鸿蒙(API 12 Beta6版)图形【使用Drawing实现图形绘制与显示 (C/C++)】方舟2D图形服务
场景介绍
Native Drawing模块提供了一系列的接口用于基本图形和字体的绘制。
Drawing绘制的内容无法直接在屏幕上显示,需要借用XComponent以及Native Window的能力支持,将绘制的内容通过Native Window送显。
接口说明
Drawing常用接口如下表所示。
| 接口名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| OH_Drawing_BitmapCreate (void) | 创建一个位图对象。 |
| OH_Drawing_BitmapBuild (OH_Drawing_Bitmap *, const uint32_t width, const uint32_t height, const OH_Drawing_BitmapFormat *) | 初始化位图对象的宽度和高度,并且为该位图设置像素格式。 |
| OH_Drawing_CanvasCreate (void) | 创建一个画布对象。 |
| OH_Drawing_CanvasBind (OH_Drawing_Canvas *, OH_Drawing_Bitmap *) | 将一个位图对象绑定到画布中,使得画布绘制的内容输出到位图中(即CPU渲染)。 |
| OH_Drawing_CanvasAttachBrush (OH_Drawing_Canvas *, const OH_Drawing_Brush *) | 设置画刷给画布,画布将会使用设置的画刷样式和颜色去填充绘制的图形形状。 |
| OH_Drawing_CanvasAttachPen (OH_Drawing_Canvas *, const OH_Drawing_Pen *) | 设置画笔给画布,画布将会使用设置画笔的样式和颜色去绘制图形形状的轮廓。 |
| OH_Drawing_CanvasDrawPath (OH_Drawing_Canvas *, const OH_Drawing_Path *) | 画一个自定义路径。 |
| OH_Drawing_PathCreate (void) | 创建一个路径对象。 |
| OH_Drawing_PathMoveTo (OH_Drawing_Path *, float x, float y) | 设置自定义路径的起始点位置。 |
| OH_Drawing_PathLineTo (OH_Drawing_Path *, float x, float y) | 添加一条到目标点的线段。 |
| OH_Drawing_PathClose (OH_Drawing_Path *) | 闭合路径,会添加一条到路径起点位置的线段。 |
| OH_Drawing_PenCreate (void) | 创建一个画笔对象。 |
| OH_Drawing_PenSetAntiAlias (OH_Drawing_Pen *, bool) | 设置抗锯齿属性,如果为真则说明画笔会启用抗锯齿功能,在绘制图形时会对图形的边缘像素进行半透明的模糊处理。 |
| OH_Drawing_PenSetWidth (OH_Drawing_Pen *, float width) | 设置画笔的厚度属性,厚度属性描述了画笔绘制图形轮廓的宽度。 |
| OH_Drawing_BrushCreate (void) | 创建一个画刷对象。 |
| OH_Drawing_BrushSetColor (OH_Drawing_Brush *, uint32_t color) | 设置画刷的颜色属性,颜色属性描述了画刷填充图形时使用的颜色,用一个32位(ARGB)的变量表示。 |
| OH_Drawing_CreateTypographyStyle (void) | 创建一个排版对象,用于定义排版样式。 |
| OH_Drawing_CreateTextStyle (void) | 创建一个文本对象,用于定义文本样式。 |
| OH_Drawing_TypographyHandlerAddText (OH_Drawing_TypographyCreate *, const char *) | 设置文本内容。 |
| OH_Drawing_TypographyPaint (OH_Drawing_Typography *, OH_Drawing_Canvas *, double, double) | 显示文本。 |
图形绘制与显示开发步骤
开发流程
使用Drawing进行图形绘制与显示时,需要使用Native Drawing模块的画布画笔绘制一个基本的2D图形;并将图形内容写入Native Window提供的图形Buffer,将Buffer提交到图形队列;再利用XComponent将C++代码层与ArkTS层对接,实现在ArkTS层调用绘制和显示的逻辑,最终在应用上显示图形。
本文以实现2D图形和文本的绘制与显示为例,给出具体的开发指导。
添加开发依赖
添加动态链接库
CMakeLists.txt中添加以下lib。
1. libace_napi.z.so
1. libace_ndk.z.so
1. libnative_window.so
1. libnative_drawing.so
头文件
#include
#include "napi/native_api.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
使用XComponent构建绘制环境
- 在Index.ets文件中添加XComponent组件。
import XComponentContext from "../interface/XComponentContext";
const TAG = '[Sample_DrawingAPI]';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
private xComponentContext: XComponentContext | undefined = undefined;
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
XComponent({ id: 'xcomponentId', type: 'surface', libraryname: 'entry' })
.onLoad((xComponentContext) => {
this.xComponentContext = xComponentContext as XComponentContext;
}).width('640px') // 64的倍数
}.height('88%')
}
}
}
若要改变XComponent的宽,值需为64的倍数,例如640px。
- 在 Native C++层获取NativeXComponent。建议使用单例模式保存XComponent。此步骤需要在napi_init的过程中处理。
创建一个PluginManger单例类,用于管理NativeXComponent。
class PluginManager {
public:
~PluginManager();
static PluginManager *GetInstance();
void SetNativeXComponent(std::string &id, OH_NativeXComponent *nativeXComponent);
SampleBitMap *GetRender(std::string &id);
void Export(napi_env env, napi_value exports);
private:
std::unordered_map nativeXComponentMap_;
std::unordered_map pluginRenderMap_;
};
SampleBitMap类会在后面的绘制2D图形步骤中创建。
void PluginManager::Export(napi_env env, napi_value exports) {
if ((env == nullptr) || (exports == nullptr)) {
DRAWING_LOGE("Export: env or exports is null");
return;
}
napi_value exportInstance = nullptr;
if (napi_get_named_property(env, exports, OH_NATIVE_XCOMPONENT_OBJ, &exportInstance) != napi_ok) {
DRAWING_LOGE("Export: napi_get_named_property fail");
return;
}
OH_NativeXComponent *nativeXComponent = nullptr;
if (napi_unwrap(env, exportInstance, reinterpret_cast(&nativeXComponent)) != napi_ok) {
DRAWING_LOGE("Export: napi_unwrap fail");
return;
}
char idStr[OH_XCOMPONENT_ID_LEN_MAX + 1] = {'\0'};
uint64_t idSize = OH_XCOMPONENT_ID_LEN_MAX + 1;
if (OH_NativeXComponent_GetXComponentId(nativeXComponent, idStr, &idSize) != OH_NATIVEXCOMPONENT_RESULT_SUCCESS) {
DRAWING_LOGE("Export: OH_NativeXComponent_GetXComponentId fail");
return;
}
std::string id(idStr);
auto context = PluginManager::GetInstance();
if ((context != nullptr) && (nativeXComponent != nullptr)) {
context->SetNativeXComponent(id, nativeXComponent);
auto render = context->GetRender(id);
if (render != nullptr) {
render->RegisterCallback(nativeXComponent);
render->Export(env, exports);
} else {
DRAWING_LOGE("render is nullptr");
}
}
}
- 注册回调函数。通过OnSurfaceCreated回调函数获取Native Window,建议将Native Window同样存储在单例中。
// 定义回调函数
void OnSurfaceCreatedCB(OH_NativeXComponent* component, void* window)
{
// 可获取 OHNativeWindow 实例
OHNativeWindow* nativeWindow = static_cast(window);
char idStr[OH_XCOMPONENT_ID_LEN_MAX + 1] = {'\0'};
uint64_t idSize = OH_XCOMPONENT_ID_LEN_MAX + 1;
if (OH_NativeXComponent_GetXComponentId(component, idStr, &idSize) != OH_NATIVEXCOMPONENT_RESULT_SUCCESS) {
DRAWING_LOGE("OnSurfaceCreatedCB: Unable to get XComponent id");
return;
}
std::string id(idStr);
auto render = SampleBitMap::GetInstance(id);
render->SetNativeWindow(nativeWindow);
uint64_t width;
uint64_t height;
int32_t xSize = OH_NativeXComponent_GetXComponentSize(component, window, &width, &height);
if ((xSize == OH_NATIVEXCOMPONENT_RESULT_SUCCESS) && (render != nullptr)) {
render->SetHeight(height);
render->SetWidth(width);
DRAWING_LOGI("xComponent width = %{public}llu, height = %{public}llu", width, height);
}
}
void OnSurfaceChangedCB(OH_NativeXComponent* component, void* window)
{
// 可获取 OHNativeWindow 实例
OHNativeWindow* nativeWindow = static_cast(window);
char idStr[OH_XCOMPONENT_ID_LEN_MAX + 1] = {'\0'};
uint64_t idSize = OH_XCOMPONENT_ID_LEN_MAX + 1;
if (OH_NativeXComponent_GetXComponentId(component, idStr, &idSize) != OH_NATIVEXCOMPONENT_RESULT_SUCCESS) {
DRAWING_LOGE("OnSurfaceChangedCB: Unable to get XComponent id");
return;
}
std::string id(idStr);
auto render = SampleBitMap::GetInstance(id);
uint64_t width;
uint64_t height;
int32_t xSize = OH_NativeXComponent_GetXComponentSize(component, window, &width, &height);
if ((xSize == OH_NATIVEXCOMPONENT_RESULT_SUCCESS) && (render != nullptr)) {
render->SetHeight(height);
render->SetWidth(width);
DRAWING_LOGI("Surface Changed : xComponent width = %{public}llu, height = %{public}llu", width, height);
}
}
void OnSurfaceDestroyedCB(OH_NativeXComponent* component, void* window)
{
// 可获取 OHNativeWindow 实例
OHNativeWindow* nativeWindow = static_cast(window);
// ...
}
void DispatchTouchEventCB(OH_NativeXComponent* component, void* window)
{
// 可获取 OHNativeWindow 实例
OHNativeWindow* nativeWindow = static_cast(window);
// ...
}
XComponent的所有Callback必须初始化,可以将不需要的Callback定义为空指针。
// OH_NativeXComponent_Callback是个struct
OH_NativeXComponent_Callback callback;
callback.OnSurfaceCreated = OnSurfaceCreatedCB;
callback.OnSurfaceChanged = OnSurfaceChangedCB;
callback.OnSurfaceDestroyed = OnSurfaceDestroyedCB;
callback.DispatchTouchEvent = DispatchTouchEventCB;
- 将OH_NativeXComponent_Callback注册给NativeXComponent。
// 注册回调函数
OH_NativeXComponent_RegisterCallback(nativeXComponent, &callback);
经过以上步骤,绘制环境已搭建完成,接下来介绍如何使用Drawing接口进行内容绘制。
绘制2D图形
以下步骤描述了如何使用Native Drawing模块的画布画笔绘制一个基本的2D图形:
- 创建Bitmap实例。使用drawing_bitmap.h的OH_Drawing_BitmapCreate接口创建一个Bitmap实例cBitmap并使用OH_Drawing_BitmapBuild指定其长宽大小和像素格式。
创建一个SampleBitMap类,并声明接下来需要的私有成员变量。
class SampleBitMap {
public:
// member functions
private:
OH_NativeXComponent_Callback renderCallback_;
uint64_t width_ = 0;
uint64_t height_ = 0;
OH_Drawing_Bitmap *cBitmap_ = nullptr;
OH_Drawing_Canvas *cCanvas_ = nullptr;
OH_Drawing_Path *cPath_ = nullptr;
OH_Drawing_Brush *cBrush_ = nullptr;
OH_Drawing_Pen *cPen_ = nullptr;
OHNativeWindow *nativeWindow_ = nullptr;
uint32_t *mappedAddr_ = nullptr;
BufferHandle *bufferHandle_ = nullptr;
struct NativeWindowBuffer *buffer_ = nullptr;
int fenceFd_ = 0;
};
```// 创建一个bitmap对象cBitmap_ = OH_Drawing_BitmapCreate();// 定义bitmap的像素格式OH_Drawing_BitmapFormat cFormat {COLOR_FORMAT_RGBA_8888, ALPHA_FORMAT_OPAQUE};// 构造对应格式的bitmap,width的值必须为 bufferHandle->stride / 4OH_Drawing_BitmapBuild(cBitmap_, width_, height_, &cFormat); ```
- 创建画布实例。使用drawing_canvas.h的 OH_Drawing_CanvasCreate 接口创建一个画布实例cCanvas,并使用 OH_Drawing_CanvasBind 接口将cBitmap实例绑定到cCanvas上,后续在画布上绘制的内容会输出到绑定的cBitmap实例中。
int len = height_ / 4;
float aX = width_ / 2;
float aY = height_ / 4;
float dX = aX - len * std::sin(18.0f);
float dY = aY + len * std::cos(18.0f);
float cX = aX + len * std::sin(18.0f);
float cY = dY;
float bX = aX + (len / 2.0);
float bY = aY + std::sqrt((cX - dX) * (cX - dX) + (len / 2.0) * (len / 2.0));
float eX = aX - (len / 2.0);
float eY = bY;
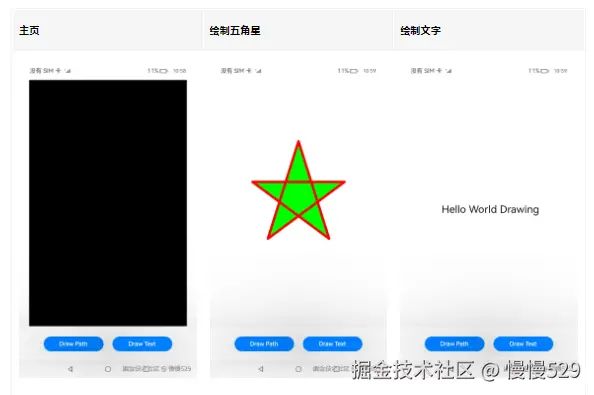
// 创建一个path对象,然后使用接口连接成一个五角星形状
cPath_ = OH_Drawing_PathCreate();
// 指定path的起始位置
OH_Drawing_PathMoveTo(cPath_, aX, aY);
// 用直线连接到目标点
OH_Drawing_PathLineTo(cPath_, bX, bY);
OH_Drawing_PathLineTo(cPath_, cX, cY);
OH_Drawing_PathLineTo(cPath_, dX, dY);
OH_Drawing_PathLineTo(cPath_, eX, eY);
// 闭合形状,path绘制完毕
OH_Drawing_PathClose(cPath_);
- 构造Path形状。使用drawing_path.h提供的接口完成一个五角星形状的构造cPath。
int len = height_ / 4;
float aX = width_ / 2;
float aY = height_ / 4;
float dX = aX - len * std::sin(18.0f);
float dY = aY + len * std::cos(18.0f);
float cX = aX + len * std::sin(18.0f);
float cY = dY;
float bX = aX + (len / 2.0);
float bY = aY + std::sqrt((cX - dX) * (cX - dX) + (len / 2.0) * (len / 2.0));
float eX = aX - (len / 2.0);
float eY = bY;
// 创建一个path对象,然后使用接口连接成一个五角星形状
cPath_ = OH_Drawing_PathCreate();
// 指定path的起始位置
OH_Drawing_PathMoveTo(cPath_, aX, aY);
// 用直线连接到目标点
OH_Drawing_PathLineTo(cPath_, bX, bY);
OH_Drawing_PathLineTo(cPath_, cX, cY);
OH_Drawing_PathLineTo(cPath_, dX, dY);
OH_Drawing_PathLineTo(cPath_, eX, eY);
// 闭合形状,path绘制完毕
OH_Drawing_PathClose(cPath_);
- 设置画笔和画刷样式。使用drawing_pen.h的OH_Drawing_PenCreate接口创建一个画笔实例cPen, 并设置抗锯齿、颜色、线宽等属性,画笔用于形状边框线的绘制。使用drawing_brush.h的OH_Drawing_BrushCreate接口创建一个画刷实例cBrush,并设置填充颜色, 画刷用于形状内部的填充。使用drawing_canvas.h的OH_Drawing_CanvasAttachPen和OH_Drawing_CanvasAttachBrush接口将画笔画刷的实例设置到画布实例中。
// 创建一个画笔Pen对象,Pen对象用于形状的边框线绘制
cPen_ = OH_Drawing_PenCreate();
OH_Drawing_PenSetAntiAlias(cPen_, true);
OH_Drawing_PenSetColor(cPen_, OH_Drawing_ColorSetArgb(0xFF, 0xFF, 0x00, 0x00));
OH_Drawing_PenSetWidth(cPen_, 10.0);
OH_Drawing_PenSetJoin(cPen_, LINE_ROUND_JOIN);
// 将Pen画笔设置到canvas中
OH_Drawing_CanvasAttachPen(cCanvas_, cPen_);
// 创建一个画刷Brush对象,Brush对象用于形状的填充
cBrush_ = OH_Drawing_BrushCreate();
OH_Drawing_BrushSetColor(cBrush_, OH_Drawing_ColorSetArgb(0xFF, 0x00, 0xFF, 0x00));
// 将Brush画刷设置到canvas中
OH_Drawing_CanvasAttachBrush(cCanvas_, cBrush_);
- 绘制Path形状。使用drawing_canvas.h的OH_Drawing_CanvasDrawPath接口将五角星绘制到画布上。
// 在画布上画path的形状,五角星的边框样式为pen设置,颜色填充为Brush设置
OH_Drawing_CanvasDrawPath(cCanvas_, cPath_);
文本绘制开发步骤
Native Drawing模块关于文本绘制提供两类API接口:
- 一类是具有定制排版能力的接口:如OH_Drawing_Typography,OH_Drawing_TypographyStyle,OH_Drawing_TextStyle等类型。支撑用户设置排版风格和文本风格,可调用OH_Drawing_TypographyHandlerAddText添加文本并调用OH_Drawing_TypographyLayout和OH_Drawing_TypographyPaint对文本进行排版和绘制。
- 另一类是不具有定制排版能力的接口:如OH_Drawing_Font,OH_Drawing_TextBlob,OH_Drawing_RunBuffer等类型。如果应用具备排版能力,支撑用户将排版结果构造为OH_Drawing_TextBlob;如果应用使用默认的排版能力,支撑用户直接调用OH_Drawing_TextBlobCreateFromText构造OH_Drawing_TextBlob。最后调用OH_Drawing_CanvasDrawTextBlob绘制OH_Drawing_TextBlob描述的文本块。
以下分别提供了如何使用这两类API接口以实现文本绘制的具体步骤。
使用定制排版能力实现文本绘制
- 创建画布和bitmap实例。
// 创建bitmap
cBitmap_ = OH_Drawing_BitmapCreate();
OH_Drawing_BitmapFormat cFormat {COLOR_FORMAT_RGBA_8888, ALPHA_FORMAT_OPAQUE};
// width的值必须为bufferHandle->stride / 4
OH_Drawing_BitmapBuild(cBitmap_, width_, height_, &cFormat);
// 创建canvas
cCanvas_ = OH_Drawing_CanvasCreate();
OH_Drawing_CanvasBind(cCanvas_, cBitmap_);
OH_Drawing_CanvasClear(cCanvas_, OH_Drawing_ColorSetArgb(0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF));
- 设置排版风格。
// 选择从左到右/左对齐等排版属性
OH_Drawing_TypographyStyle* typoStyle = OH_Drawing_CreateTypographyStyle();
OH_Drawing_SetTypographyTextDirection(typoStyle, TEXT_DIRECTION_LTR);
OH_Drawing_SetTypographyTextAlign(typoStyle, TEXT_ALIGN_LEFT);
- 设置文本风格。
// 设置文字颜色,例如黑色
OH_Drawing_TextStyle* txtStyle = OH_Drawing_CreateTextStyle();
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleColor(txtStyle, OH_Drawing_ColorSetArgb(0xFF, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00));
// 设置文字大小、字重等属性
double fontSize = width_ / 15;
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleFontSize(txtStyle, fontSize);
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleFontWeight(txtStyle, FONT_WEIGHT_400);
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleBaseLine(txtStyle, TEXT_BASELINE_ALPHABETIC);
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleFontHeight(txtStyle, 1);
// 如果需要多次测量,建议fontCollection作为全局变量使用,可以显著减少内存占用
OH_Drawing_FontCollection* fontCollection = OH_Drawing_CreateSharedFontCollection();
// 注册自定义字体
const char* fontFamily = "myFamilyName"; // myFamilyName为自定义字体的family name
const char* fontPath = "/data/storage/el2/base/haps/entry/files/myFontFile.ttf"; // 设置自定义字体所在的沙箱路径
OH_Drawing_RegisterFont(fontCollection, fontFamily, fontPath);
// 设置系统字体类型
const char* systemFontFamilies[] = {"Roboto"};
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleFontFamilies(txtStyle, 1, systemFontFamilies);
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleFontStyle(txtStyle, FONT_STYLE_NORMAL);
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleLocale(txtStyle, "en");
// 设置自定义字体类型
auto txtStyle2 = OH_Drawing_CreateTextStyle();
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleFontSize(txtStyle2, fontSize);
const char* myFontFamilies[] = {"myFamilyName"}; //如果已经注册自定义字体,填入自定义字体的family name使用自定义字体
OH_Drawing_SetTextStyleFontFamilies(txtStyle2, 1, myFontFamilies);
- 生成最终文本显示效果。
OH_Drawing_TypographyCreate* handler = OH_Drawing_CreateTypographyHandler(typoStyle,
fontCollection);
OH_Drawing_TypographyHandlerPushTextStyle(handler, txtStyle);
OH_Drawing_TypographyHandlerPushTextStyle(handler, txtStyle2);
// 设置文字内容
const char* text = "Hello World Drawing\n";
OH_Drawing_TypographyHandlerAddText(handler, text);
OH_Drawing_TypographyHandlerPopTextStyle(handler);
OH_Drawing_Typography* typography = OH_Drawing_CreateTypography(handler);
// 设置页面最大宽度
double maxWidth = width_;
OH_Drawing_TypographyLayout(typography, maxWidth);
// 设置文本在画布上绘制的起始位置
double position[2] = {width_ / 5.0, height_ / 2.0};
// 将文本绘制到画布上
OH_Drawing_TypographyPaint(typography, cCanvas_, position[0], position[1]);
- 释放变量。
OH_Drawing_DestroyTypography(typography);
OH_Drawing_DestroyTypographyHandler(handler);
OH_Drawing_DestroyFontCollection(fontCollection);
OH_Drawing_DestroyTextStyle(txtStyle);
OH_Drawing_DestroyTextStyle(txtStyle2);
OH_Drawing_DestroyTypographyStyle(typoStyle);
使用非定制排版能力实现文本绘制
- 创建画布和bitmap实例。
// 创建bitmap
cBitmap_ = OH_Drawing_BitmapCreate();
OH_Drawing_BitmapFormat cFormat {COLOR_FORMAT_RGBA_8888, ALPHA_FORMAT_OPAQUE};
// width的值必须为bufferHandle->stride / 4
OH_Drawing_BitmapBuild(cBitmap_, width_, height_, &cFormat);
// 创建canvas
cCanvas_ = OH_Drawing_CanvasCreate();
OH_Drawing_CanvasBind(cCanvas_, cBitmap_);
OH_Drawing_CanvasClear(cCanvas_, OH_Drawing_ColorSetArgb(0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF));
- 面向应用具备自排版能力的文本绘制场景。
// 创建字体,并设置文字大小
OH_Drawing_Font* font = OH_Drawing_FontCreate();
OH_Drawing_FontSetTextSize(font, 40);
// 创建文本构造器
OH_Drawing_TextBlobBuilder* builder = OH_Drawing_TextBlobBuilderCreate();
// 申请一块内存
const OH_Drawing_RunBuffer* runBuffer = OH_Drawing_TextBlobBuilderAllocRunPos(builder, font, count, nullptr);
// glyphs、posX和posY是开发者自排版产生的数据,使用该数据填充内存
for (int idx = 0; idx < count; idx++) {
runBuffer->glyphs[idx] = glyphs[idx];
runBuffer->pos[idx * 2] = posX[idx];
runBuffer->pos[idx * 2 + 1] = posY[idx];
}
// 通过文本构造器创建文本
OH_Drawing_TextBlob* textBlob = OH_Drawing_TextBlobBuilderMake(builder);
// 释放内存
OH_Drawing_TextBlobBuilderDestroy(builder);
- 面向应用使用默认排版能力的文本绘制场景。
// 创建字体,并设置文字大小
OH_Drawing_Font* font = OH_Drawing_FontCreate();
OH_Drawing_FontSetTextSize(font, 40);
// 创建要显示的字符
size_t size = 19;
const char16_t* buffer = u"Hello World Drawing";
// 通过字符和对应的编码格式创建默认排版的文本
OH_Drawing_TextBlob* textBlob = OH_Drawing_TextBlobCreateFromText(buffer, size * sizeof(char16_t), font, OH_Drawing_TextEncoding::TEXT_ENCODING_UTF16);
- 设置画笔和画刷样式。
// 创建一个画刷Brush对象,Brush对象用于形状的填充
cBrush_ = OH_Drawing_BrushCreate();
OH_Drawing_BrushSetColor(cBrush_, OH_Drawing_ColorSetArgb(0xFF, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00));
// 将Brush画刷设置到canvas中
OH_Drawing_CanvasAttachBrush(cCanvas_, cBrush_);
- 生成最终文本显示效果。
// 设置文本在画布上绘制的起始位置
double position[2] = {width_ / 5.0, height_ / 2.0};
// 将文本绘制到画布上
OH_Drawing_CanvasDrawTextBlob(canvas_, textBlob, position[0], position[1]);
// 释放内存
OH_Drawing_TextBlobDestroy(textBlob);
OH_Drawing_FontDestroy(font);
绘制内容送显
前面我们已经通过Drawing API实现了Path绘制以及文字绘制。现在需要将其呈现在Native Window上。
- 通过前面OnSurfaceCreatedCB回调保存的Native Window指针,来申请Native Window Buffer。
// 通过 OH_NativeWindow_NativeWindowRequestBuffer 获取 OHNativeWindowBuffer 实例
int32_t ret = OH_NativeWindow_NativeWindowRequestBuffer(nativeWindow_, &buffer_, &fenceFd_);
- 通过OH_NativeWindow_GetBufferHandleFromNative获取bufferHandle。
bufferHandle_ = OH_NativeWindow_GetBufferHandleFromNative(buffer_);
- 使用系统mmap接口拿到bufferHandle的内存虚拟地址。
mappedAddr_ = static_cast(
// 使用内存映射函数mmap将bufferHandle对应的共享内存映射到用户空间,可以通过映射出来的虚拟地址向bufferHandle中写入图像数据
// bufferHandle->virAddr是bufferHandle在共享内存中的起始地址,bufferHandle->size是bufferHandle在共享内存中的内存占用大小
mmap(bufferHandle_->virAddr, bufferHandle_->size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, bufferHandle_->fd, 0));
if (mappedAddr_ == MAP_FAILED) {
DRAWING_LOGE("mmap failed");
}
- 使用drawing_bitmap.h的OH_Drawing_BitmapGetPixels接口获取到画布绑定bitmap实例的像素地址,该地址指向的内存包含画布刚刚绘制的像素数据。将绘制内容填充到申请的Native Window Buffer中。
// 画完后获取像素地址,地址指向的内存包含画布画的像素数据
void *bitmapAddr = OH_Drawing_BitmapGetPixels(cBitmap_);
uint32_t *value = static_cast(bitmapAddr);
// 使用mmap获取到的地址来访问内存
uint32_t *pixel = static_cast(mappedAddr_);
for (uint32_t x = 0; x < width_; x++) {
for (uint32_t y = 0; y < height_; y++) {
*pixel++ = *value++;
}
}
- 设置刷新区域,并将其送显。
// 如果Region中的Rect为nullptr,或者rectNumber为0,则认为OHNativeWindowBuffer全部有内容更改。
Region region {nullptr, 0};
// 通过OH_NativeWindow_NativeWindowFlushBuffer 提交给消费者使用,例如:显示在屏幕上。
OH_NativeWindow_NativeWindowFlushBuffer(nativeWindow_, buffer_, fenceFd_, region);
- 内存释放。
Drawing内存释放。
// 去掉内存映射
int result = munmap(mappedAddr_, bufferHandle_->size);
if (result == -1) {
DRAWING_LOGE("munmap failed!");
}
// 销毁创建的对象
OH_Drawing_BrushDestroy(cBrush_);
cBrush_ = nullptr;
OH_Drawing_PenDestroy(cPen_);
cPen_ = nullptr;
OH_Drawing_PathDestroy(cPath_);
cPath_ = nullptr;
OH_Drawing_CanvasDestroy(cCanvas_);
cCanvas_ = nullptr;
OH_Drawing_BitmapDestroy(cBitmap_);
cBitmap_ = nullptr;
Surface内存释放。
void OnSurfaceDestroyedCB(OH_NativeXComponent *component, void *window) {
DRAWING_LOGI("OnSurfaceDestroyedCB");
if ((component == nullptr) || (window == nullptr)) {
DRAWING_LOGE("OnSurfaceDestroyedCB: component or window is null");
return;
}
char idStr[OH_XCOMPONENT_ID_LEN_MAX + 1] = {'\0'};
uint64_t idSize = OH_XCOMPONENT_ID_LEN_MAX + 1;
if (OH_NativeXComponent_GetXComponentId(component, idStr, &idSize) != OH_NATIVEXCOMPONENT_RESULT_SUCCESS) {
DRAWING_LOGE("OnSurfaceDestroyedCB: Unable to get XComponent id");
return;
}
std::string id(idStr);
SampleBitMap::Release(id);
}
用户调用
以上为Native层C++代码,用户想要调用还需要通过ArkTS层代码对接。
- 定义ArkTS接口文件,命名XComponentContext.ts,用来对接Native代码。
export default interface XComponentContext {
drawPattern(): void;
drawText(): void;
};
在SampleBitMap类中添加初始化函数以及代码。
void SampleBitMap::Export(napi_env env, napi_value exports) {
if ((env == nullptr) || (exports == nullptr)) {
DRAWING_LOGE("Export: env or exports is null");
return;
}
napi_property_descriptor desc[] = {
{"drawPattern", nullptr, SampleBitMap::NapiDrawPattern, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr},
{"drawText", nullptr, SampleBitMap::NapiDrawText, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr}};
napi_define_properties(env, exports, sizeof(desc) / sizeof(desc[0]), desc);
if (napi_define_properties(env, exports, sizeof(desc) / sizeof(desc[0]), desc) != napi_ok) {
DRAWING_LOGE("Export: napi_define_properties failed");
}
}
- 添加button控件供用户点击,并调用已定义的接口。
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
XComponent({ id: 'xcomponentId', type: 'surface', libraryname: 'entry' })
.onLoad((xComponentContext) => {
this.xComponentContext = xComponentContext as XComponentContext;
}).width('640px') // Multiples of 64
}.height('88%')
Row() {
Button('Draw Path')
.fontSize('16fp')
.fontWeight(500)
.margin({ bottom: 24, right: 12 })
.onClick(() => {
console.log(TAG, "Draw Path click");
if (this.xComponentContext) {
console.log(TAG, "Draw Path");
this.xComponentContext.drawPattern();
}
})
.width('33.6%')
.height(40)
.shadow(ShadowStyle.OUTER_DEFAULT_LG)
Button('Draw Text')
.fontSize('16fp')
.fontWeight(500)
.margin({ bottom: 24, left: 12 })
.onClick(() => {
console.log(TAG, "draw text click");
if (this.xComponentContext) {
console.log(TAG, "draw text");
this.xComponentContext.drawText();
}
})
.width('33.6%')
.height(40)
.shadow(ShadowStyle.OUTER_DEFAULT_LG)
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.shadow(ShadowStyle.OUTER_DEFAULT_SM)
.alignItems(VerticalAlign.Bottom)
.layoutWeight(1)
}
}
- 绘制与显示的效果图如下:
最后呢
很多开发朋友不知道需要学习那些鸿蒙技术?鸿蒙开发岗位需要掌握那些核心技术点?为此鸿蒙的开发学习必须要系统性的进行。
而网上有关鸿蒙的开发资料非常的少,假如你想学好鸿蒙的应用开发与系统底层开发。你可以参考这份资料,少走很多弯路,节省没必要的麻烦。由两位前阿里高级研发工程师联合打造的《鸿蒙NEXT星河版OpenHarmony开发文档》里面内容包含了(ArkTS、ArkUI开发组件、Stage模型、多端部署、分布式应用开发、音频、视频、WebGL、OpenHarmony多媒体技术、Napi组件、OpenHarmony内核、Harmony南向开发、鸿蒙项目实战等等)鸿蒙(Harmony NEXT)技术知识点
如果你是一名Android、Java、前端等等开发人员,想要转入鸿蒙方向发展。可以直接领取这份资料辅助你的学习。下面是鸿蒙开发的学习路线图。
![]()
针对鸿蒙成长路线打造的鸿蒙学习文档。话不多说,我们直接看详细鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )手册(共计1236页)与鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )开发入门视频,帮助大家在技术的道路上更进一步。
- 《鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony)开发学习视频》
- 《鸿蒙生态应用开发V2.0白皮书》
- 《鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony)开发基础到实战手册》
- OpenHarmony北向、南向开发环境搭建
- 《鸿蒙开发基础》
- 《鸿蒙开发进阶》
- 《鸿蒙开发实战》
![]()
总结
鸿蒙—作为国家主力推送的国产操作系统。部分的高校已经取消了安卓课程,从而开设鸿蒙课程;企业纷纷跟进启动了鸿蒙研发。
并且鸿蒙是完全具备无与伦比的机遇和潜力的;预计到年底将有 5,000 款的应用完成原生鸿蒙开发,未来将会支持 50 万款的应用。那么这么多的应用需要开发,也就意味着需要有更多的鸿蒙人才。鸿蒙开发工程师也将会迎来爆发式的增长,学习鸿蒙势在必行! 自↓↓↓拿
![]()