Redis源码解析之ziplist
Ziplist是用字符串来实现的双向链表,对于容量较小的键值对,为其创建一个结构复杂的哈希表太浪费内存,所以redis 创建了ziplist来存放这些键值对,这可以减少存放节点指针的空间,因此它被用来作为哈希表初始化时的底层实现。下图即ziplist 的内部结构。
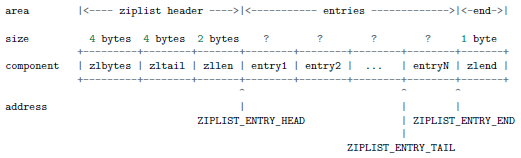
Zlbytes是整个ziplist 所占用的空间,必要时需要重新分配。
Zltail便于快速的访问到表尾节点,不需要遍历整个ziplist。
Zllen表示包含的节点数。
Entries表示用户增加上去的节点。
Zlend是一个255的值,表示ziplist末尾
Ziplist比dict更节省内存,所以在创建hash的时候默认ziplist作为其底层实现,当有需要时,再转换回来。
举例:用户创建一个以ziplist为底层的hash键:
Redis-cli > hset book name "programing"
首先进入hsetCommand()函数的hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate()函数
void hsetCommand(redisClient *c) { int update; robj *o; if ((o = hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(c,c->argv[1])) == NULL) return; hashTypeTryConversion(o,c->argv,2,3); hashTypeTryObjectEncoding(o,&c->argv[2], &c->argv[3]); update = hashTypeSet(o,c->argv[2],c->argv[3]); addReply(c, update ? shared.czero : shared.cone); signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]); notifyKeyspaceEvent(REDIS_NOTIFY_HASH,"hset",c->argv[1],c->db->id); server.dirty++; } robj *hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(redisClient *c, robj *key) { robj *o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key); if (o == NULL) { o = createHashObject(); dbAdd(c->db,key,o); } else { if (o->type != REDIS_HASH) { addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr); return NULL; } } return o; }
先创建一个空的ziplist,编码方式默认为ziplist ,再add这个Key(book)到DB中
主要的添加操作在hashTpyeSet()中
/* Add an element, discard the old if the key already exists. * Return 0 on insert and 1 on update. * This function will take care of incrementing the reference count of the * retained fields and value objects. */ int hashTypeSet(robj *o, robj *field, robj *value) { int update = 0; if (o->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) { unsigned char *zl, *fptr, *vptr; field = getDecodedObject(field); value = getDecodedObject(value); zl = o->ptr; fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, ZIPLIST_HEAD); if (fptr != NULL) { fptr = ziplistFind(fptr, field->ptr, sdslen(field->ptr), 1); if (fptr != NULL) { /* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */ vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr); redisAssert(vptr != NULL); update = 1; /* Delete value */ zl = ziplistDelete(zl, &vptr); /* Insert new value */ zl = ziplistInsert(zl, vptr, value->ptr, sdslen(value->ptr)); } } if (!update) { /* Push new field/value pair onto the tail of the ziplist */ zl = ziplistPush(zl, field->ptr, sdslen(field->ptr), ZIPLIST_TAIL); zl = ziplistPush(zl, value->ptr, sdslen(value->ptr), ZIPLIST_TAIL); } o->ptr = zl; decrRefCount(field); decrRefCount(value); /* Check if the ziplist needs to be converted to a hash table */ if (hashTypeLength(o) > server.hash_max_ziplist_entries) hashTypeConvert(o, REDIS_ENCODING_HT); } else if (o->encoding == REDIS_ENCODING_HT) { if (dictReplace(o->ptr, field, value)) { /* Insert */ incrRefCount(field); } else { /* Update */ update = 1; } incrRefCount(value); } else { redisPanic("Unknown hash encoding"); } return update; }
首先会搜索ziplist ,如果发现有相同的键值,则替换掉,如果找不到,则把新加入的键值push到ziplist 的末尾,在源码中可以发现当其长度大于hash_max_ziplist_entries就需要转换为hash table的编码方式。
完成上述操作之后,就使用addReply()把结果存到buffer中传给客户端。