Android学习——界面编程!
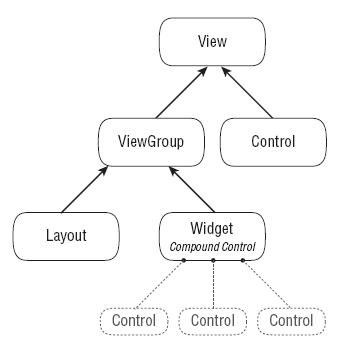
在Android系统中,组成界面的元素主要有:
- Views:所有用户界面展示信息的基类,包括通用控件,自定义控件,就相当于C#编程中的Controls;
- ViewGroups:是Views的继承类,支持多个控件进行组合,有点象C#编程的UserControls;
- Activities:是窗体的基类,相当于C#中的Form。
看个类图:
常用的控件有:TextView、EditText、ListView、Spinner(相当于Combox)、Button、CheckBox、RadioButton等等。控件比较多,以后可以边用边学,跟C#界面控件还差不多,下面我们就看看用法吧,现在再回头看看我们的Hello World程序:
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
这里,setContentView(R.layout.main);就是把我们定义在resource中的控件加载进来,同样,换成程序写法:
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle icicle) {
super.onCreate(icicle);
TextView myTextView = new TextView(this);
setContentView(myTextView);
myTextView.setText(“Hello, Android”);
}
看到这段代码,大家可能就会想到一个控件位置,在C#编程中,我们在一个Form中会定义一个界面里,会将多个控件加载到主窗体中,然后定义好坐标(x,y)即可。
在Android界面中,控件布局有5种:
-
FrameLayout:层叠,新加的控件会叠加到原控件上面,遮挡。
-
LinearLayout:直线添加控件,可垂直,可水平,依次排开部署控件,通过android:orientation属性来改变方向。
-
RelativeLayout:相对布局,相对一个控件的ID,如例如toLeft:”okbutton”, below:”text”。
-
TableLayout:表格布局,用table的行列来定位控件。
-
AbsoluteLayout:绝对位置,用x,y来定位。
使用布局:
LinearLayout ll = new LinearLayout(this);
ll.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
TextView myTextView = new TextView(this);
EditText myEditText = new EditText(this);
myTextView.setText(“Enter Text Below”);
myEditText.setText(“Text Goes Here!”);
int lHeight = LinearLayout.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT;
int lWidth = LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
ll.addView(myTextView, new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(lHeight, lWidth));
ll.addView(myEditText, new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(lHeight, lWidth));
setContentView(ll);
或用xml:
<?xml version=”1.0” encoding=”utf-8”?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
android:orientation=”vertical”
android:layout_width=”fill_parent”
android:layout_height=”fill_parent”>
<TextView
android:layout_width=”fill_parent”
android:layout_height=”wrap_content”
android:text=”Enter Text Below”
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width=”fill_parent”
android:layout_height=”wrap_content”
android:text=”Text Goes Here!”
/>
</LinearLayout>
开发自定义控件:
在用了己有控件后,我们就想自己开发自定义控件,当然开发很简单,只要继承一下View类或者是继承继承View类的现有控件。
public class CompassView extends View{
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//绘制, 这里的canvas就想当于C#中的graphics,能画点线面。
}
}
消息处理可以用对应的虚函数,如:
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent keyEvent) {
...处理按钮消息
postInvalidate();//用于重绘界面
}
好了,有了这些基本方法也就可以开始我们的界面之旅了。