Android开发学习之使用ViewPager打造应用引导界面面
在上一篇文章中,我们使用 ViewFilpper实现一个滑动切换的简单例子,但是毫无疑问地是,ViewFilpper实现的效果总体显得生硬,在滑动的过程中十分地不自然。那么,有没有解决这个问题的办法呢?答案是有的,就是我们今天要说的ViewPager。ViewPager用于实现多页面的切换效果,该类存在于Google的兼容包里面,所以在引用时记得在BuilldPath中加入“android-support-v4.jar”。所以,到目前为止,可以帮助我们实现滑动切换的效果的控件有两个,ViewFilpper和ViewPager。到底两个控件在具体使用的时候,会有什么不同呢?请跟着我的思路来学习下面的程序示例。
首先来分析布局代码:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<android.support.v4.view.ViewPager
android:id="@+id/ViewPager"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"/>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/LayoutForPoint"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dip"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ImageView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:clickable="true"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:src="@drawable/point_normal"
android:contentDescription="@string/Description" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ImageView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:src="@drawable/point_normal"
android:contentDescription="@string/Description"
android:clickable="true" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ImageView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:src="@drawable/point_normal"
android:contentDescription="@string/Description"
android:clickable="true" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/ImageView4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:contentDescription="@string/Description"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:src="@drawable/point_normal"
android:clickable="true" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout> 在上面的布局代码中,我们可以发现ViewPager节点下并没有其他的控件节点,因此,在使用ViewPager的时候,我们不需要在这里加入我们具体的布局代码,换言之,到底每一页要显示什么样的内容,可以不再这里定义。那么,到底在哪里定义呢?我们后面会提到。你也许会问,为什么下面会有四个ImageView吧?呵呵,这四个ImageView可不是用来显示每一个要显示的具体内容的,这里是四个点,用于标识当前选中的页面。好了,我们继续。在使用ViewPager的时候,我们需要继承PagerAdapter类,就像使用Gallery要继承BaseAdapter一样,具体的代码如下:
package com.Android.ViewPaper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager;
import android.support.v4.view.PagerAdapter;
import android.view.View;
public class ViewAdapter extends PagerAdapter {
private ArrayList<View> Views;//存放View的ArrayList
/*
* ViewAdapter构造函数
* @author:Robin
*/
public ViewAdapter(ArrayList<View> Views)
{
this.Views=Views;
}
/*
* 返回View的个数
*/
@Override
public int getCount()
{
if(Views!=null)
{
return Views.size();
}
return 0;
}
/*
* 销毁View
*/
@Override
public void destroyItem(View container, int position, Object object)
{
((ViewPager)container).removeView(Views.get(position));
}
/*
* 初始化
*/
@Override
public Object instantiateItem(View container, int position)
{
((ViewPager)container).addView(Views.get(position),0);
return Views.get(position);
}
/*
* 判断View是否来自Object
*/
@Override
public boolean isViewFromObject(View view, Object object)
{
return (view==object);
}
}
这个类的编写大家可以参考BaseAdapter的继承,我感觉差不多啦,而且这些方法的用途都很清楚,一目了然。
下面是主要的逻辑代码,程序中有详细的注释说明,不再赘述
package com.Android.ViewPaper;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager.OnPageChangeListener;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener, OnPageChangeListener {
//存放View的ArrayList
private ArrayList<View> Views;
//ViewAdapter适配器
private ViewAdapter mAdapter;
//引导图片资源
private int[] Resources=new int[]{R.drawable.guide1,R.drawable.guide2,R.drawable.guide3,R.drawable.guide4};
//提示切换的Point
private ImageView[] Points;
//当前索引
private int index;
//ViewPager
private ViewPager mPager;
//点的状态图片资源
private int[] PointState=new int[]{R.drawable.point_normal,R.drawable.point_select};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//初始化View
Views=new ArrayList<View>();
for(int i=0;i<Resources.length;i++)
{
ImageView Image=new ImageView(this);
Image.setImageResource(Resources[i]);
Views.add(Image);
}
//初始化Points
LinearLayout Layout=(LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.LayoutForPoint);
Points=new ImageView[Resources.length];
for(int i=0;i<Resources.length;i++)
{
Points[i]=(ImageView)Layout.getChildAt(i);
Points[i].setImageResource(PointState[0]);
Points[i].setOnClickListener(this);
Points[i].setTag(i);
}
//获取ViewPaper
mPager=(ViewPager)findViewById(R.id.ViewPager);
//实例化适配器
mAdapter=new ViewAdapter(Views);
mPager.setAdapter(mAdapter);
mPager.setOnPageChangeListener(this);
//显示第一页
index=0;
Points[index].setImageResource(PointState[1]);;
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu)
{
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
index=(Integer)v.getTag();
setPoint(index);
setView(index);
}
/*
* 设置索引为index的View
*/
private void setView(int index)
{
if(index<0||index>Resources.length)
{
return;
}
mPager.setCurrentItem(index);
}
/*
* 设置索引为position的Point
*/
private void setPoint(int position)
{
if (position < 0 || position > Resources.length - 1 || index == position) {
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<Resources.length;i++)
{
Points[i].setImageResource(PointState[0]);;
}
Points[position].setImageResource(PointState[1]);;
index = position;
}
public void onPageSelected(int position)
{
setPoint(position);
}
@Override
public void onPageScrollStateChanged(int arg0)
{
}
@Override
public void onPageScrolled(int arg0, float arg1, int arg2)
{
}
}
在这个程序中,我们必须实现的一个接口是OnPageChangeListener接口,即对页面切换行为的监听接口,这个程序中原来的作者实现了OnClickListener接口,根据本人亲自测试,这个接口是不能监听到页面切换的行为的,或者说监听那四个点的的思路本身就是有问题的,应该是监听页面的切换事件,然后让那四个点去响应这个变化。最后说一点的是,这个程序中,我使用了两张照片来表示每个点的正常、选中的状态。其实,这里还可以写个selector资源文件来解决的,好了,这个例子实现的测试效果如下:


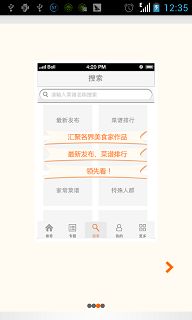
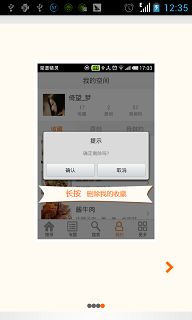
ViewPager相关文章:
1、Android开发之ViewPager+ActionBar+Fragment实现响应式可滑动Tab
2、Android开发学习之基于ViewPager实现Gallery画廊效果
3、Android开发学习之使用ViewPager+PagerTabStrip制作可滑动的Tab
4、Android开发学习之使用ViewPager打造应用引导界面面