c# 操作符原理及概念
1操作符概览
2操作符的本质
操作符的本质是函数(即算法)的简记法
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person people1 = new Person();
Person people2 = new Person();
people1.Name = "王小丫";
people2.Name = "陈雪梅";
List nation = Person.GetMarry(people1, people2);
foreach (var p in nation)
{
Console.WriteLine(p.Name);
}
}
class Person
{
public string Name;
public static List GetMarry ( Person p1 , Person p2 )
{
List people = new List();
people.Add(p1);
people.Add(p2);
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++)
{
Person chid = new Person();
chid.Name = p1.Name + "&" + p2.Name + "&"+i;
people.Add(chid);
}
return people;
}
} static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person people1 = new Person();
Person people2 = new Person();
people1.Name = "王小丫";
people2.Name = "陈雪梅";
List nation = people1+people2;
foreach (var p in nation)
{
Console.WriteLine(p.Name);
}
}
class Person
{
public string Name;
public static List operator+ ( Person p1 , Person p2 )
{
List people = new List();
people.Add(p1);
people.Add(p2);
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++)
{
Person chid = new Person();
chid.Name = p1.Name + "&" + p2.Name + "&"+i;
people.Add(chid);
}
return people;
}
} 操作符不能脱离与它关联的数据类型(操作符与固定数据类型的一套基本算法的简记法)
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 5;
int y = 4;
int z = x / y;
Console.WriteLine(z);//输出1
double a = 5;
double b = 4;
double c = a / b;
Console.WriteLine(c);//输出1.25
}
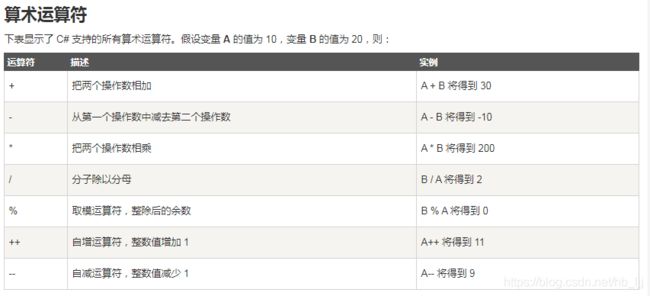
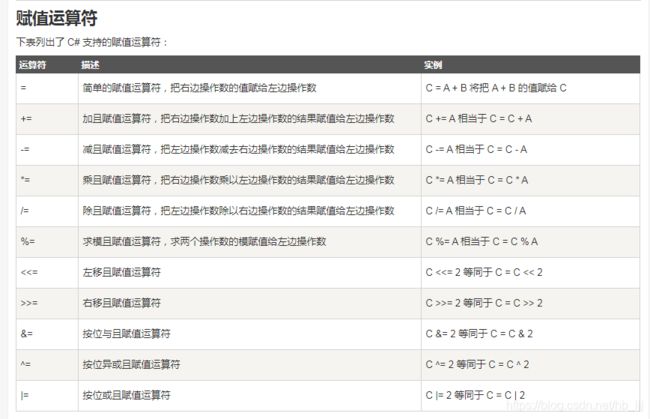
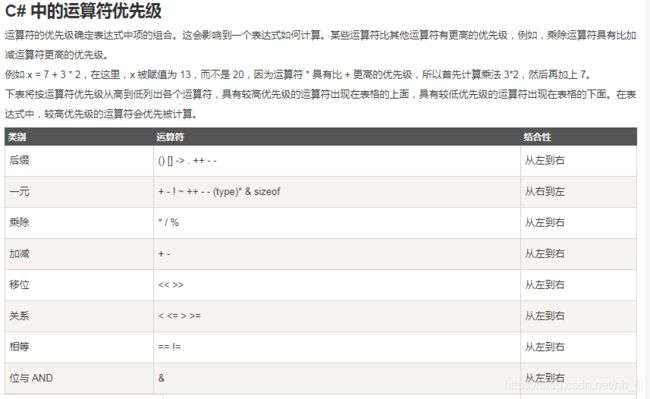
3操作符的优先级
带有赋值功能运算符 右向左
x+=y+=z
x+=y
+不带赋值功能运算符 左向右
x=x+y+z
4统计操作符的运算顺序
5各类操作符的示例
.点 成员访问操作符
1外层空间名称的子集空间名称
访问名称空间的类型 访问类型的静态成员 访问对象的成员
System.IO.File.Create("D:\\helo.txt");
//System外层空间名称//IO子集空间 //File名称空间的类型//Create访问类型的静态成员//Create访问对象的成员
f(x) 方法调用操作符 方法函数(参数)
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person c = new Person();
double x= c.Add(3.0,5.0);
Console.WriteLine(x);
//委托
Action myaction = new Action(c.PrintHellod);
myaction();
}
class Person
{
public double Add(double a, double b)
{
return a + b;
}
public void PrintHellod()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
}
}o[x]元素访问操作符
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//访问数组
int[] myintArray = new int[10];
int[] myintArray1 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
Console.WriteLine(myintArray1[0]);
//访问字典
Dictionary perdic = new Dictionary();
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
Person per = new Person();
per.Name = "s_" + i.ToString();
per.Scone = 100 + i;
perdic.Add(per.Name,per);
}
Person per6 = perdic["s_6"];
Console.WriteLine(per6.Scone);
}
class Person
{
public string Name;
public int Scone;
} x++ x-- 后置自增 后置自减
int x = 100;
x++;
//可以理解为 x=x+1;
Console.WriteLine(x);
int x = 100;
int y = x++;
//相当于 y=x;x=x+1;
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine(y);
typeof default 查看一个类型的内部结构
//Metadata
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Type t = typeof(int);
Console.WriteLine(t.Namespace);//名称空间
Console.WriteLine(t.FullName);//全称
Console.WriteLine(t.Name);
int c = t.GetMembers().Length;
foreach (var mi in t.GetMembers())
{
Console.WriteLine(mi.Name);
}
Console.WriteLine(c);
}new 在内存中创建一个实例,立即调用实例构造器
还能调用初始化器
Form myForm=new Form(){Text="Hello"}.ShowDialog();
var 声明一个隐式变量,类型确定了,就不能换类型;
var person = new { Name = "Mr.Okay", Age = "34" };
Console.WriteLine(person.Name);
Console.WriteLine(person.Age);
Console.WriteLine(person.GetType().Name);checked unchecked
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//无符号整形 32位
uint x = uint.MaxValue;
Console.WriteLine(x);
string binStr = Convert.ToString(x, 2);
Console.WriteLine(binStr);
uint y = x + 1;
Console.WriteLine(y);
try
{
uint y1 = checked(x + 1);
}
catch (OverflowException ex)
{ Console.WriteLine("溢出"); }
}delegate