listview优化
http://www.2cto.com/kf/201108/99928.html
项目用到ListView,由于要用到ImageView,图片源不是在资源里面的,没法使用资源ID,因此无法直接使用SimpleAdapter,要自己写一个Adapter。在使用ListView和Adapter需要注意以下几点:
1. Adapter.getView()
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent){...}
这个方法就是用来获得指定位置要显示的View。官网解释如下:
Get a View that displays the data at the specified position in the data set. You can either create a View manually or inflate it from an XML layout file.
当要显示一个View就调用一次这个方法。这个方法是ListView性能好坏的关键。方法中有个convertView,这个是Android在为我们而做的缓存机制。
ListView中每个item都是通过getView返回并显示的,假如item有很多个,那么重复创建这么多对象来显示显然是不合理。因此,Android提供了Recycler,将没有正在显示的item放进RecycleBin,然后在显示新视图时从RecycleBin中复用这个View。
Recycler的工作原理大致如下:
假设屏幕最多能看到11个item,那么当第1个item滚出屏幕,这个item的View进入RecycleBin中,第12个要出现前,通过getView从回收站(RecycleBin)中重用这个View,然后设置数据,而不必重新创建一个View。
我们用Android提供的APIDemos来验证这个过程:
先看关键代码:
Java代码
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
// A ViewHolder keeps references to children views to avoid unneccessary calls
// to findViewById() on each row.
ViewHolder holder;
// When convertView is not null, we can reuse it directly, there is no need
// to reinflate it. We only inflate a new View when the convertView supplied
// by ListView is null.
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.list_item_icon_text, null);
Log.v("tag", "positon " + position + " convertView is null, " + "new: " + convertView);
// Creates a ViewHolder and store references to the two children views
// we want to bind data to.
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.text = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.text);
holder.icon = (ImageView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.icon);
convertView.setTag(holder);
} else {
// Get the ViewHolder back to get fast access to the TextView
// and the ImageView.
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
Log.v("tag", "positon " + position + " convertView is not null, " + convertView);
}
// Bind the data efficiently with the holder.
holder.text.setText(DATA[position]);
holder.icon.setImageBitmap((position & 1) == 1 ? mIcon1 : mIcon2);
return convertView;
}
static class ViewHolder {
TextView text;
ImageView icon;
}
效果图:
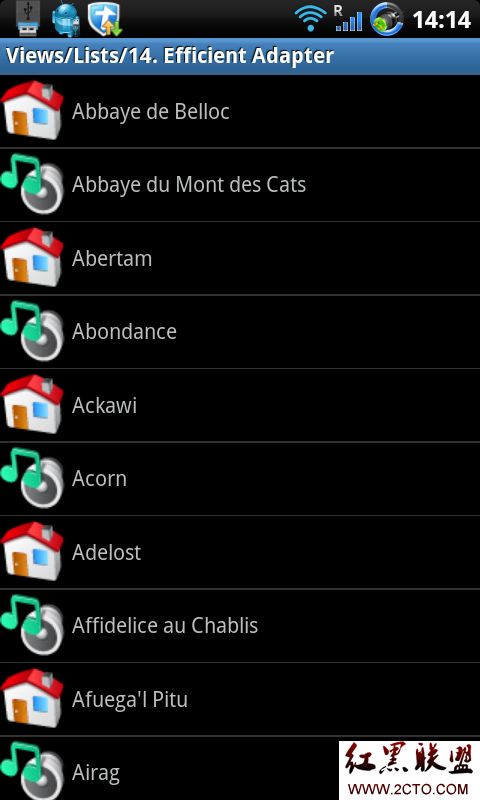
可以看到,一打开Activity,看到10个item.
我们看看Log信息:

可以看出,每次convertView都是null, 都是新建一个View来显示的。
当我们向下滑动,如下图,
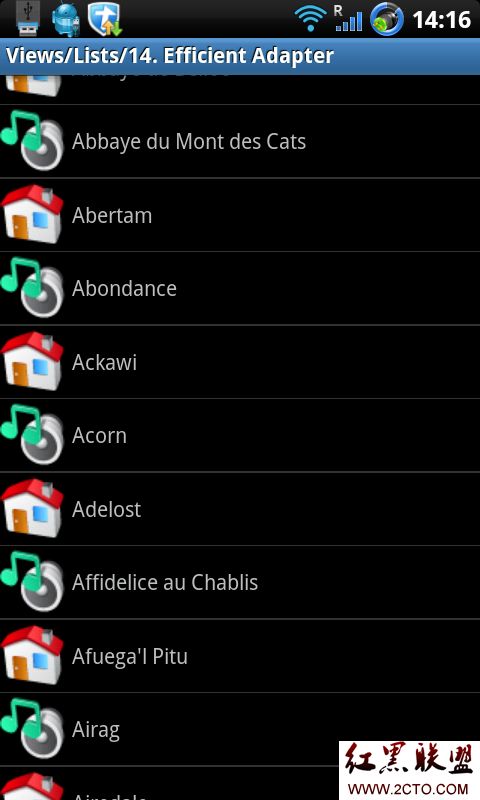
由于item0和item10都显示一半,所以item10也是新建出来,但是当要显示item11的时候,由于item0已经不在屏幕上,所以item11复用了item0的实例。可以从
以下Log信息看出:

我们分析Log信息,可以看出item11的对象是item0,item12的对象是item1,如此类推。
这样,通过复用convertView,就可以避免每次都新建View,节省内存而且优化ListView的滑动效果。
2. ListView的Layout XML
除了上述说的,还有一个要点就是ListView在Layout XML中的描述。
先看问题:
有时,我们可能会看到一打开ListView,getView会重复调用好次(假设屏幕最多可以看到6个item),如下图:
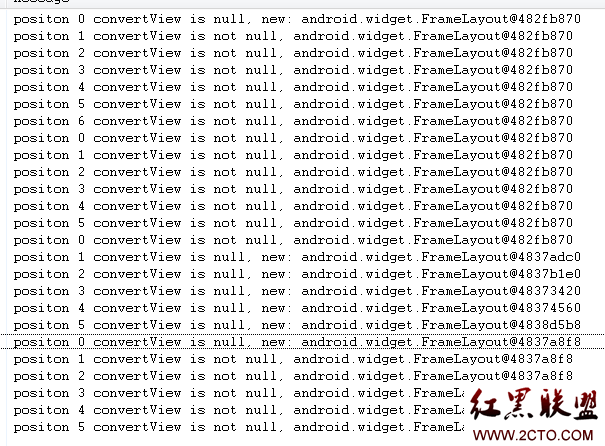
一直重复0-6, 0-5,0-5,0-5,0-5,0-5。而且,convertView一开始都是同一个View,这个是因为ListView的
android:layout_height="wrap_content"。
我们修改为android:layout_height="fill_parent",Log信息如下:
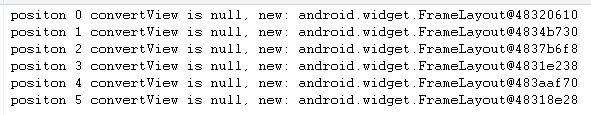
可以看出,修改之后ListView的getView调用恢复和Recycler的行为一致。
至于为什么使用wrap_content会出现重复调用的情况,我还没有研究过。不过初步觉得是因为在Android描绘ListView的时候,由于不清楚高度,所以使用一个item去试探ListView在屏幕中的最大高度所引起。希望有知道的朋友能够告诉,先谢谢了!
最后,如果上面有什么地方说错的话,希望能够指出,互相进步嘛。