windows网络编程第二版 第一章 winsock简介 读书笔记
Network Programming for Microsoft Windows, 2nd Edition Chapter 1 Winsock介绍
1. Winsock是微软做的网络通讯库,以前winsock是1.1版本,现在winsock有了winsock 2.2版本,winsock2版本变动比较大,做了很多工作。Winsock的接口设计在很大程度上参考了UNIX平台上的BSD的socket实现,在 Winsock 2里面接口做了一些变动,目的是做到winsock真正和协议无关,是一个通用的开发平台。
2. 本章介绍了TCP和UPD的两个最简单的winsock例子,实际上,这样的例子对于一般的网络通讯程序来说已经够用了。这些例子都是block的网络通讯方式,第五章会讲解non-block的winsock编程。
3. Winsock 1和Winsock 2的函数的命名方式。一般来说,Winsock 2的函数都以WSA开头,比如创建一个socket在winsock 1中就是调用socket函数,在winsock 2中我们就可以使用WSASocket,相比socket,WSASocket提供了更多的特性。Winsock 2兼容Winsock 1的所有函数。上述的命名方式有一些例外,他们是:WSAStartup, WSACleanup, WSARecvEx, and WSAGetLastError,这四个函数在Winsock 1中就定义了。
4. winsock的头文件和lib文件。这是开发winsock程序必须的了。在目前大部分的windows平台下,winsock 2都是ready的。Windows CE只支持winsock 1。在开发winsock 2的程序的时候,我们需要include winsock2.h,在开发winsock 1的程序的时候,我们需要include winsock.h。还有一个叫做mswsock.h,这里面定义的函数是只有在微软平台上运行的函数,这些函数能提供高性能,在我们书写需要高性能的网 络通讯程序的时候,我们使用这些函数,具体内容在第六章中描述。
lib文件。winsock 2的程序需要链接ws2_32.lib, winsock 1的程序需要链接wsock32.lib,如果使用mswsock,需要链接mswsock.dll
5. Winsock初始化。调用WSAStartup可以初始化winsock,也就是程序load winsock的dll文件。如果没有初始化winsock就调用了winsock中的函数,函数会返回 SOCKET_ERROR,SOCKET_ERROR是一个generic的返回值表示winsock操作失败,详细的错误信息可以通过调用 WSAGetLastError来获得,对于上述描述的错误,得到的错误码是WSANOTINITIALISED。WSAStartup函数的原型如下:
wVersionRequested 参数用来指定我们要使用的winsock版本。WORD中高字节部分用来指定使用的winsock的minor版本,低字节用来指定使用winsock的 major版本。我们可以使用MAKEWORD(x,y)宏来生成这样一个WORD, x是minor version,y是major version。
lpWSAData参数是一个struct指针,WSAStartup函数会填写这个struct中的内容,这个struct的定义是:
wVersion -- 使用的winsock版本
wHighVersion -- 目前平台上可用的winsock的最高版本
szDescription, szSystemStatus -- 用作特殊用途,一般不常用
iMaxSockets, iMaxUdpDg -- 不用使用这两个字段。他们定义了最大的并发连接数和最大的udp datagram size。然而,要找出正确的这些值,可能还要参考协议本身中的一些限制。
lpVendorInfo -- 保留用,用来存放vendor-specific information.不用使用这个字段。
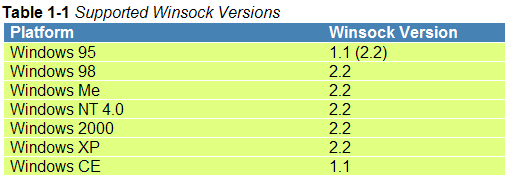
6. 各种windows平台支持的winsock版本:
附件1
可见,大部分windows都支持winsock 2
7. winsock 1的程序可以在支持winsock 2的windows上良好运行。实际上,在winsock 2的windows上,所有的winsock 1的请求都会被映射到winsock 2的dll中。微软的兼容工作做的还是不错的。如果我们在WSAStartup中申请了一个高于目前平台支持的winsock版本,WSAStartup 会失败,同时WSADATA中的wHighVersion中会存放该平台上支持的winsock的最高版本。
8. 调用WSACleanup用来结束一个winsock程序。
int WSACleanup(void);
这个函数会释放所有资源,关闭所有pending的请求等。实际上,就算我们的程序不调用这个函数,操作系统也会把这些资源回收,但是,一个良好的程序,必须调用这个函数。
9. 错误处理。前面说过了,大多数的winsock函数失败的时候,都会返回SOCKET_ERROR,使用WSAGetLastError能获得详细的错误 码,这些错误码都定义在winsock2.h, winsock.h中。有些函数例外,他们不返回SOCKET_ERROR而是其他的返回值。下面是一个使用WSAGetLastError函数的例子:
10. Addressing a Protocol. 本节只介绍基于IP的协议,参考第三章有很多关于网络协议的东西。本节只介绍在winsock中定义一个IPv4的信息结构。定义这样的结构对于winsock中的bind等这样的函数来说是必须的。
sockaddr_in其实是针对Internet,也就是TCP/IP的一个结构。在后面我们会看到,任何结构将来都会转换成SOCKADDR这个结构,有点类似SOCKADDR是基类,sockaddr_in这些都是SOCKADDR的派生类一样。
sin_family -- 必须设成AF_INET,表示我们要使用IP地址family
sin_port -- 指定端口,不过要考虑网络次序和主机次序的问题,下面会介绍
sin_addr -- 指定IP地址。其实是指定这个struct中的一个字段。IP地址也是以long的类型存放的,也要处理网络次序和主机次序的问题。微软提供了一个function来让我们把一个IP字符串转换成一个long型的数值。这个函数是:
注意,调用了inet_addr函数之后生成的long,就不需要再做主机次序,网络次序的转换了。但是后面会看到,如果没用inet_addr,比如给出的IP地址是INADDR_ANY的话,还是要调用htonl函数的。
sin_zero -- 没有用,完全是放在这里为了和SOCKADDR的大小兼容
11. 主机次序和网络次序。这个问题的起源是因为在上述的结构中,我们需要指定一个数字类型的变量,比如port和long型的IP地址。由于数字是多字节的一 块内容,所以就有字节摆放顺序的问题。众所周知,数字类型的变量在不同的计算机(主机)中存放的次序是不一样的,有把高位字节存在前面,低位字节存在后面 的,也有反过来的。对于网络通讯来说,必需要把这种情况统一起来,否则这些关键的信息就会解析错误了。于是就有了所谓的主机次序和网络次序的相互转换了。
winsock中提供了一组函数用来做这个事情,下面的四个函数用来将主机次序转成网络次序:
带 l的是处理4字节的数,带s的是处理2字节的数。不带WSA的函数传入主机次序的数值,返回网络次序的数;带WSA的是把主机次序的数传入 hostlong, hostshort参数,处理后的网络次序的数被填充在lpnetlong, lpnetshort指针指向的变量中。
以下四个函数从网络次序转成主机次序:
12. 给出一个例子用来示范怎么创建这么一个sockadd_in的东西:
第三章会讲述如何在填写IP地址的时候,填写一个域名,以及winsock中包含的一些域名和IP地址互转换的函数。
13. 创建一个socket。socket是网络通讯程序中必须的一个数据结构,他不同于文件描述符,他有单独的数据类型定义-SOCKET。创建一个 socket可以调用socket方法或WSASocket。这里我们用socket函数来举例,后面会详细介绍这些方法。
af -- 定义协议的address family,对于IPv4,当然是AF_INET
type -- 定义socket类型。对于TCP,填写SOCK_STREAM,对于UDP,填写SOCK_DGRAM
protocol -- 定义协议。如果我们在af或type中定义了多种类型的话,这里可以定义一个协议的组合。对于TCP,设置此项为IPPROTO_TCP,对于UDP,设置为IPPROTO_UDP
1. Winsock是微软做的网络通讯库,以前winsock是1.1版本,现在winsock有了winsock 2.2版本,winsock2版本变动比较大,做了很多工作。Winsock的接口设计在很大程度上参考了UNIX平台上的BSD的socket实现,在 Winsock 2里面接口做了一些变动,目的是做到winsock真正和协议无关,是一个通用的开发平台。
2. 本章介绍了TCP和UPD的两个最简单的winsock例子,实际上,这样的例子对于一般的网络通讯程序来说已经够用了。这些例子都是block的网络通讯方式,第五章会讲解non-block的winsock编程。
3. Winsock 1和Winsock 2的函数的命名方式。一般来说,Winsock 2的函数都以WSA开头,比如创建一个socket在winsock 1中就是调用socket函数,在winsock 2中我们就可以使用WSASocket,相比socket,WSASocket提供了更多的特性。Winsock 2兼容Winsock 1的所有函数。上述的命名方式有一些例外,他们是:WSAStartup, WSACleanup, WSARecvEx, and WSAGetLastError,这四个函数在Winsock 1中就定义了。
4. winsock的头文件和lib文件。这是开发winsock程序必须的了。在目前大部分的windows平台下,winsock 2都是ready的。Windows CE只支持winsock 1。在开发winsock 2的程序的时候,我们需要include winsock2.h,在开发winsock 1的程序的时候,我们需要include winsock.h。还有一个叫做mswsock.h,这里面定义的函数是只有在微软平台上运行的函数,这些函数能提供高性能,在我们书写需要高性能的网 络通讯程序的时候,我们使用这些函数,具体内容在第六章中描述。
lib文件。winsock 2的程序需要链接ws2_32.lib, winsock 1的程序需要链接wsock32.lib,如果使用mswsock,需要链接mswsock.dll
5. Winsock初始化。调用WSAStartup可以初始化winsock,也就是程序load winsock的dll文件。如果没有初始化winsock就调用了winsock中的函数,函数会返回 SOCKET_ERROR,SOCKET_ERROR是一个generic的返回值表示winsock操作失败,详细的错误信息可以通过调用 WSAGetLastError来获得,对于上述描述的错误,得到的错误码是WSANOTINITIALISED。WSAStartup函数的原型如下:
- Code: Select all
-
int WSAStartup(
WORD wVersionRequested,
LPWSADATA lpWSAData
);
wVersionRequested 参数用来指定我们要使用的winsock版本。WORD中高字节部分用来指定使用的winsock的minor版本,低字节用来指定使用winsock的 major版本。我们可以使用MAKEWORD(x,y)宏来生成这样一个WORD, x是minor version,y是major version。
lpWSAData参数是一个struct指针,WSAStartup函数会填写这个struct中的内容,这个struct的定义是:
- Code: Select all
-
typedef struct WSAData
{
WORD wVersion;
WORD wHighVersion;
char szDescription[WSADESCRIPTION_LEN + 1];
char szSystemStatus[WSASYS_STATUS_LEN + 1];
unsigned short iMaxSockets;
unsigned short iMaxUdpDg;
char FAR * lpVendorInfo;
} WSADATA, * LPWSADATA;
wVersion -- 使用的winsock版本
wHighVersion -- 目前平台上可用的winsock的最高版本
szDescription, szSystemStatus -- 用作特殊用途,一般不常用
iMaxSockets, iMaxUdpDg -- 不用使用这两个字段。他们定义了最大的并发连接数和最大的udp datagram size。然而,要找出正确的这些值,可能还要参考协议本身中的一些限制。
lpVendorInfo -- 保留用,用来存放vendor-specific information.不用使用这个字段。
6. 各种windows平台支持的winsock版本:
附件1
可见,大部分windows都支持winsock 2
7. winsock 1的程序可以在支持winsock 2的windows上良好运行。实际上,在winsock 2的windows上,所有的winsock 1的请求都会被映射到winsock 2的dll中。微软的兼容工作做的还是不错的。如果我们在WSAStartup中申请了一个高于目前平台支持的winsock版本,WSAStartup 会失败,同时WSADATA中的wHighVersion中会存放该平台上支持的winsock的最高版本。
8. 调用WSACleanup用来结束一个winsock程序。
int WSACleanup(void);
这个函数会释放所有资源,关闭所有pending的请求等。实际上,就算我们的程序不调用这个函数,操作系统也会把这些资源回收,但是,一个良好的程序,必须调用这个函数。
9. 错误处理。前面说过了,大多数的winsock函数失败的时候,都会返回SOCKET_ERROR,使用WSAGetLastError能获得详细的错误 码,这些错误码都定义在winsock2.h, winsock.h中。有些函数例外,他们不返回SOCKET_ERROR而是其他的返回值。下面是一个使用WSAGetLastError函数的例子:
- Code: Select all
-
#include <winsock2.h>
void main(void)
{
WSADATA wsaData;
// Initialize Winsock version 2.2
if ((Ret = WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2), &wsaData)) != 0)
{
// NOTE: Since Winsock failed to load we cannot use
// WSAGetLastError to determine the specific error for
// why it failed. Instead we can rely on the return
// status of WSAStartup.
printf("WSAStartup failed with error %d\n", Ret);
return;
}
// Setup Winsock communication code here
// When your application is finished call WSACleanup
if (WSACleanup() == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("WSACleanup failed with error %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
}
}
10. Addressing a Protocol. 本节只介绍基于IP的协议,参考第三章有很多关于网络协议的东西。本节只介绍在winsock中定义一个IPv4的信息结构。定义这样的结构对于winsock中的bind等这样的函数来说是必须的。
- Code: Select all
-
struct sockaddr_in
{
short sin_family;
u_short sin_port;
struct in_addr sin_addr;
char sin_zero[8];
};
sockaddr_in其实是针对Internet,也就是TCP/IP的一个结构。在后面我们会看到,任何结构将来都会转换成SOCKADDR这个结构,有点类似SOCKADDR是基类,sockaddr_in这些都是SOCKADDR的派生类一样。
sin_family -- 必须设成AF_INET,表示我们要使用IP地址family
sin_port -- 指定端口,不过要考虑网络次序和主机次序的问题,下面会介绍
sin_addr -- 指定IP地址。其实是指定这个struct中的一个字段。IP地址也是以long的类型存放的,也要处理网络次序和主机次序的问题。微软提供了一个function来让我们把一个IP字符串转换成一个long型的数值。这个函数是:
- Code: Select all
-
unsigned long inet_addr(
const char FAR *cp
);
注意,调用了inet_addr函数之后生成的long,就不需要再做主机次序,网络次序的转换了。但是后面会看到,如果没用inet_addr,比如给出的IP地址是INADDR_ANY的话,还是要调用htonl函数的。
sin_zero -- 没有用,完全是放在这里为了和SOCKADDR的大小兼容
11. 主机次序和网络次序。这个问题的起源是因为在上述的结构中,我们需要指定一个数字类型的变量,比如port和long型的IP地址。由于数字是多字节的一 块内容,所以就有字节摆放顺序的问题。众所周知,数字类型的变量在不同的计算机(主机)中存放的次序是不一样的,有把高位字节存在前面,低位字节存在后面 的,也有反过来的。对于网络通讯来说,必需要把这种情况统一起来,否则这些关键的信息就会解析错误了。于是就有了所谓的主机次序和网络次序的相互转换了。
winsock中提供了一组函数用来做这个事情,下面的四个函数用来将主机次序转成网络次序:
- Code: Select all
-
u_long htonl(u_long hostlong);
int WSAHtonl(
SOCKET s,
u_long hostlong,
u_long FAR * lpnetlong
);
u_short htons(u_short hostshort);
int WSAHtons(
SOCKET s,
u_short hostshort,
u_short FAR * lpnetshort
);
带 l的是处理4字节的数,带s的是处理2字节的数。不带WSA的函数传入主机次序的数值,返回网络次序的数;带WSA的是把主机次序的数传入 hostlong, hostshort参数,处理后的网络次序的数被填充在lpnetlong, lpnetshort指针指向的变量中。
以下四个函数从网络次序转成主机次序:
- Code: Select all
-
u_long ntohl(u_long netlong);
int WSANtohl(
SOCKET s,
u_long netlong,
u_long FAR * lphostlong
);
u_short ntohs(u_short netshort);
int WSANtohs(
SOCKET s,
u_short netshort,
u_short FAR * lphostshort
);
12. 给出一个例子用来示范怎么创建这么一个sockadd_in的东西:
- Code: Select all
-
SOCKADDR_IN InternetAddr;
INT nPortId = 5150;
InternetAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
// Convert the proposed dotted Internet address 136.149.3.29
// to a four-byte integer, and assign it to sin_addr
InternetAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("136.149.3.29");
// The nPortId variable is stored in host-byte order. Convert
// nPortId to network-byte order, and assign it to sin_port.
InternetAddr.sin_port = htons(nPortId);
第三章会讲述如何在填写IP地址的时候,填写一个域名,以及winsock中包含的一些域名和IP地址互转换的函数。
13. 创建一个socket。socket是网络通讯程序中必须的一个数据结构,他不同于文件描述符,他有单独的数据类型定义-SOCKET。创建一个 socket可以调用socket方法或WSASocket。这里我们用socket函数来举例,后面会详细介绍这些方法。
- Code: Select all
-
SOCKET socket (
int af,
int type,
int protocol
);
af -- 定义协议的address family,对于IPv4,当然是AF_INET
type -- 定义socket类型。对于TCP,填写SOCK_STREAM,对于UDP,填写SOCK_DGRAM
protocol -- 定义协议。如果我们在af或type中定义了多种类型的话,这里可以定义一个协议的组合。对于TCP,设置此项为IPPROTO_TCP,对于UDP,设置为IPPROTO_UDP
14. 基于TCP的winsock代码编写例子(包含server端和client端程序)。服务器端的程序需要依次调用如下函 数:socket/WSASocket, bind, listen, accept/WSAAccept,注意,本节中没有说bind, listen有对应的WSA的函数
bind:
示例代码:
这里IP地址指定成INADDR_ANY,表示绑定在本机,也就是说,如果本机有多块网卡的话,往任何一块网卡上指定的端口上发送的数据都能被上述程序得到。
bind 的错误处理。bind失败,返回SOCKET_ERROR,错误码是WSAEADDRINUSE,表示本机有另外一个进程已经使用了我们指定的IP地址和 端口或者是这个IP地址或端口处于TIME_WAIT状态(TIME_WAIT状态在下面会描述);此外,如果我们bind了一次之后又再次往同样的端 口,IP bind,那错误码是WSAEFAULT。
listen:
backlog -- 处理并发请求的数量。比如设成2,如果同时有三个并发请求过来,那么前两个会放入排队队列,第三个请求就会被拒绝,同时返回 WSAECONNREFUSED错误。一旦一个请求被accept处理之后,排队队列中就会清除这个请求,新的请求就可以进来了。backlog的最大值 和协议有关系,没有一个确切的方法可以给出一个具体的最大值,如果我们指定的backlog值超过了允许的范围,函数会帮我们把这个值设成最大允许的值。
listen的错误处理,一般返回WSAEINVAL,表示在listen之前没有调用bind。
accept:
accept 中除了socket之外的两个参数是OUT类型的,也就是accept会填写这两个参数。accept会取出排队队列中的第一个request,然后处 理,addr中会存放client的IP地址,端口等信息,addrlen中存放的是addr结构的大小。此外,accept返回一个SOCKET变量, 利用这个socket变量,server端程序就能和client端程序进行send/recv这样的操作了。
accept的错误处理, 出错时,accept的返回值是INVALID_SOCKET,错误码有WSAEWOULDBLOCK,当我们使用非阻塞的non-block的 listen方法,而当前队列中没有可服务的request的时候,会产生这个错误码。WSAAccept方法是winsock 2中的方法,这个方法比accept增强了一些特性,比如可以给定一个condition,这个condition返回true的时候才accept一个 connection。具体看第10章
下面给出示例代码,这段代码是核心代码演示,不一定完整,而且这段代码只会accept一次就退出了,正常程序应该有个while循环:
bind:
- Code: Select all
-
int bind(
SOCKET s,
const struct sockaddr FAR* name,
int namelen
);
示例代码:
- Code: Select all
-
SOCKET s;
SOCKADDR_IN tcpaddr;
int port = 5150;
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
tcpaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
tcpaddr.sin_port = htons(port);
tcpaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
bind(s, (SOCKADDR *)&tcpaddr, sizeof(tcpaddr));
这里IP地址指定成INADDR_ANY,表示绑定在本机,也就是说,如果本机有多块网卡的话,往任何一块网卡上指定的端口上发送的数据都能被上述程序得到。
bind 的错误处理。bind失败,返回SOCKET_ERROR,错误码是WSAEADDRINUSE,表示本机有另外一个进程已经使用了我们指定的IP地址和 端口或者是这个IP地址或端口处于TIME_WAIT状态(TIME_WAIT状态在下面会描述);此外,如果我们bind了一次之后又再次往同样的端 口,IP bind,那错误码是WSAEFAULT。
listen:
- Code: Select all
-
int listen(
SOCKET s,
int backlog
);
backlog -- 处理并发请求的数量。比如设成2,如果同时有三个并发请求过来,那么前两个会放入排队队列,第三个请求就会被拒绝,同时返回 WSAECONNREFUSED错误。一旦一个请求被accept处理之后,排队队列中就会清除这个请求,新的请求就可以进来了。backlog的最大值 和协议有关系,没有一个确切的方法可以给出一个具体的最大值,如果我们指定的backlog值超过了允许的范围,函数会帮我们把这个值设成最大允许的值。
listen的错误处理,一般返回WSAEINVAL,表示在listen之前没有调用bind。
accept:
- Code: Select all
-
SOCKET accept(
SOCKET s,
struct sockaddr FAR* addr,
int FAR* addrlen
);
accept 中除了socket之外的两个参数是OUT类型的,也就是accept会填写这两个参数。accept会取出排队队列中的第一个request,然后处 理,addr中会存放client的IP地址,端口等信息,addrlen中存放的是addr结构的大小。此外,accept返回一个SOCKET变量, 利用这个socket变量,server端程序就能和client端程序进行send/recv这样的操作了。
accept的错误处理, 出错时,accept的返回值是INVALID_SOCKET,错误码有WSAEWOULDBLOCK,当我们使用非阻塞的non-block的 listen方法,而当前队列中没有可服务的request的时候,会产生这个错误码。WSAAccept方法是winsock 2中的方法,这个方法比accept增强了一些特性,比如可以给定一个condition,这个condition返回true的时候才accept一个 connection。具体看第10章
下面给出示例代码,这段代码是核心代码演示,不一定完整,而且这段代码只会accept一次就退出了,正常程序应该有个while循环:
- Code: Select all
-
#include <winsock2.h>
void main(void)
{
WSADATA wsaData;
SOCKET ListeningSocket;
SOCKET NewConnection;
SOCKADDR_IN ServerAddr;
SOCKADDR_IN ClientAddr;
int Port = 5150;
// Initialize Winsock version 2.2
WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2), &wsaData);
// Create a new socket to listen for client connections.
ListeningSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
// Set up a SOCKADDR_IN structure that will tell bind that we
// want to listen for connections on all interfaces using port
// 5150. Notice how we convert the Port variable from host byte
// order to network byte order.
ServerAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
ServerAddr.sin_port = htons(Port);
ServerAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
// Associate the address information with the socket using bind.
bind(ListeningSocket, (SOCKADDR *)&ServerAddr,
sizeof(ServerAddr));
// Listen for client connections. We used a backlog of 5, which
// is normal for many applications.
listen(ListeningSocket, 5);
// Accept a new connection when one arrives.
NewConnection = accept(ListeningSocket, (SOCKADDR *)
&ClientAddr,&ClientAddrLen));
// At this point you can do two things with these sockets. Wait
// for more connections by calling accept again on ListeningSocket
// and start sending or receiving data on NewConnection. We will
// describe how to send and receive data later in the chapter.
// When you are finished sending and receiving data on the
// NewConnection socket and are finished accepting new connections
// on ListeningSocket, you should close the sockets using the
// closesocket API. We will describe socket closure later in the
// chapter.
closesocket(NewConnection);
closesocket(ListeningSocket);
// When your application is finished handling the connections,
// call WSACleanup.
WSACleanup();
}
15. 下面讲述基于Client的程序如何写。相比server端的程序,client端的程序简单很多。在此之前,书中补充了一些TCP/IP中的知识,我觉得在这里摘录下来很有必要。
16. TCP States.
每个TCP socket的初始状态都是CLOSED状态。当一个client初始化一个连接时,他向server发送一个SYN的packet,然后将自己 socket的状态设成SYN_SENT;server收到SYN,发送SYN-ACK;client受到SYN-ACK,发送ACK,此时client 的socket的状态变成ESTABLISHED。如果server没有发送SYN-ACK,那么client的socket在timeout之后自动变 回CLOSED状态。
看server这边。当一个server处于监听状态时,他的socket状态是LISTEN;当收到一个client的SYN后,server 反馈SYN-ACK,同时socket的状态变成SYN_RCVD;最后client反馈ACK,此时server的socket状态变成 ESTABLISHED
下面来看在关闭连接的时候SOCKET的变化状态。首先一个连接的关闭分成两种-主动关闭和被动关闭。所谓主动关闭就是由自身发起的一个连接关 闭。当主动关闭开始时,我方发送一个FIN给对方,同时socket状态变成FIN_WAIT_1,这个动作一般是我们在调用shutdown或 closesocket的时候产生;对方回馈一个ACK,此时我方的socket状态变成FIN_WAIT_2;如果对方也关闭了连接,那么我方会收到对 方的FIN,此时我方反馈一个ACK,同时我方将socket的状态置成TIME_WAIT。
TIME_WAIT状态也称为2MSL状态。MSL是Maximum Segment Lifetime的意思,他用来表示一个packet能在网络上的存活时间。当一个程序进入TIME_WAIT状态的时候,他将保持两倍的MSL时间,保 持这个时间是为了保证TCP能发送FIN,ACK这些packet能正确被收发。当2MSL时间到达后,socket将进入CLOSED状态。
前面我们在讲述bind的时候提到,bind失败有一种可能就是socket处于TIME_WAIT状态,当socket处于TIME_WAIT 状态的时候,我方的IP地址和端口,以及对方的IP地址和端口,都处于不可用的状态,这称为一对socket。很多TCP的实现库是不允许在 TIME_WAIT的时候创建socket的,bind的,微软的winsock在这方面做了一些小的工作,他允许我们使用socket option SO_REUSEADDR来使用一个已经处于TIME_WAIT状态的socket,具体在第七章讨论。
OK,回到前面的连接关闭上来。主动关闭还有两种可能的情况。当我方发送FIN后,此时对方不返回ACK,而是也返回FIN,此时我方发送一个 ACK给对方,同时将自己socket的状态置成CLOSING状态;然后我方收到对方的ACK,我方将socket的状态置成TIME_WAIT。第三 种主动关闭的情况:我方发送FIN;对方发送FIN-ACK;我方发送ACK,同时将socket状态立即置成TIME_WAIT
现在讨论被动关闭,被动关闭其实是收到了对方正在关闭连接的notify,此时自己关闭连接的流程:我方收到对方的FIN;我方回馈ACK,同时 将自己socket的状态置成CLOSE_WAIT状态;然后我方发送FIN给对方,同时将自己socket的状态置成LAST_ACK;我方收到对方的 ACK,socket状态变成CLOSED
上面有关主动关闭和被动关闭的描述请参考下图:
附件1
17. 回头来讲client端的winsock程序写法,关键函数只有一个:connect
name是sockaddr的结构,里面填写服务器的IP地址和端口号,namelen是结构的长度。
connect的出错:如果服务器上没有启动服务器端的程序,connect设置出错码WSAECONNREFUSED;如果connect设置了出错码WSAETIMEDOUT,那可能是网络不通。
下面演示了一个客户端程序:
18. 数据传输。关键函数是send, WSASend, recv, WSARecv,不要和sendto, recvfrom, WSASendTo, WSARecvFrom混淆,这四个是UDP的数据传输函数,由于UDP实现不需要建立连接,所以每次发送数据都要指定对方的地址和端口,收数据也是一 样,所以他们的函数才有To, From这样的后缀。
send, WSASend, recv, WSARecv这些函数的出错返回值都是SOCKET_ERROR。最常见的出错码有WSAECONNABORTED, WSAECONNRESET,这两个出错码一般都指示数据超时或对方关闭了连接。还有一个出错码WSAEWOULDBLOCK,在我们使用异步I/O的时 候会发生,第五章会介绍。
send:
buf -- 存放发送数据的buffer
len -- buffer的大小
flags -- 设为0,表示没有flag;还可设为MSG_DONTROUTE, MSG_OOB,这些flags可以用或 | 符号合并使用。MSG_DONTROUTE表示发送的数据包不要被路由,当然,这需要底层协议的支持,协议不支持,设置这个flag将被 ignore;MSG_OOB表示发送一个Out Of Band的数据,下面会专门介绍OOB
正常情况下,send函数返回实际发送的 数据数量(字节数)。否则,返回SOCKET_ERROR,出错码有WSAECO-NNABORTED,表示协议出错或 timeout;WSAECONNRESET,对方关闭了连接或对方程序以外终止;WSAETIMEDOUT,网络不通。
WSASend:
带WSA的收发函数和不带WSA的都差不多是这样的一个原型。
lpBuffers -- 指向WSABUF的指针。这个指针可以指向一个WSABUF,也可以指向一批WSABUF,比如一个WSABUF的数组。
dwBufferCount -- WSABUF的数量。不是字节数哦,是一共有多少个WSABUF
lpNumberOfBytesSent -- 实际发送的字节数,由WSASend函数填写
dwFlags -- 和send函数的flag一样
lpOverlapped, lpCompletionRoutine -- 用于overlapped I/O,第五章介绍
WSASend正常返回0,否则返回SOCKET_ERROR
在 这里我们可能会想为什么WSASend中要让我们可以设置发送一批WSABUF呢?这是基于scatter-gather I/O的思想。比如我们在实际程序中,经常会将我们的消息这样定义:前4个字节用于命令字;中间4个字节用于实际数据长度;最后N个字节存放具体数据。这 样就有了三段的数据,有了WSASend之后,我们可以使用三个WSABUF来存放这三块数据,然后用WSASend一起发送出去,而对方使用 WSARecv也可以一并接受下来,这就是scatter-gather I/O的想法,也就是说,虽然我们提供了多个buffer,但是使用这种模式的时候,函数就把这些buffer当成连续的数据来处理。以前没有这个,我们 要手动把三块buffer add成一个,然后发送,收的时候也是收到整个数据,然后一块一块拆下来。
19. Out of Band Data. 这里介绍一下OOB数据的背景知识。当一个应用在一个流式的socket上(比如TCP)需要发送一个比普通数据重要的数据的时候,就可以使用OOB。从理论上来说,对方可以在一个独立的通道中接受并处理OOB数据。
在 TCP中,OOB data的实现是通过设置一个urgent 1-bit marker(called URG),和在TCP头增加一个16位长度的指针来实现的。通过这个指针,就可以寻找到OOB数据。我们可以使用函数ioctlsocket,配合 SIOCATMARK option来检查数据中是否包含OOB data,第七章会讨论这个问题。
OOB数据可以被包含在一个普通的数据包中,也可以单独封装在一个数据包中,Winsock对这两种情况都有API的封装,第七章将讨论这个问题。
Telnet和Rlogin这样的程序使用了OOB数据。
20. WSASendDisconnect函数:
这 个函数能graceful的关闭一个connection,同时发送disconnect data。目前还没有哪个transport provider支持disconnect data,因为关闭了connection,就不能再发送数据了,微软的winsock支持disconnect data,lpOutboundDisconnectData存放的就是我们想发送的disconnect data。graceful的关闭一个connection,其实就类似使用shutdown函数(带上SD_SEND参数),下面会讲到 shutdown函数。
21. recv, WSARecv:
buf, len -- 接受数据的缓冲区和大小
flags -- 0, 表示无flag;还可设置成MSG_PEEK或MSG_OOB或很多flag的组合。MSG_PEEK表示窥视接受到的数据,也就是说,仅仅查看而已,数 据将不会从系统的网络接受缓冲区中除掉。我们都知道,无论是send,还是recv,被操作的数据都需要从用户缓冲区拷贝到系统缓冲区然后发送,或是从系 统缓冲区拷贝到用户缓冲区(recv的时候)。MSG_PEEK设置了之后,数据将不会从系统缓冲区被移除,这是一个不好的东西,因为这样会减少系统缓冲 区接受数据的能力,从而TCP将不得不减小windows的大小(TCP中的window概念在学网络的时候接触过)来告知对方,我方的接受能力正在减 小。
题外话:在使用message-based或datagram-based 的协议中(比如UDP),recv函数会产生WSAEMSGSIZE这样的错误,这表示接受缓冲区过小,无法装下所有的数据。但是在TCP中,不会碰到这 样的情况,因为TCP是有连接的通讯方式,一般我们的程序都会循环取数据,直到所有的数据都取完,在没有取完之前,数据会被cache或resend,从 而保证我们接受到所有的数据。
和 WSASend一样,我们可以设置多个WSABUF来接受数据。这里需要提的是lpFlags,这里注意到,这个flags是一个指针,不是 WSASend中的一个DWORD,这表示这个flag有可能会被WSARecv函数所修改。为什么要这么做呢?这是因为在WSARecv中,有个 MSG_PARTIAL flag的存在。MSG_PARTIAL这个flag只能用于message-based的协议,而且这个协议还要支持MSG Partial,比如AppleTalk协议。当我们调用在WSARecv的时候,设置了MSG_PARTIAL的话,这表示本次recv的动作要尽可能 快的结束,因为我们只需要接受一部分的数据。如果我们在调用WSARecv的时候,没有设置MSG_PARTIAL,但是在WSARecv返回的时候,我 们检查flag,发现WSARecv设置了MSG_PARTIAL这个flag,这表示本次接受的数据只是整个message中的一部分,我们应该继续接 受数据,直至MSG_PARTIAL flag消息,这就表示整个消息接受完了。
lpOverlapped, lpCompletionRoutine -- 第五章介绍,用于overlapped I/O
22. WSARecvDisconnect
和WSASendDisconnect一样,用来接受disconnect data
23. 下面来看流式协议(比如TCP)下,send和recv的例子代码。和message, datagram based的协议不同,TCP有连接,有数据传输安全保证,所以我们应该用循环来保证所有的数据都被正确发送和接受。而象UDP这样的协议,在发送和接受 的时候,都必须保证buffer足够大,能装下数据,否则多余的数据就会被截断,再也无法找回。
send数据的例子:
recv的例子:
24. shutdown, closesocket
shutdown的做法其实就是一种graceful关闭连接的方法。就好比我们在关闭连接的时候要通知对方一下一样(参考TCP states一节)。how这个参数有几种选择:SD_SEND, SD_RECEIVE, SD_BOTH。使用SD_SEND,表示我方程序不再发送数据了;使用SD_RECEIVE,表示我方不再接受数据了。使用SD_SEND调用 shutdown,功能类似WSASendDisconnect函数前半部分的工作(WSASendDisconnect接着还会发送 disconnect数据)。SD_RECEIVE类似WSARecvDisconnect
shutdown函数只需要用于那些有连接的协议。对于UDP这样的协议,本身没有连接的概念,所以不需要调用shutdown,直接调用closesocket即可:
int closesocket (SOCKET s);
closesocket用来释放所有和该socket相关的资源。对于一个已经close的socket而言,调用closesocket,会产 生WSAENOTSOCK错误码。closesocket没有一个双方协商关闭连接的过程,这是shutdown做的,closesocket仅仅是释放 资源而已。不要和WSACleanup函数混淆,这个函数是用来卸载winsock的,和WSAStartup配对使用。
16. TCP States.
每个TCP socket的初始状态都是CLOSED状态。当一个client初始化一个连接时,他向server发送一个SYN的packet,然后将自己 socket的状态设成SYN_SENT;server收到SYN,发送SYN-ACK;client受到SYN-ACK,发送ACK,此时client 的socket的状态变成ESTABLISHED。如果server没有发送SYN-ACK,那么client的socket在timeout之后自动变 回CLOSED状态。
看server这边。当一个server处于监听状态时,他的socket状态是LISTEN;当收到一个client的SYN后,server 反馈SYN-ACK,同时socket的状态变成SYN_RCVD;最后client反馈ACK,此时server的socket状态变成 ESTABLISHED
下面来看在关闭连接的时候SOCKET的变化状态。首先一个连接的关闭分成两种-主动关闭和被动关闭。所谓主动关闭就是由自身发起的一个连接关 闭。当主动关闭开始时,我方发送一个FIN给对方,同时socket状态变成FIN_WAIT_1,这个动作一般是我们在调用shutdown或 closesocket的时候产生;对方回馈一个ACK,此时我方的socket状态变成FIN_WAIT_2;如果对方也关闭了连接,那么我方会收到对 方的FIN,此时我方反馈一个ACK,同时我方将socket的状态置成TIME_WAIT。
TIME_WAIT状态也称为2MSL状态。MSL是Maximum Segment Lifetime的意思,他用来表示一个packet能在网络上的存活时间。当一个程序进入TIME_WAIT状态的时候,他将保持两倍的MSL时间,保 持这个时间是为了保证TCP能发送FIN,ACK这些packet能正确被收发。当2MSL时间到达后,socket将进入CLOSED状态。
前面我们在讲述bind的时候提到,bind失败有一种可能就是socket处于TIME_WAIT状态,当socket处于TIME_WAIT 状态的时候,我方的IP地址和端口,以及对方的IP地址和端口,都处于不可用的状态,这称为一对socket。很多TCP的实现库是不允许在 TIME_WAIT的时候创建socket的,bind的,微软的winsock在这方面做了一些小的工作,他允许我们使用socket option SO_REUSEADDR来使用一个已经处于TIME_WAIT状态的socket,具体在第七章讨论。
OK,回到前面的连接关闭上来。主动关闭还有两种可能的情况。当我方发送FIN后,此时对方不返回ACK,而是也返回FIN,此时我方发送一个 ACK给对方,同时将自己socket的状态置成CLOSING状态;然后我方收到对方的ACK,我方将socket的状态置成TIME_WAIT。第三 种主动关闭的情况:我方发送FIN;对方发送FIN-ACK;我方发送ACK,同时将socket状态立即置成TIME_WAIT
现在讨论被动关闭,被动关闭其实是收到了对方正在关闭连接的notify,此时自己关闭连接的流程:我方收到对方的FIN;我方回馈ACK,同时 将自己socket的状态置成CLOSE_WAIT状态;然后我方发送FIN给对方,同时将自己socket的状态置成LAST_ACK;我方收到对方的 ACK,socket状态变成CLOSED
上面有关主动关闭和被动关闭的描述请参考下图:
附件1
17. 回头来讲client端的winsock程序写法,关键函数只有一个:connect
- Code: Select all
-
int connect(
SOCKET s,
const struct sockaddr FAR* name,
int namelen
);
name是sockaddr的结构,里面填写服务器的IP地址和端口号,namelen是结构的长度。
connect的出错:如果服务器上没有启动服务器端的程序,connect设置出错码WSAECONNREFUSED;如果connect设置了出错码WSAETIMEDOUT,那可能是网络不通。
下面演示了一个客户端程序:
- Code: Select all
-
#include <winsock2.h>
void main(void)
{
WSADATA wsaData;
SOCKET s;
SOCKADDR_IN ServerAddr;
int Port = 5150;
// Initialize Winsock version 2.2
WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2), &wsaData);
// Create a new socket to make a client connection.
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
// Set up a SOCKADDR_IN structure that will be used to connect
// to a listening server on port 5150. For demonstration
// purposes, let's assume our server's IP address is 136.149.3.29.
// Obviously, you will want to prompt the user for an IP address
// and fill in this field with the user's data.
ServerAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
ServerAddr.sin_port = htons(Port);
ServerAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("136.149.3.29");
// Make a connection to the server with socket s.
connect(s, (SOCKADDR *) &ServerAddr, sizeof(ServerAddr));
// At this point you can start sending or receiving data on
// the socket s. We will describe sending and receiving data
// later in the chapter.
// When you are finished sending and receiving data on socket s,
// you should close the socket using the closesocket API. We will
// describe socket closure later in the chapter.
closesocket(s);
// When your application is finished handling the connection, call
// WSACleanup.
WSACleanup();
}
18. 数据传输。关键函数是send, WSASend, recv, WSARecv,不要和sendto, recvfrom, WSASendTo, WSARecvFrom混淆,这四个是UDP的数据传输函数,由于UDP实现不需要建立连接,所以每次发送数据都要指定对方的地址和端口,收数据也是一 样,所以他们的函数才有To, From这样的后缀。
send, WSASend, recv, WSARecv这些函数的出错返回值都是SOCKET_ERROR。最常见的出错码有WSAECONNABORTED, WSAECONNRESET,这两个出错码一般都指示数据超时或对方关闭了连接。还有一个出错码WSAEWOULDBLOCK,在我们使用异步I/O的时 候会发生,第五章会介绍。
send:
- Code: Select all
-
int send(
SOCKET s,
const char FAR * buf,
int len,
int flags
);
buf -- 存放发送数据的buffer
len -- buffer的大小
flags -- 设为0,表示没有flag;还可设为MSG_DONTROUTE, MSG_OOB,这些flags可以用或 | 符号合并使用。MSG_DONTROUTE表示发送的数据包不要被路由,当然,这需要底层协议的支持,协议不支持,设置这个flag将被 ignore;MSG_OOB表示发送一个Out Of Band的数据,下面会专门介绍OOB
正常情况下,send函数返回实际发送的 数据数量(字节数)。否则,返回SOCKET_ERROR,出错码有WSAECO-NNABORTED,表示协议出错或 timeout;WSAECONNRESET,对方关闭了连接或对方程序以外终止;WSAETIMEDOUT,网络不通。
WSASend:
- Code: Select all
-
int WSASend(
SOCKET s,
LPWSABUF lpBuffers,
DWORD dwBufferCount,
LPDWORD lpNumberOfBytesSent,
DWORD dwFlags,
LPWSAOVERLAPPED lpOverlapped,
LPWSAOVERLAPPED_COMPLETION_ROUTINE lpCompletionRoutine
);
带WSA的收发函数和不带WSA的都差不多是这样的一个原型。
lpBuffers -- 指向WSABUF的指针。这个指针可以指向一个WSABUF,也可以指向一批WSABUF,比如一个WSABUF的数组。
dwBufferCount -- WSABUF的数量。不是字节数哦,是一共有多少个WSABUF
lpNumberOfBytesSent -- 实际发送的字节数,由WSASend函数填写
dwFlags -- 和send函数的flag一样
lpOverlapped, lpCompletionRoutine -- 用于overlapped I/O,第五章介绍
WSASend正常返回0,否则返回SOCKET_ERROR
在 这里我们可能会想为什么WSASend中要让我们可以设置发送一批WSABUF呢?这是基于scatter-gather I/O的思想。比如我们在实际程序中,经常会将我们的消息这样定义:前4个字节用于命令字;中间4个字节用于实际数据长度;最后N个字节存放具体数据。这 样就有了三段的数据,有了WSASend之后,我们可以使用三个WSABUF来存放这三块数据,然后用WSASend一起发送出去,而对方使用 WSARecv也可以一并接受下来,这就是scatter-gather I/O的想法,也就是说,虽然我们提供了多个buffer,但是使用这种模式的时候,函数就把这些buffer当成连续的数据来处理。以前没有这个,我们 要手动把三块buffer add成一个,然后发送,收的时候也是收到整个数据,然后一块一块拆下来。
19. Out of Band Data. 这里介绍一下OOB数据的背景知识。当一个应用在一个流式的socket上(比如TCP)需要发送一个比普通数据重要的数据的时候,就可以使用OOB。从理论上来说,对方可以在一个独立的通道中接受并处理OOB数据。
在 TCP中,OOB data的实现是通过设置一个urgent 1-bit marker(called URG),和在TCP头增加一个16位长度的指针来实现的。通过这个指针,就可以寻找到OOB数据。我们可以使用函数ioctlsocket,配合 SIOCATMARK option来检查数据中是否包含OOB data,第七章会讨论这个问题。
OOB数据可以被包含在一个普通的数据包中,也可以单独封装在一个数据包中,Winsock对这两种情况都有API的封装,第七章将讨论这个问题。
Telnet和Rlogin这样的程序使用了OOB数据。
20. WSASendDisconnect函数:
- Code: Select all
-
int WSASendDisconnect (
SOCKET s,
LPWSABUF lpOutboundDisconnectData
);
这 个函数能graceful的关闭一个connection,同时发送disconnect data。目前还没有哪个transport provider支持disconnect data,因为关闭了connection,就不能再发送数据了,微软的winsock支持disconnect data,lpOutboundDisconnectData存放的就是我们想发送的disconnect data。graceful的关闭一个connection,其实就类似使用shutdown函数(带上SD_SEND参数),下面会讲到 shutdown函数。
21. recv, WSARecv:
- Code: Select all
-
int recv(
SOCKET s,
char FAR* buf,
int len,
int flags
);
buf, len -- 接受数据的缓冲区和大小
flags -- 0, 表示无flag;还可设置成MSG_PEEK或MSG_OOB或很多flag的组合。MSG_PEEK表示窥视接受到的数据,也就是说,仅仅查看而已,数 据将不会从系统的网络接受缓冲区中除掉。我们都知道,无论是send,还是recv,被操作的数据都需要从用户缓冲区拷贝到系统缓冲区然后发送,或是从系 统缓冲区拷贝到用户缓冲区(recv的时候)。MSG_PEEK设置了之后,数据将不会从系统缓冲区被移除,这是一个不好的东西,因为这样会减少系统缓冲 区接受数据的能力,从而TCP将不得不减小windows的大小(TCP中的window概念在学网络的时候接触过)来告知对方,我方的接受能力正在减 小。
题外话:在使用message-based或datagram-based 的协议中(比如UDP),recv函数会产生WSAEMSGSIZE这样的错误,这表示接受缓冲区过小,无法装下所有的数据。但是在TCP中,不会碰到这 样的情况,因为TCP是有连接的通讯方式,一般我们的程序都会循环取数据,直到所有的数据都取完,在没有取完之前,数据会被cache或resend,从 而保证我们接受到所有的数据。
- Code: Select all
-
int WSARecv(
SOCKET s,
LPWSABUF lpBuffers,
DWORD dwBufferCount,
LPDWORD lpNumberOfBytesRecvd,
LPDWORD lpFlags,
LPWSAOVERLAPPED lpOverlapped,
LPWSAOVERLAPPED_COMPLETION_ROUTINE lpCompletionRoutine
);
和 WSASend一样,我们可以设置多个WSABUF来接受数据。这里需要提的是lpFlags,这里注意到,这个flags是一个指针,不是 WSASend中的一个DWORD,这表示这个flag有可能会被WSARecv函数所修改。为什么要这么做呢?这是因为在WSARecv中,有个 MSG_PARTIAL flag的存在。MSG_PARTIAL这个flag只能用于message-based的协议,而且这个协议还要支持MSG Partial,比如AppleTalk协议。当我们调用在WSARecv的时候,设置了MSG_PARTIAL的话,这表示本次recv的动作要尽可能 快的结束,因为我们只需要接受一部分的数据。如果我们在调用WSARecv的时候,没有设置MSG_PARTIAL,但是在WSARecv返回的时候,我 们检查flag,发现WSARecv设置了MSG_PARTIAL这个flag,这表示本次接受的数据只是整个message中的一部分,我们应该继续接 受数据,直至MSG_PARTIAL flag消息,这就表示整个消息接受完了。
lpOverlapped, lpCompletionRoutine -- 第五章介绍,用于overlapped I/O
22. WSARecvDisconnect
- Code: Select all
-
int WSARecvDisconnect(
SOCKET s,
LPWSABUF lpInboundDisconnectData
);
和WSASendDisconnect一样,用来接受disconnect data
23. 下面来看流式协议(比如TCP)下,send和recv的例子代码。和message, datagram based的协议不同,TCP有连接,有数据传输安全保证,所以我们应该用循环来保证所有的数据都被正确发送和接受。而象UDP这样的协议,在发送和接受 的时候,都必须保证buffer足够大,能装下数据,否则多余的数据就会被截断,再也无法找回。
send数据的例子:
- Code: Select all
-
char sendbuff[2048];
int nBytes = 2048,
nLeft,
idx;
// Fill sendbuff with 2048 bytes of data
// Assume s is a valid, connected stream socket
nLeft = nBytes;
idx = 0;
while (nLeft > 0)
{
ret = send(s, &sendbuff[idx], nLeft, 0);
if (ret == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
// Error
}
nLeft -= ret;
idx += ret;
}
recv的例子:
- Code: Select all
-
char recvbuff[1024];
int ret,
nLeft,
idx;
nLeft = 512;
idx = 0;
while (nLeft > 0)
{
ret = recv(s, &recvbuff[idx], nLeft, 0);
if (ret == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
// Error
}
idx += ret;
nLeft -= ret;
}
24. shutdown, closesocket
- Code: Select all
-
int shutdown(
SOCKET s,
int how
);
shutdown的做法其实就是一种graceful关闭连接的方法。就好比我们在关闭连接的时候要通知对方一下一样(参考TCP states一节)。how这个参数有几种选择:SD_SEND, SD_RECEIVE, SD_BOTH。使用SD_SEND,表示我方程序不再发送数据了;使用SD_RECEIVE,表示我方不再接受数据了。使用SD_SEND调用 shutdown,功能类似WSASendDisconnect函数前半部分的工作(WSASendDisconnect接着还会发送 disconnect数据)。SD_RECEIVE类似WSARecvDisconnect
shutdown函数只需要用于那些有连接的协议。对于UDP这样的协议,本身没有连接的概念,所以不需要调用shutdown,直接调用closesocket即可:
int closesocket (SOCKET s);
closesocket用来释放所有和该socket相关的资源。对于一个已经close的socket而言,调用closesocket,会产 生WSAENOTSOCK错误码。closesocket没有一个双方协商关闭连接的过程,这是shutdown做的,closesocket仅仅是释放 资源而已。不要和WSACleanup函数混淆,这个函数是用来卸载winsock的,和WSAStartup配对使用。

25. 本节描述UDP的编程-Connectionless Communication. UDP简单多了,先来看server端的UDP程序。server端的UDP程序不需要调用listen和accept,直接socket,bind,然 后用recvfrom/WSARecvFrom即可。
buf, len -- 接受缓冲区和缓冲区大小
from, fromlen -- sockaddr结构和这个结构的大小。里面会由recvfrom来填写对方的sockaddr信息。
flags -- 0, MSG_OOB, MSG_PEEK
和WSARecv一样,不解释了。lpFlags可能取值0, MSG_OOB, MSG_PEEK, MSG_PARTIAL。含义都和WSARecv一样,本参数我们可以设定,WSARecvFrom函数也会修改这个参数。
一 个比较好玩的事情:winsock支持在UDP程序中,调用connect,建立一个逻辑意义上的“连接”,其实这个连接是不存在的,调用了 connect之后,我们就可以用recv,WSARecv了,这样做的唯一好处就是如果我们只需要和单一的host通信,可以用这种方法,这样以后收发 数据就不需要填对方的IP地址,端口这些东西了。如果我们要取消connect中指定的host绑定,再调用一次connect,host参数设成 INETADDR_ANY即可。
完整的receiver的程序:
26. UPD Sender
不解释了,send的时候也可以调用connect哦,和receive一样。
完整的sender程序:
27. 注意点。前面提过了,message-based, datagram-based的协议,在发送和接受数据的时候,需要注意buffer的大小。对于支持MSG_PARTIAL的协议,比如 AppleTalk,可以解决buffer不够大的问题,因为数据可以一部分一部分的取。
另外一个常见问题:在UDP sender程序中,如果我们调用了bind,会有什么效果呢?这里书中解释了一下,调用了bind之后,会在UDP的数据包中将sender的IP地址 和端口设置成我们bind的那些数据,但是实际数据在发送时,winsock还是会根据路由表,把数据从正确的网络端口上发送出去。并不是我们调用了 bind,UDP包就会一定从我们指定的IP地址上发送出去,bind仅仅是修改了sender UDP包中的数据而已。
联想到TCP编 程中,如果我们在client端程序的connect之前也调用了bind,会有什么效果呢?我估计效果是一样的,具体数据从哪个网卡出去,还是要根据路 由表来的,否则数据就有可能发送不到对方,bind应该是仅仅修改数据包中的source ip address/port而已。
- Code: Select all
-
int recvfrom(
SOCKET s,
char FAR* buf,
int len,
int flags,
struct sockaddr FAR* from,
int FAR* fromlen
);
buf, len -- 接受缓冲区和缓冲区大小
from, fromlen -- sockaddr结构和这个结构的大小。里面会由recvfrom来填写对方的sockaddr信息。
flags -- 0, MSG_OOB, MSG_PEEK
- Code: Select all
-
int WSARecvFrom(
SOCKET s,
LPWSABUF lpBuffers,
DWORD dwBufferCount,
LPDWORD lpNumberOfBytesRecvd,
LPDWORD lpFlags,
struct sockaddr FAR * lpFrom,
LPINT lpFromlen,
LPWSAOVERLAPPED lpOverlapped,
LPWSAOVERLAPPED_COMPLETION_ROUTINE lpCompletionRoutine
);
和WSARecv一样,不解释了。lpFlags可能取值0, MSG_OOB, MSG_PEEK, MSG_PARTIAL。含义都和WSARecv一样,本参数我们可以设定,WSARecvFrom函数也会修改这个参数。
一 个比较好玩的事情:winsock支持在UDP程序中,调用connect,建立一个逻辑意义上的“连接”,其实这个连接是不存在的,调用了 connect之后,我们就可以用recv,WSARecv了,这样做的唯一好处就是如果我们只需要和单一的host通信,可以用这种方法,这样以后收发 数据就不需要填对方的IP地址,端口这些东西了。如果我们要取消connect中指定的host绑定,再调用一次connect,host参数设成 INETADDR_ANY即可。
完整的receiver的程序:
- Code: Select all
-
#include <winsock2.h>
void main(void)
{
WSADATA wsaData;
SOCKET ReceivingSocket;
SOCKADDR_IN ReceiverAddr;
int Port = 5150;
char ReceiveBuf[1024];
int BufLength = 1024;
SOCKADDR_IN SenderAddr;
int SenderAddrSize = sizeof(SenderAddr);
// Initialize Winsock version 2.2
WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2), &wsaData);
// Create a new socket to receive datagrams on.
ReceivingSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
// Set up a SOCKADDR_IN structure that will tell bind that we
// want to receive datagrams from all interfaces using port
// 5150.
ReceiverAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
ReceiverAddr.sin_port = htons(Port);
ReceiverAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
// Associate the address information with the socket using bind.
bind(ReceivingSocket, (SOCKADDR *)&SenderAddr, sizeof(SenderAddr));
// At this point you can receive datagrams on your bound socket.
recvfrom(ReceivingSocket, ReceiveBuf, BufLength, 0,
(SOCKADDR *)&SenderAddr, &SenderAddrSize);
// When your application is finished receiving datagrams close
// the socket.
closesocket(ReceivingSocket);
// When your application is finished call WSACleanup.
WSACleanup();
}
26. UPD Sender
- Code: Select all
-
int sendto(
SOCKET s,
const char FAR * buf,
int len,
int flags,
const struct sockaddr FAR * to,
int tolen
);
int WSASendTo(
SOCKET s,
LPWSABUF lpBuffers,
DWORD dwBufferCount,
LPDWORD lpNumberOfBytesSent,
DWORD dwFlags,
const struct sockaddr FAR * lpTo,
int iToLen,
LPWSAOVERLAPPED lpOverlapped,
LPWSAOVERLAPPED_COMPLETION_ROUTINE lpCompletionRoutine
);
不解释了,send的时候也可以调用connect哦,和receive一样。
完整的sender程序:
- Code: Select all
-
#include <winsock2.h>
void main(void)
{
WSADATA wsaData;
SOCKET SendingSocket;
SOCKADDR_IN ReceiverAddr;
int Port = 5150;
char SendBuf[1024];
int BufLength = 1024;
// Initialize Winsock version 2.2
WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2), &wsaData);
// Create a new socket to receive datagrams on.
SendingSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
// Set up a SOCKADDR_IN structure that will identify who we
// will send datagrams to. For demonstration purposes, let's
// assume our receiver's IP address is 136.149.3.29 and waits
// for datagrams on port 5150.
ReceiverAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
ReceiverAddr.sin_port = htons(Port);
ReceiverAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("136.149.3.29");
// Send a datagram to the receiver.
sendto(SendingSocket, SendBuf, BufLength, 0,
(SOCKADDR *)&ReceiverAddr, sizeof(RecieverAddr));
// When your application is finished sending datagrams close
// the socket.
closesocket(SendingSocket);
// When your application is finished call WSACleanup.
WSACleanup();
}
27. 注意点。前面提过了,message-based, datagram-based的协议,在发送和接受数据的时候,需要注意buffer的大小。对于支持MSG_PARTIAL的协议,比如 AppleTalk,可以解决buffer不够大的问题,因为数据可以一部分一部分的取。
另外一个常见问题:在UDP sender程序中,如果我们调用了bind,会有什么效果呢?这里书中解释了一下,调用了bind之后,会在UDP的数据包中将sender的IP地址 和端口设置成我们bind的那些数据,但是实际数据在发送时,winsock还是会根据路由表,把数据从正确的网络端口上发送出去。并不是我们调用了 bind,UDP包就会一定从我们指定的IP地址上发送出去,bind仅仅是修改了sender UDP包中的数据而已。
联想到TCP编 程中,如果我们在client端程序的connect之前也调用了bind,会有什么效果呢?我估计效果是一样的,具体数据从哪个网卡出去,还是要根据路 由表来的,否则数据就有可能发送不到对方,bind应该是仅仅修改数据包中的source ip address/port而已。
28. 其他的一些实用的API。
这个函数可以用来取到对方的sockaddr信息。对于TCP,没什么好说的,因为TCP本身是有连接的;对于UDP,如果我们的UDP程序中调用了connect方法,那么该函数返回connect方法中定义的sockaddr信息,否则,该函数什么都得不到。
这个函数的作用和getpeername相反,用来取得本地的sockaddr信息。只有server端的程序调用这个函数才有用(客户端不需要bind)
这个函数用来复制一个socket,这个函数会填充WSAPROTOCOL_INFO结构,这个结构被填充后,可以用来传递给其他的进程,换句话 说,当多个进程需要同时用一个socket的时候,可以用这个函数复制socket,然后传递。对于线程,没有必要用这个函数,线程之间,可以直接传递 socket变量即可。
要注意的是,进程中取道的socket是一个被复制的socket,对该socket的操作会影响到其他进程,比如,在这个socket上设置的 一些状态变量(通过setsockopt函数),会影响到其他进程中的socket,但是,进程对socket调用closesocket函数,只会影响 到该进程。也就是说,要等所有的进程都调用了closesocket之后,这个socket才会被真正析构。
29. Windows CE上的winsock编程:
(1) windows CE只支持winsock 1.1
(2) windows CE只支持UNICODE,不过对于数据传送来说,无所谓了,因为网络传送都是以字节为操作对象的。
(3) windows CE中没有console application的概念,所以程序中只能出现winmain函数,不能出现main函数
- Code: Select all
-
int getpeername(
SOCKET s,
struct sockaddr FAR* name,
int FAR* namelen
);
这个函数可以用来取到对方的sockaddr信息。对于TCP,没什么好说的,因为TCP本身是有连接的;对于UDP,如果我们的UDP程序中调用了connect方法,那么该函数返回connect方法中定义的sockaddr信息,否则,该函数什么都得不到。
- Code: Select all
-
int getsockname(
SOCKET s,
struct sockaddr FAR* name,
int FAR* namelen
);
这个函数的作用和getpeername相反,用来取得本地的sockaddr信息。只有server端的程序调用这个函数才有用(客户端不需要bind)
- Code: Select all
-
int WSADuplicateSocket(
SOCKET s,
DWORD dwProcessId,
LPWSAPROTOCOL_INFO lpProtocolInfo
);
这个函数用来复制一个socket,这个函数会填充WSAPROTOCOL_INFO结构,这个结构被填充后,可以用来传递给其他的进程,换句话 说,当多个进程需要同时用一个socket的时候,可以用这个函数复制socket,然后传递。对于线程,没有必要用这个函数,线程之间,可以直接传递 socket变量即可。
要注意的是,进程中取道的socket是一个被复制的socket,对该socket的操作会影响到其他进程,比如,在这个socket上设置的 一些状态变量(通过setsockopt函数),会影响到其他进程中的socket,但是,进程对socket调用closesocket函数,只会影响 到该进程。也就是说,要等所有的进程都调用了closesocket之后,这个socket才会被真正析构。
29. Windows CE上的winsock编程:
(1) windows CE只支持winsock 1.1
(2) windows CE只支持UNICODE,不过对于数据传送来说,无所谓了,因为网络传送都是以字节为操作对象的。
(3) windows CE中没有console application的概念,所以程序中只能出现winmain函数,不能出现main函数