特定的任务,还可以采用封装性,将一些私有属性和方法隐藏起来。我们可以实例化一个"Chef"对象,然后调用对象的方法来完成整个做饭过程。此外,我们还可以使用继承和多态性来扩展做饭的能力,比如可以创建一个"ChineseChef"类来继承"Chef"类,并且扩展了一些中式烹饪的方法。
2 -> 类的引入
C语言结构体中只能定义变量,而在C++中,结构体内不仅可以定义变量,也可以定义函数。
比如实现栈:
#include
using namespace std;
typedef int DataType;
struct Stack
{
void Init(size_t capacity)
{
_array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType) * capacity);
if (nullptr == _array)
{
perror("malloc申请空间失败");
return;
}
_capacity = capacity;
_size = 0;
}
void Push(const DataType& data)
{
// 扩容
_array[_size] = data;
++_size;
}
DataType Top()
{
return _array[_size - 1];
}
void Destroy()
{
if (_array)
{
free(_array);
_array = nullptr;
_capacity = 0;
_size = 0;
}
}
DataType* _array;
size_t _capacity;
size_t _size;
};
int main()
{
Stack s;
s.Init(10);
s.Push(1);
s.Push(2);
s.Push(3);
cout << s.Top() << endl;
s.Destroy();
return 0;
} 上面结构体的定义,在C++中更喜欢用class来代替。
3 -> 类的定义
#include
using namespace std;
class ClassName
{
};
int main()
{
return 0;
} 其中,class为定义类的关键字,ClassName为类的名字,{}中为类的主体,注意类定义结束时后面的分号不能省略。
类体中内容称为类的成员:
- 类中的变量称为类的属性或成员变量;
- 类中的函数称为类的方法或者成员函数。
类的两种定义方式:
- 声明和定义全部放在类体中,需注意:成员函数如果在类中定义,编译器可能会将其当成内联函数处理。
#include
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
void Show()
{
cout << _name << "-" << _sex << "-" << _id << endl;
}
public:
char* _name;
char* _sex;
int _id;
};
int main()
{
return 0;
} - 类声明放在.h文件中,成员函数定义放在.cpp文件中,注意:成员函数名前需要加类名::
声明放在类的头文件Student.h中
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
void Show();
public:
char* _name;
char* _sex;
int _id;
}; 定义放在类的实现文件Student.cpp中
#include "Student.h"
void Student::Show()
{
cout << _name << "-" << _sex << "-" << _id << endl;
}
4 -> 类的访问限定符及封装
4.1 -> 访问限定符
C++实现封装的方式:用类将对象的属性与方法结合在一起,让对象更加完善,通过访问权限选择性的将其接口提供给外部的用户使用。
- public修饰的成员在类外可以直接被访问;
- protected和private修饰的成员在类外不能直接被访问(此处protected和private类似);
- 访问权限作用域从该访问限定符出现的位置开始直到下一个访问限定符出现为止;
- 如果后面没有访问限定符,作用域到"}"即类结束;
- class的默认访问权限是private,struct为public(因为struct要兼容C)。
注意:访问限定符只在编译时有用,当数据映射到内存时,没有任何访问限定符上的区别。
那么,C++中的struct和class的区别是什么呢?
C++需要兼容C语言,所以C++中struct一样可以当成结构体使用。另外C++中struct还可以用来定义类。和class定义类一样,区别时struct定义的类默认访问权限是public,class定义的类默认访问权限是private。
注意:在继承和模板参数列表位置,struct和class也有区别。
4.2 -> 封装
面向对象的三大特性:封装、继承、多态。
在类和对象阶段,主要是研究类的封装特性,那么什么是封装呢?
封装:将数据和操作数据的方法进行有机结合,隐藏对象的属性和实现细节,仅对外公开接口来和对象进行交互。
封装本质上是一种管理,让用户更方便使用类。比如:对于电脑这样一个复杂的设备,提供给用户的只有开关机键、通过键盘输入、显示器、USB插孔等,让用户和计算机进行交互,完成日常事务。但实际上电脑真正工作的却是CPU、显卡、内存等一些硬件元件。
对于计算机使用者而言,不用关心内部核心部件,比如主板上线路如何布局,CPU内部是如何设计等,用户只需要知道,如何开关机,怎么通过键盘鼠标与计算机交互即可。因此计算机厂商在出厂时,在外部套一个外壳,将内部实现的细节隐藏起来,仅仅对外提供开关机、键盘鼠标插孔等,让用户可以与计算机交互即可。
在C++中实现封装,可以通过类将数据以及操作数据的方法有机结合,通过访问权限来隐藏对象内部实现细节,控制具体哪些方法可以在类的外部直接被使用。
5 -> 类的作用域
类定义了一个新的作用域,类的所有成员都在类的作用域中。在类体外定义成员时,需要使用::作用域操作符指明成员属于哪个类域。
#pragma once
#include
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
void Show();
public:
char* _name;
char* _sex;
int _id;
}; #include "Student.h"
// 指明Show属于Student类域
void Student::Show()
{
cout << _name << "-" << _sex << "-" << _id << endl;
}
6 -> 类的实例化
用类类型创建对象的过程,称为类的实例化。
- 类时对对象进行描述的,是一个类似模型的东西,限定了类有哪些成员,定义出一个类并没有分配实际的内存空间来存储它;比如,入学填写学生信息表,表格可看成一个类,用来描述具体的学生信息;
- 一个类可以实例化出多个对象,实例化出的对象,占用实际的物理空间,存储类成员变量;
- 类实例化出对象就像现实中使用图纸建造房子,类就是这个图纸,只设计出需要什么,并没有实体存在,同样类也只是一个设计,实例化出的对象才能实际存储数据,占用物理空间。
class Student
{
public:
void Show();
public:
char* _name;
char* _sex;
int _id;
};void Test()
{
Student stu;
stu._name = "zzl";
stu._sex = "男";
stu._id = 001;
stu.Show();
}7 -> 类对象模型
7.1 -> 如何计算类对象的大小
#include
using namespace std;
class S
{
public:
void Show()
{
cout << _id << endl;
}
private:
int _id;
}; 类中既可以有成员变量,又可以有成员函数,那么一个类的对象中包含了什么?如何计算一个类的大小?
7.2 -> 类对象存储方式的猜测
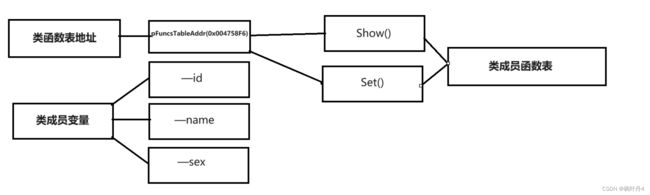
- 对象中包含类的各个成员
- 代码只保存了一份,在对象中保存存放代码的地址
- 只保存成员变量,成员函数存放在公共代码段
7.3 -> 结构体内存对齐规则
-
第一个成员在与结构体偏移量为0的地址处。
-
其他成员变量要对齐到某个数字(对齐数)的整数倍的地址处。注意:对齐数 = 编译器默认的一个对齐数 与 该成员大小的较小值。(VS中默认的对齐数为8)
-
结构体总大小为:最大对齐数(所有变量类型最大者与默认对齐参数取最小)的整数倍。
-
如果嵌套了结构体的情况,嵌套的结构体对齐到自己的最大对齐数的整数倍处,结构体的整体大小就是所有最大对齐数(含嵌套结构体的对齐数)的整数倍。
8 -> this指针
8.1 -> this指针的引出
先定义一个日期类Date:
class Date
{
public:
void Init(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
private:
int _year; // 年
int _month; // 月
int _day; // 日
};
int main()
{
Date d1, d2;
d1.Init(2022, 1, 11);
d2.Init(2022, 1, 12);
d1.Print();
d2.Print();
return 0;
}8.2 -> this指针的特性
- this指针的类型:类类型* const,即成员函数中,不能给this指针赋值;
- 只能在“成员函数”的内部使用;
-
this指针本质上是“成员函数”的形参,当对象调用成员函数时,将对象地址作为实参传递给this形参。所以对象中不存储this指针;
-
this指针是“成员函数”第一个隐含的指针形参,一般情况由编译器通过ecx寄存器自动传递,不需要用户传递。
8.3 -> C语言和C++实现Stack的对比
#include
#include
#include
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
DataType* array;
int capacity;
int size;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType) * 3);
if (NULL == ps->array)
{
assert(0);
return;
}
ps->capacity = 3;
ps->size = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->array)
{
free(ps->array);
ps->array = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->size = 0;
}
}
void CheckCapacity(Stack* ps)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity * 2;
DataType* temp = (DataType*)realloc(ps->array,
newcapacity * sizeof(DataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc申请空间失败!!!");
return;
}
ps->array = temp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, DataType data)
{
assert(ps);
CheckCapacity(ps);
ps->array[ps->size] = data;
ps->size++;
}
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return 0 == ps->size;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
if (StackEmpty(ps))
return;
ps->size--;
}
DataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->array[ps->size - 1];
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->size;
}
int main()
{
Stack s;
StackInit(&s);
StackPush(&s, 1);
StackPush(&s, 2);
StackPush(&s, 3);
StackPush(&s, 4);
printf("%d\n", StackTop(&s));
printf("%d\n", StackSize(&s));
StackPop(&s);
StackPop(&s);
printf("%d\n", StackTop(&s));
printf("%d\n", StackSize(&s));
StackDestroy(&s);
return 0;
} 可以看到,在用C语言实现时,Stack相关操作函数有以下共性:
- 每个函数的第一个参数都是Stack*;
- 函数中必须要对第一个参数检测,因为该参数可能会为NULL;
- 函数中都是通过Stack*参数操作栈的;
- 调用时必须传递Stack结构体变量的地址。
C++实现:
#include
using namespace std;
typedef int DataType;
class Stack
{
public:
void Init()
{
_array = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType) * 3);
if (NULL == _array)
{
perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");
return;
}
_capacity = 3;
_size = 0;
}
void Push(DataType data)
{
CheckCapacity();
_array[_size] = data;
_size++;
}
void Pop()
{
if (Empty())
return;
_size--;
}
DataType Top()
{
return _array[_size - 1];
}
int Empty()
{
return 0 == _size;
}
int Size()
{
return _size;
}
void Destroy()
{
if (_array)
{
free(_array);
_array = NULL;
_capacity = 0;
_size = 0;
}
}
private:
void CheckCapacity()
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;
DataType* temp = (DataType*)realloc(_array, newcapacity *
sizeof(DataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc申请空间失败!!!");
return;
}
_array = temp;
_capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
private:
DataType* _array;
int _capacity;
int _size;
};
int main()
{
Stack s;
s.Init();
s.Push(1);
s.Push(2);
s.Push(3);
s.Push(4);
printf("%d\n", s.Top());
printf("%d\n", s.Size());
s.Pop();
s.Pop();
printf("%d\n", s.Top());
printf("%d\n", s.Size());
s.Destroy();
return 0;
} 感谢大佬们的支持!!!互三啦