第十一部分_Struts2.1类型转换精析
首先,我们用第一种方式:继承ognl包下面的DefaultTypeConverter类,做一个类型转换:
新建一个input.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'input.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>请输入一个点的坐标(使用逗号分隔)</h1>
<form action="converterAction.action" method="post">
坐标:<input type="text" name="point" size="20"><br>
坐标2:<input type="text" name="point2" size="20"><br>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" size="20"><br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" size="20"/><br/>
出生日期:<input type="text" name="birthday" size="20"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>"
</form>
</body>
</html>
接下来编写处理类,在com.test.action包下建立一个PointAction类:
package com.test.action;
import java.util.Date;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.test.bean.Point;
public class PointAction extends ActionSupport
{
private Point point;
private Point point2;
private String username;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public Point getPoint2()
{
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2)
{
this.point2 = point2;
}
public Point getPoint()
{
return point;
}
public void setPoint(Point point)
{
this.point = point;
}
public String getUsername()
{
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username)
{
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday()
{
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date brithday)
{
this.birthday = brithday;
}
public String execute() throws Exception
{
return "success";
}
}
对于坐标的赋值,需要新建一个类,在com.test.bean包下新建一个类Point:
package com.test.bean;
public class Point
{
private int x;
private int y;
public int getX()
{
return x;
}
public void setX(int x)
{
this.x = x;
}
public int getY()
{
return y;
}
public void setY(int y)
{
this.y = y;
}
}
然后再com.test.converter包下面建立一个点坐标的转换类PointConverter(该类需要继承ognl包下面的DefaultTypeConverter类):
package com.test.converter;
import java.util.Map;
import ognl.DefaultTypeConverter;
import com.test.bean.Point;
public class PointConverter extends DefaultTypeConverter
{
@Override
public Object convertValue(Map context, Object value, Class toType)
{
if(Point.class==toType)
{
String[] str = (String[])value;
String firstValue = str[0];
String[] resultValue = firstValue.split(",");
Point point = new Point();
point.setX(Integer.parseInt(resultValue[0]));
point.setY(Integer.parseInt(resultValue[1]));
return point;
}
else if(String.class == toType)
{
Point point = (Point)value;
int x = point.getX();
int y = point.getY();
String result = "X: " + x + " Y: " + y;
return result;
}
return null;
}
}
此外,我们需要做一些相关的配置让struts2找到这个处理类,在com.test.action下建立一个文件:PointAction-conversion.properties,注意到这个文件在'-'后的字符都是固定的,只用前面是可以变化的,此外他必须和PointAction放在同一个包下面:
point=com.test.converter.PointConverter point2=com.test.converter.PointConverter
然后配置struts.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<package name="struts2" extends="struts-default">
<action name="helloworld" class="com.test.action.HelloWorld">
<result name="success">/helloworld.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="login" class="com.test.action.LoginAction">
<result name="success">/result.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="converterAction" class="com.test.action.PointAction">
<result name="success">/output.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
最后写一个output.jsp,输出有几种选择:JSP脚本;EL;Struts2的标签库。这里我们使用后者:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'output.jsp' starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
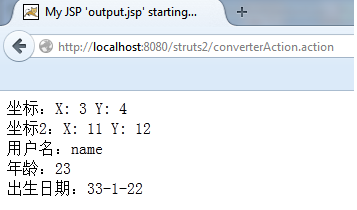
坐标:<s:property value="point"/><br/>
坐标2:<s:property value="point2"/><br/>
用户名:<s:property value="username"/><br>
年龄:<s:property value="age"/><br>
出生日期:<s:property value="birthday"/>
</body>
</html>
下面是运行结果的一个截图:
其次,我们用Struts2提供的StrutsTypeConverter(它也继承了ognl包下面的DefaultTypeConverter类,如何在MyEclipse中查看其源代码?MyEclipse中找到struts2-core-2.1.6.jar,展开,找到org.apach.struts2.util,找到旗下的Struts TypeConverter.class,打开,点击Attach Source->External Folder,找到struts-2.1.6的解压缩目录,找到目录下的src,在src下面展开core,展开main,main下面有一个java,选择java,确定,这样就把硬盘上的源码和MyEclipse关联起来了)抽象类:
在com.test.converter包下面新建一个类PointConverter2:
package com.test.converter;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.struts2.util.StrutsTypeConverter;
import com.test.bean.Point;
public class PointConverter2 extends StrutsTypeConverter
{
@Override
public Object convertFromString(Map context, String[] values, Class toClass)
{
Point point = new Point();
String value = values[0];
String[] result = value.split(",");
point.setX(Integer.parseInt(result[0]));
point.setY(Integer.parseInt(result[1]));
return point;
}
@Override
public String convertToString(Map context, Object o)
{
Point point = (Point)o;
int x =point.getX();
int y = point.getY();
String result = "x: " + x + " y: " + y;
return result;
}
}
修改PointAction-conversion.properties:
point=com.test.converter.PointConverter2 point2=com.test.converter.PointConverter2
浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/struts2/input.jsp,运行结果和用第一种方式实现的结果一样。
一个问题:如何进行批量处理(假如有100个point,难道要从point1定义到point100)?
我们假设有三个坐标表示"很多个坐标",在input.jsp中,注意到这些点的name属性都是相同的:
<form action="converterAction.action" method="post">
坐标:<input type="text" name="point" size="20"><br>
坐标2:<input type="text" name="point" size="20"><br>
坐标3:<input type="text" name="point" size="20"><br>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" size="20"><br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" size="20"/><br/>
出生日期:<input type="text" name="birthday" size="20"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>"
</form>
修改PointAction类:
package com.test.action;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.test.bean.Point;
public class PointAction extends ActionSupport
{
/*private Point point;
private Point point2;*/
private List<Point> point;
private String username;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public List<Point> getPoint()
{
return point;
}
public void setPoint(List<Point> point)
{
this.point = point;
}
/*public Point getPoint2()
{
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2)
{
this.point2 = point2;
}
public Point getPoint()
{
return point;
}
public void setPoint(Point point)
{
this.point = point;
}*/
public String getUsername()
{
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username)
{
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday()
{
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date brithday)
{
this.birthday = brithday;
}
public String execute() throws Exception
{
return "success";
}
}
然后编写转换类PointConverter3:
package com.test.converter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.struts2.util.StrutsTypeConverter;
import com.test.bean.Point;
public class PointConverter3 extends StrutsTypeConverter
{
@Override
public Object convertFromString(Map context, String[] values, Class toClass)
{
List<Point> list = new ArrayList<Point>();
for(String value : values)
{
String[] result = value.split(",");
Point point = new Point();
point.setX(Integer.parseInt(result[0]));
point.setY(Integer.parseInt(result[1]));
list.add(point);
}
return list;
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public String convertToString(Map context, Object o)
{
List<Point> list = (List<Point>)o;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int number = 0;
for(Point point : list)
{
number++;
int x = point.getX();
int y = point.getY();
// 这里不要使用以前PointConverter里那种直接拼接的方式,字符串太多,效率太低
sb.append(number).append(".x=").append(x).append(" y=").append(y).append(" ");
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
更改配置文件PointAction-conversion.properties:
#point=com.test.converter.PointConverter2 #point2=com.test.converter.PointConverter2 point=com.test.converter.PointConverter3
最后更改output.jsp:
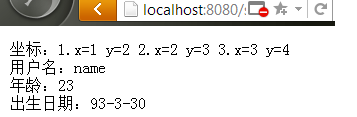
<body> 坐标:<s:property value="point"/><br/> 用户名:<s:property value="username"/><br> 年龄:<s:property value="age"/><br> 出生日期:<s:property value="birthday"/> </body>
下面是运行结果的一个截图:
此外,还用一种类型转换的方式(要求用户输入坐标分别在两个输入框中):
修改input.jsp:
<body>
<h1>请输入一个点的坐标(使用逗号分隔)</h1>
<form action="converterAction.action" method="post">
<!--
坐标:<input type="text" name="point" size="20"><br>
坐标2:<input type="text" name="point" size="20"><br>
坐标3:<input type="text" name="point" size="20"><br>
-->
x:<input type="text" name="point.x" size="20"/><br/>
y:<input type="text" name="point.y" size="20"/><br/>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" size="20"><br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" size="20"/><br/>
出生日期:<input type="text" name="birthday" size="20"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>"
</form>
PointAction类内容如下:
package com.test.action;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.test.bean.Point;
public class PointAction extends ActionSupport
{
private Point point;
private String username;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public Point getPoint()
{
return point;
}
public void setPoint(Point point)
{
this.point = point;
}
public String getUsername()
{
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username)
{
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday()
{
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date brithday)
{
this.birthday = brithday;
}
public String execute() throws Exception
{
// 两行测试语句,输出到控制台
System.out.println("X: " + point.getX());
System.out.println("Y: " + point.getY());
return "success";
}
}
更改Point类,重写其toString方法:
package com.test.bean;
public class Point
{
private int x;
private int y;
public int getX()
{
return x;
}
public void setX(int x)
{
this.x = x;
}
public int getY()
{
return y;
}
public void setY(int y)
{
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
String result = "x: " + x + " y: " + y;
return result;
}
}
注释掉PointAction-conversion.properties:
#point=com.test.converter.PointConverter2 #point2=com.test.converter.PointConverter2 #point=com.test.converter.PointConverter3
output.jsp如下:
<body> 坐标:<s:property value="point"/><br/> 用户名:<s:property value="username"/><br> 年龄:<s:property value="age"/><br> 出生日期:<s:property value="birthday"/> </body>
浏览器运行结果:
坐标:x: 1 y: 2
用户名:name
年龄:20
出生日期:93-3-30
此外,附送一个小知识点:如果我们的Action有多个,比如增删查改,那么类就有点多了,我们可以用同一个action来处理多个业务需求,如下修改PointAction(增加了一个test方法,struts2要求这个方法除了方法名和execute不同外,其他签名包括public修饰符、抛出异常等必须完全一致):
package com.test.action;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
import com.test.bean.Point;
public class PointAction extends ActionSupport
{
private Point point;
private String username;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public Point getPoint()
{
return point;
}
public void setPoint(Point point)
{
this.point = point;
}
public String getUsername()
{
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username)
{
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge()
{
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age)
{
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday()
{
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date brithday)
{
this.birthday = brithday;
}
public String test() throws Exception
{
System.out.println("test invoked");
System.out.println("X: " + point.getX());
System.out.println("Y: " + point.getY());
return SUCCESS; // 读过Action的源代码,就知道它定义了一个叫做SUCCESS的常量,其值就是“success”,因此这里的效果和 return "success"相同
}
public String execute() throws Exception
{
System.out.println("X: " + point.getX());
System.out.println("Y: " + point.getY());
return "success";
}
}
那么如何让我们的程序不执行默认的execute而是执行test方法呢?方法就是修改对应的struts.xml文件:
<action name="converterAction" class="com.test.action.PointAction" method="test"> <result name="success">/output.jsp</result> </action>
可以看到在原有的基础上我们为其增加了一个method属性,并将其赋值为test,这样浏览器中访问http://localhost:8080/struts2/input.jsp,输出依旧,回到控制台可以看到test invoked,说明我们的做法成功了。
补充:注意到上面程序中我给return SUCCESS语句添加了注释,提到了Action源码,其源码不在Struts2中,需要根据版本单独下载,比如我们这里是xwork-2.1.2,下载XWork源代码,找到对应的目录,比如我下载完成后,解压放到了struts2下面的D:\ProgramFiles\struts-2.1.6\xwork-2.1.2\src\java。MyEclipse中关联起来即可。
我们怎么知道这个类的呢?
因为我们的PointAction继承了ActionSupport,而ActionSupport实现了Action。
再补充:如果我们要转换的Point在除了PointAction中还有其他的Action类需要对同样地Point转换,我们是不是针对每一个Action都得在它对应的包下面写一个同样的配置文件呢?答案是不需要,struts考虑到这点,给我们提供了一个全局转换的功能,在src(不要定义在某个包里,否则这个全局转换就失效了)下面新建一个文件命名为xwork-conversion.properties,注意到这里每个字符都是固定的。内容如下:
#要转换的对象的类的全名=右边是转换器的名字 com.test.bean.Point=com.test.converter.PointConverter2
将input.jsp的坐标部分更改为:坐标:<input type="text" name="point" size="20"/><br/>
注释掉PointAction-conversion.properties,浏览器访问,输出结果正常,说明我们的配置是正确的。