html5 Websockets development guidance
1. WebSockets -- full-duplex communication
The main HTML5 pillars include Markup, CSS3, and JavaScript APIs
For whole set of HTML5, visit html5rocks.com (google product)
The URL
The following image shows the WebSocket URL example in tokens:
schema host port server
ws://example.com:8000/chat.php
wss is supported as well and is the WebSocket equivalent to https for secure connections (SSL).
Who's using WebSockets
Name Website Description
Gamooga http://www.gamooga.com/ Real-time backend for apps and games
GitLive http://gitlive.com/ Notifications on GitHub projects
Superfeedr http://superfeedr.com/ Real-time data pushing
Pusher http://pusher.com/ Scalable real-time functionality API for web and mobile apps
Smarkets https://smarkets.com/ Real-time betting
IRC Cloud https://www.irccloud.com/ Chatting
Two great resources containing a large variety of WebSocket demos are as follows:
• http://www.websocket.org/demos.html
• http://www.html5rocks.com/en/features/connectivity
2. The WebSocket API web client
WebSocket communication and data transmission is bidirectional, so we need two parties to establish it: a server and a client.
HTML5 basics:
- Markup HTML (.html)
For more information about the HTML5 markup, consider visiting http://html5doctor.com/. There is a complete reference for the supported HTML5 tags at http://html5doctor.com/element-index/.
- Styling CSS (.css)
http://www.css3.info/ is a great resource for CSS3 and further reading.
- Logic JavaScript (.js)
The markup defines the structure and the CSS rules apply the styling. What about event handling and user actions? Well, here comes JavaScript! The WebSocket API is pure JavaScript, too!
WebSocket API allows you to connect to a local or remote server, listen for messages, send data, and close the connection. Typical WebSocket workflow shows below:

JavaScript provides an easy way to find out whether a browser can execute WebSocket-specific code:
if (window.WebSocket) { // validation check console.log("WebSockets supported."); // Continue with the rest of the WebSockets-specific functionality… } else { console.log("WebSockets not supported."); alert("Consider updating your browser for a richer experience."); }
Want to see which browsers do support the WebSocket protocol? There is an up-to-date resource available at http://caniuse.com/#feat=websockets.
- The WebSocket object :var socket = new WebSocket("ws://echo.websocket.org");
- Events: Open, Message, Close, and Error.
You can handle them either by implementing the onopen, onmessage, onclose, and onerror functions respectively, or by using the addEventListener method.
- Actions: The WebSocket protocol supports two main actions: send() and close().
- Properties:
Properties Description
url Returns the URL of the WebSocket protocol Returns the protocol used by the server
readyState Reports the state of the connection and can take one of the following selfexplanatory values:
WebSocket.OPEN
WebSocket.CLOSED
WebSocket.CONNECTING
WebSocket.CLOSING
bufferedAmount Returns the total number of bytes that were queued when the send() method was called
binaryType Returns the binary data format we
received when the onmessage event was raised
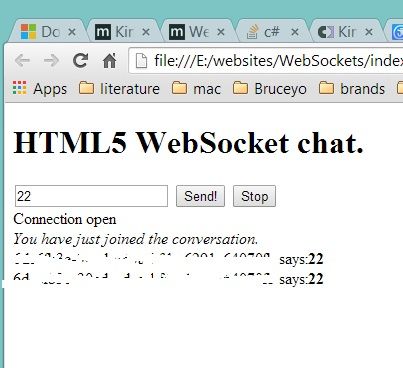
The complete client example:
index.html:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>HTML5 WebSockets</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" /> <script src="chat.js"></script> </head> <body> <h1> HTML5 WebSocket chat. </h1> <input type="text" id="text-view" /> <input type="button" id="send-button" value="Send!" /> <input type="button" id="stop-button" value="Stop" /> </br> <label id="status-label">Status</label> </body> </html>
Chat.js:

1 window.onload = function() { 2 var textView = document.getElementById("text-view"); 3 var buttonSend = document.getElementById("send-button"); 4 var buttonStop = document.getElementById("stop-button"); 5 var label = document.getElementById("status-label"); 6 var socket = new WebSocket("ws://echo.websocket.org"); 7 socket.onopen = function(event) { 8 label.innerHTML = "Connection open"; 9 } 10 socket.onmessage = function(event) { 11 if (typeof event.data === "string") { 12 label.innerHTML = label.innerHTML + "<br />" + event.data; 13 } 14 } 15 socket.onclose = function(event) { 16 var code = event.code; 17 var reason = event.reason; 18 var wasClean = event.wasClean; 19 if (wasClean) { 20 label.innerHTML = "Connection closed normally."; 21 } 22 else { 23 label.innerHTML = "Connection closed with message: " + 24 reason + " (Code: " + code + ")"; 25 } 26 } 27 socket.onerror = function(event) { 28 label.innerHTML = "Error: " + event; 29 } 30 buttonSend.onclick = function() { 31 if (socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) { 32 socket.send(textView.value); 33 } 34 } 35 buttonStop.onclick = function() { 36 if (socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) { 37 socket.close(); 38 } 39 } 40 }
Server side:
Server Client
Create a server on localhost:8181
Start running
Initial handshake: establish connection <----------- Request connection
Handle the incoming message --------------------> Send message
refer to book (p. 31):http://www.amazon.com/Getting-Started-HTML5-WebSocket-Programming/dp/1782166963
create dll file in c#