【C013】ArcPy - 入门学习
加入字段:
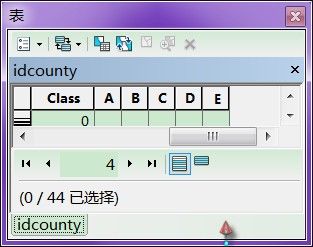
>>> arc = ['A','B','C','D','E']
>>> for i in range(5):
... arcpy.AddField_management("idcounty",arc[i],"TEXT")
给idcounty空间数据批量加入五个字段~
Buffer缓冲区
arcpy.Buffer_analysis("thermal","buffer","10 kilometers")
集合面积与几何长度
>>> arcpy.CalculateField_management("idcounty","ID_Area","!shape.area@squarekilometers!","PYTHON_9.3")
>>> arcpy.CalculateField_management("idcounty","ID_Area","!shape.length@kilometers!","PYTHON_9.3")
改变工作空间
>>> arcpy.env.workspace = "F:/Data"
>>> result = arcpy.Buffer_analysis("thermal","t_Buffer","10 kilometers")
>>> print result
F:/Data\t_Buffer.shp
返回要素数目
>>> result = arcpy.GetCount_management("idcounty")
>>> print result.getOutput(0)
44
调用工具的方法,就是工具的英文名称,去掉中间的空格,然后下划线,加入工具集的名称
字段名称:
>>> fieldList = arcpy.ListFields("idcounty")
>>> for field in fieldList:
... print field.aliasname + field.type
获取工作空间内所有要素类的字段名:
>>> fes = arcpy.ListFeatureClasses() >>> for fe in fes: ... print fe ... nl = '' ... fs = arcpy.ListFields(fe) ... for f in fs: ... nl = nl + ' ' + f.aliasName ... print nl
复制(工作空间中的可以直接写名字)
arcpy.Copy_management("i_Copy.shp","F:/Data/data/qq.shp")
列表的一些函数
>>> a = [1]*10 >>> for i in range(10): ... a[i] = i ... >>> a [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] >>> b = [1]*2 >>> b [1, 1] >>> a.extend(b) >>> >>> a [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1, 1] >>> a + b [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1, 1, 1, 1] >>> a [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1, 1] >>> a.count(1) 3 >>> a.append(100) >>> a [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1, 1, 100] >>> a.index(100) 12 >>> a.insert(0,'I') >>> a ['I', 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1, 1, 100] >>> a.pop(0) 'I' >>> a [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1, 1, 100] >>> a.remove(100) >>> a [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1, 1] >>> a.reverse() >>> a [1, 1, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0] >>> a.sort() >>> a [0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] >>>
Python数据类型
>>> type(3)
<type 'int'>
>>> type(3.0)
<type 'float'>
>>> type(1111111111)
<type 'int'>
>>> type(111111111111111)
<type 'long'>
>>> type(3.00000000)
<type 'float'>
>>> type(3.000000000000)
<type 'float'>
>>> type(1+2j)
<type 'complex'>
>>> type(True)
<type 'bool'>
>>> type('Alex')
<type 'str'>
>>> type([2,4])
<type 'list'>
>>> type((3,4))
<type 'tuple'>
>>>
详见:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4b5039210100e9ya.html
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------ ESRI培训 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
地图文件mxd
>>> mxd = arcpy.mapping.MapDocument("current")
>>> print mxd.filePath
F:\MY_OWN_WORK\Exercise\中国.mxd
数据框架data frame
>>> mxd = arcpy.mapping.MapDocument("current")
>>> dfs = arcpy.mapping.ListDataFrames(mxd)
>>> for df in dfs:
... print df.name
...
图层
Data Frame II
图层layer
>>> mxd = arcpy.mapping.MapDocument("current")
>>> df = arcpy.mapping.ListDataFrames(mxd)[0]
>>> ls = arcpy.mapping.ListLayers(df)
>>> for l in ls:
... print l
...
Cities (population > 5 Million)
Geogrid
Rivers
Lakes
Continents
Ocean
dataframe.extent = layers[0].getSelectedExtent()