erlang 监督树
OTP Design Principles: Supervisor Behaviour
http://hideto.iteye.com/blog/232618
Supervisor Behaviour是一个用来实现一个supervisor进程来监控其他子进程的模块
子进程可以是另一个supervisor,也可以是一个worker进程
worker进程一般使用gen_event,gen_fsm或gen_server behaviour来实现
一个使用该模块来实现的supervisor有一个接口方法的标准集,包括跟踪和错误报告的功能
supervisor用来构建一个分层进程结构,称为supervision tree,这是组织一个容错系统的好方式
1,Supervision原则
supervisor负责启动、停止和监控它的子进程
supervisor在必要时通过重启它的子进程来保持它们活着
supervisor的子被定义为一个子规范的list
当supervisor启动时,子进程按list从左至右的顺序启动
当supervisor终止时,它首先按启动顺序的反顺序终止它的子进程
2,例子
启动服务器的supervisor的callback模块:
one_for_one是重启策略之一
1和60定义了最大重启频率
tuple {ch3, ...}是子规范
3,重启策略
3.1 one_for_one
如果一个子进程停止,则只重启该进程
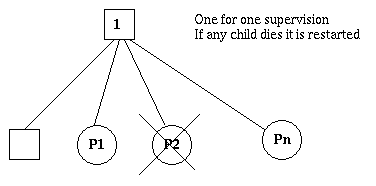
3.2 one_for_all
如果一个子进程停止,所有其他子进程也停止,然后所有进程重启
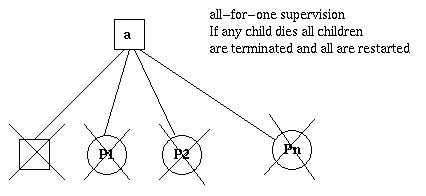
3.3 rest_for_one
如果一个子进程停止,则启动顺序中在它之后的所有其他子进程也停止,然后停止的这些进程重启(跟楼上那位不一样)
3.4 simple_one_for_one
一个简化的one_for_one supervisor,所有的子进程都是同样进程类型并且是动态添加的实例
4,最大重启频率
supervisor有一个自带的机制来限制给定时间内重启的次数
这是通过MaxR和MaxT这两个参数来决定的
如果在最近的MaxT秒之内有超过MaxR次数的重启,则supervisor停止它本身和它所有的子进程
当supervisor停止后,下一个更高级别的supervisor进行下一步动作,重启该停止的supervisor或者终止本身
重启机制的意图是防止一个进程由于某些原因重复性的死掉
5,子规范
这是子规范的类型定义:
Id是用来让supervisor内部识别子规范的名字
StartFunc定义了用来启动子进程的的方法,符合module-function-arguments tuple{M, F, A}
它应该调用supervisor:start_link,gen_server:start_link,gen_fsm:start_link或gen_event:start_link,或相适应的方法
Restart定义了子进程什么时候重启
1)permanent表示子进程始终重启
2)temporary表示子进程决不重启
3)transient表示只有在子进程异常终止时才重启,即除了normal以外的终止原因
Shutdown定义了子进程怎样终止
1)brutal_kill表示子进程使用exit(Child, kill)来无条件的终止
2)一个整数timeout值表示supervisor告诉子进程通过调用exit(Child, shutdown)来终止,然后等待一个exit信号返回
如果没有在指定的时间内接收到exit信号,则子进程使用exit(Child, kill)来无条件的终止
3)如果子进程是另一个supervisor,它应该设置为infinity来给子树足够的时间来终止
Type指定子进程是一个supervisor还是一个worker
Modules应该是一个list,含有一个元素[Module]
如果子进程是一个supervisor,gen_server或gen_fsm则Module是callback模块的名字
如果子进程是一个gen_event,则Modules应该为dynamic
该信息用来在升级和降级时供release handler使用
例子:启动服务器ch3的子规范
例子:启动event manager的子规范
服务器和event manager都是注册进程,可以在任何时候访问,这样它们都指定为permanent
ch3不需要在终止之前做任何清理工作,这样就不需要timeout,但是必须满足brutal_kill,error_man可能需要一些时间来让event handler清理,这样Shutdown设置为5000ms
例子:启动另一个supervisor的子规范
6,启动一个supervisor
上面的例子通过调用ch_sup:start_link()来启动supervisor:
ch_sup:start_link调用方法supervisor:start_link/2,这个方法启动一个新的supervisor进程并连接它
1)第一个参数ch_sup是callback模块的名字,它是init callback方法所在的位置
2)第二个参数[]是传给init callback方法的参数
一个supervisor进程调用callback方法ch_sup:init([]),返回{ok, StateSpec}:
然后根据指定的子规范的入口来启动它的所有子进程,在这里有一个子进程ch3
注意supervisor:start_link是同步带,当作有子进程启动之后才会返回
7,添加一个子进程
除了静态的supervision tree,我们也可以添加动态子进程到已有的supervisor里:
Sup是supervisor的pid或名字,ChildSpec是子规范
使用start_child/2来添加的子进程表现出像其他子进程一样的行为,除了这点:如果supervisor死掉然后重启,则所有动态添加的子进程都将丢失
8,停止一个子进程
任何子进程,不管静态的还是动态的,都可以使用shutdown规范来停止:
停止的子进程的子规范使用如下调用来删除:
Sup是supervisor的pid或name,Id是子规范里指定的id
就像动态添加的子进程一样,如果supervisor本身重启,那么删除静态子进程的效果会丢失
9,simple_one_for_one supervisor
simple_one_for_one重启策略的supervisor是一个简化的one_for_one supervisor,所有的子进程都是动态添加的同一进程的实例
一个simple_one_for_one supervisor callback模块的例子:
当启动后,supervisor将不会启动任何子进程,而是通过调用如下代码来动态添加所有的子进程:
Sup是supervisor的pid或name,List是一个任意的term列表,将会被动态添加到子规范的参数列表里
如果启动方法指定为{M, F, A},则子进程通过调用apply(M, F, A++List)来启动
例如,添加一个子进程到simple_sup:
这将会通过调用apply(call, start_link, []++[id1])即call:start_link(id1)来启动子进程
10,终止
既然supervisor是supervision tree的一部分,则它将自动被它的supervisor终止
当终止时,它会按启动的反顺序根据相应的shudown规范来自动终止它所有的子进程,然后终止本身
补充:supervisor exports and callbacks
子进程可以是另一个supervisor,也可以是一个worker进程
worker进程一般使用gen_event,gen_fsm或gen_server behaviour来实现
一个使用该模块来实现的supervisor有一个接口方法的标准集,包括跟踪和错误报告的功能
supervisor用来构建一个分层进程结构,称为supervision tree,这是组织一个容错系统的好方式
1,Supervision原则
supervisor负责启动、停止和监控它的子进程
supervisor在必要时通过重启它的子进程来保持它们活着
supervisor的子被定义为一个子规范的list
当supervisor启动时,子进程按list从左至右的顺序启动
当supervisor终止时,它首先按启动顺序的反顺序终止它的子进程
2,例子
启动服务器的supervisor的callback模块:
- -module(ch_sup).
- -behaviour(supervisor).
- -export([start_link/0]).
- -export([init/1]).
- start_link() ->
- supervisor:start_link(ch_sup, []).
- init(_Args) ->
- {ok, {{one_for_one, 1, 60},
- [{ch3, {ch3, start_link, []},
- permanent, brutal_kill, worker, [ch3]}]}}.
one_for_one是重启策略之一
1和60定义了最大重启频率
tuple {ch3, ...}是子规范
3,重启策略
3.1 one_for_one
如果一个子进程停止,则只重启该进程

3.2 one_for_all
如果一个子进程停止,所有其他子进程也停止,然后所有进程重启

3.3 rest_for_one
如果一个子进程停止,则启动顺序中在它之后的所有其他子进程也停止,然后停止的这些进程重启(跟楼上那位不一样)
3.4 simple_one_for_one
一个简化的one_for_one supervisor,所有的子进程都是同样进程类型并且是动态添加的实例
4,最大重启频率
supervisor有一个自带的机制来限制给定时间内重启的次数
这是通过MaxR和MaxT这两个参数来决定的
- init(...) ->
- {ok, {{RestartStrategy, MaxR, MaxT},
- [ChildSpec, ...]}}.
如果在最近的MaxT秒之内有超过MaxR次数的重启,则supervisor停止它本身和它所有的子进程
当supervisor停止后,下一个更高级别的supervisor进行下一步动作,重启该停止的supervisor或者终止本身
重启机制的意图是防止一个进程由于某些原因重复性的死掉
5,子规范
这是子规范的类型定义:
- {Id, StartFunc, Restart, Shutdown, Type, Modules}
- Id = term()
- StartFunc = {M, F, A}
- M = F = atom()
- A = [term()]
- Restart = permanent | transient | temporary
- Shutdown = brutal_kill | integer() >=0 | infinity
- Type = worker | supervisor
- Modules = [Module] | dynamic
- Module = atom()
Id是用来让supervisor内部识别子规范的名字
StartFunc定义了用来启动子进程的的方法,符合module-function-arguments tuple{M, F, A}
它应该调用supervisor:start_link,gen_server:start_link,gen_fsm:start_link或gen_event:start_link,或相适应的方法
Restart定义了子进程什么时候重启
1)permanent表示子进程始终重启
2)temporary表示子进程决不重启
3)transient表示只有在子进程异常终止时才重启,即除了normal以外的终止原因
Shutdown定义了子进程怎样终止
1)brutal_kill表示子进程使用exit(Child, kill)来无条件的终止
2)一个整数timeout值表示supervisor告诉子进程通过调用exit(Child, shutdown)来终止,然后等待一个exit信号返回
如果没有在指定的时间内接收到exit信号,则子进程使用exit(Child, kill)来无条件的终止
3)如果子进程是另一个supervisor,它应该设置为infinity来给子树足够的时间来终止
Type指定子进程是一个supervisor还是一个worker
Modules应该是一个list,含有一个元素[Module]
如果子进程是一个supervisor,gen_server或gen_fsm则Module是callback模块的名字
如果子进程是一个gen_event,则Modules应该为dynamic
该信息用来在升级和降级时供release handler使用
例子:启动服务器ch3的子规范
- {ch3,
- {ch3, start_link, []},
- permanent, brutal_kill, worker, [ch3]}
例子:启动event manager的子规范
- {error_man,
- {gen_event, start_link, [{local, error_man}]},
- permanent, 5000, worker, dynamic}
服务器和event manager都是注册进程,可以在任何时候访问,这样它们都指定为permanent
ch3不需要在终止之前做任何清理工作,这样就不需要timeout,但是必须满足brutal_kill,error_man可能需要一些时间来让event handler清理,这样Shutdown设置为5000ms
例子:启动另一个supervisor的子规范
- {sup,
- {sup, start_link, []},
- transient, infinity, supervisor, [sup]}
6,启动一个supervisor
上面的例子通过调用ch_sup:start_link()来启动supervisor:
- start_link() ->
- supervisor:start_link(ch_sup, []).
ch_sup:start_link调用方法supervisor:start_link/2,这个方法启动一个新的supervisor进程并连接它
1)第一个参数ch_sup是callback模块的名字,它是init callback方法所在的位置
2)第二个参数[]是传给init callback方法的参数
一个supervisor进程调用callback方法ch_sup:init([]),返回{ok, StateSpec}:
- init(_Args) ->
- {ok, {{one_for_one, 1, 60},
- [{ch3, {ch3, start_link, []},
- permanent, brutal_kill, worker, [ch3]}]}}.
然后根据指定的子规范的入口来启动它的所有子进程,在这里有一个子进程ch3
注意supervisor:start_link是同步带,当作有子进程启动之后才会返回
7,添加一个子进程
除了静态的supervision tree,我们也可以添加动态子进程到已有的supervisor里:
- supervisor:start_child(Sup, ChildSpec)
Sup是supervisor的pid或名字,ChildSpec是子规范
使用start_child/2来添加的子进程表现出像其他子进程一样的行为,除了这点:如果supervisor死掉然后重启,则所有动态添加的子进程都将丢失
8,停止一个子进程
任何子进程,不管静态的还是动态的,都可以使用shutdown规范来停止:
- supervisor:terminate_child(Sup, Id)
停止的子进程的子规范使用如下调用来删除:
- supervisor:delete_child(Sup, Id)
Sup是supervisor的pid或name,Id是子规范里指定的id
就像动态添加的子进程一样,如果supervisor本身重启,那么删除静态子进程的效果会丢失
9,simple_one_for_one supervisor
simple_one_for_one重启策略的supervisor是一个简化的one_for_one supervisor,所有的子进程都是动态添加的同一进程的实例
一个simple_one_for_one supervisor callback模块的例子:
- -module(simple_sup).
- -behaviour(supervisor).
- -export([start_link/0]).
- -export([init/1]).
- start_link() ->
- supervisor:start_link(simple_sup, []).
- init(_Args) ->
- {ok, {{simple_one_for_one, 0, 1},
- [{call, {call, start_link, []},
- temporary, brutal_kill, worker, [call]}]}}.
当启动后,supervisor将不会启动任何子进程,而是通过调用如下代码来动态添加所有的子进程:
- supervisor:start_child(Sup, List)
Sup是supervisor的pid或name,List是一个任意的term列表,将会被动态添加到子规范的参数列表里
如果启动方法指定为{M, F, A},则子进程通过调用apply(M, F, A++List)来启动
例如,添加一个子进程到simple_sup:
- supervisor:start_child(Pid, [id1])
这将会通过调用apply(call, start_link, []++[id1])即call:start_link(id1)来启动子进程
10,终止
既然supervisor是supervision tree的一部分,则它将自动被它的supervisor终止
当终止时,它会按启动的反顺序根据相应的shudown规范来自动终止它所有的子进程,然后终止本身
补充:supervisor exports and callbacks
- supervisor module Callback module
- supervisor:start_link Module:init/1
- supervisor:start_child
- supervisor:terminate_child
- supervisor:delete_child
- supervisor:restart_child
- supervisor:which_children
- supervisor:check_childspecs