Android学习笔记29:切换卡TabHost控件的使用
在Android中,通常可以使用切换卡(选项卡)实现切换显示不同页面内容的功能。这一功能可以通过TabHost控件来实现。
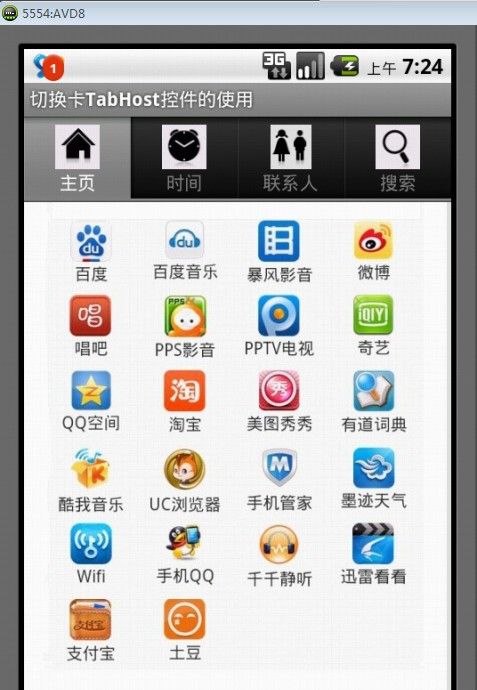
下面我们就通过一个简单的实例演示如何使用TabHost控件完成切换卡功能,完成后的运行效果如图1所示。
图1 主页显示效果
可以看出,在该实例中,总共设置了四个TabHost标签,分别为主页、时间、联系人和搜索。在点击这些标签时,便可以完成相应页面内容的显示。
1.界面布局
TabHost是整个Tab的容器,是由TabWidget和FrameLayout 两部分组成的。其中,TabWidget是每个tab的标签,而FrameLayout则是tab所要显示的内容。
根据以上的描述,我们就可以对整个显示界面进行合理的布局了。我们以LinearLayout的垂直布局方式将整个TabHost分成上下两部分,上面使用TabWidget控件显示标签,下面使用FrameLayout布局显示每个标签下的对应内容。
具体的xml布局文件源码如下:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:id="@android:id/tabhost" 4 android:layout_width="match_parent" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent" > 6 7 <LinearLayout 8 android:orientation="vertical" 9 android:layout_width="match_parent" 10 android:layout_height="match_parent"> 11 12 <!-- TabHost的标签 --> 13 <TabWidget 14 android:id="@android:id/tabs" 15 android:layout_width="match_parent" 16 android:layout_height="wrap_content" > 17 </TabWidget> 18 19 <!-- TabHost的内容 --> 20 <FrameLayout 21 android:id="@android:id/tabcontent" 22 android:layout_width="match_parent" 23 android:layout_height="match_parent" > 24 25 <!-- 第一个标签要显示的内容 --> 26 <ImageView 27 android:id="@+id/homeimage" 28 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 29 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 30 android:src="@+drawable/homeimage" 31 android:background="#FFFFFF" ></ImageView> 32 33 <!-- 第二个标签要显示的内容 --> 34 <LinearLayout 35 android:id="@+id/time" 36 android:layout_width="match_parent" 37 android:layout_height="match_parent" 38 android:orientation="vertical" 39 android:background="#000000"> 40 <AnalogClock 41 android:layout_marginTop="30dp" 42 android:layout_width="match_parent" 43 android:layout_height="wrap_content" ></AnalogClock> 44 <DigitalClock 45 android:textColor="#FFFFFF" 46 android:gravity="center_horizontal" 47 android:layout_marginTop="10dp" 48 android:layout_width="match_parent" 49 android:layout_height="wrap_content" ></DigitalClock> 50 </LinearLayout> 51 52 <!-- 第三个标签要显示的内容 --> 53 <TextView 54 android:id="@+id/personlist" 55 android:layout_width="match_parent" 56 android:layout_height="match_parent" 57 android:text="联系人列表"> 58 </TextView> 59 60 <!-- 第四个标签要显示的内容 --> 61 <LinearLayout 62 android:id="@+id/searcher" 63 android:orientation="horizontal" 64 android:layout_width="match_parent" 65 android:layout_height="match_parent" > 66 <EditText 67 android:layout_weight="5" 68 android:layout_width="0dp" 69 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 70 android:hint="请输入搜索关键字" ></EditText> 71 <Button 72 android:layout_weight="1" 73 android:layout_width="0dp" 74 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 75 android:text="搜索"> </Button> 76 </LinearLayout> 77 78 </FrameLayout> 79 </LinearLayout> 80 </TabHost>
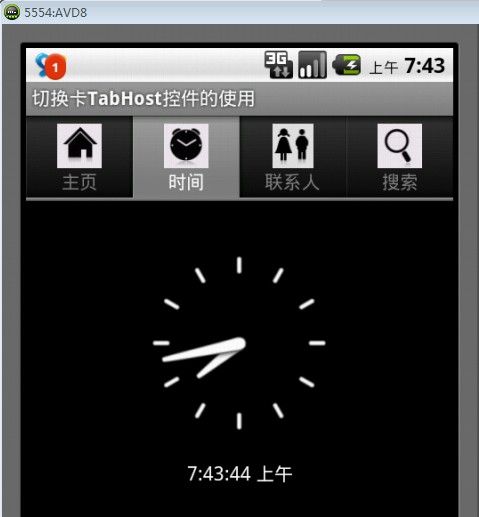
通过以上代码可以看出,在FrameLayout布局中分别实现了四个标签下所要显示的内容的布局设置。比如,在第二个标签“时间”中,我们以LinearLayout的垂直布局方式显示了一个指针式时钟AnalogClock和数字式时钟DigitalClock,其显示效果如图2所示。
此外,在使用TabHost控件时有一点需要特别注意,TabHost、TabWidget以及FrameLayout的id是固定的,必须按如下形式进行设置。
(1)TabHost的android:id必须设置为:android:id="@android:id/tabhost"
(2)TabWidget的android:id必须设置为:android:id="@android:id/tabs"
(3)FrameLayout的android:id必须设置为:android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
图2 时间显示效果
2.TabHost控件的常用方法
了解了如何对TabHost控件进行布局之后,我们还需要了解TabHost控件的一些常用方法。具体如下:
(1)public void addTab (TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec); //添加Tab
(2)public int getCurrentTab (); //获取当前Tab的index
(3)public String getCurrentTabTag (); //获取当前Tab的tag
(4)public View getCurrentTabView (); //获取当前Tab的视图
(5)public void setCurrentTab (int index); //设置当前显示哪个Tab
(6)public void setCurrentTabByTag (String tag); //设置当前显示哪个Tab
3.TabHost.TabSpec
从TabHost控件的常用方法中可以看出,要将Tab加入到TabHost中,需要使用到addTab (TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec)方法,而这个方法的参数是一个TabHost.TabSpec对象,那么TabHost的内部类TabHost.TabSpec是用来干嘛的呢?
我们已经知道,每个Tab都是由TabWidget和FrameLayout 两部分组成的。而TabHost.TabSpec可以为每个Tab设置一个Tag(类型为String),以此来跟踪每一个Tab。此外,TabHost.TabSpec还可以为Tab设置标签、图标以及内容。由此可以看出TabHost.TabSpec类对TabHost控件来说是及其重要的。
TabHost.TabSpec类的常用方法如图3所示。
图3 TabHost.TabSpec类的常用方法
由图3可以看出,在TabHost.TabSpec类中提供了设置Tab标签和图标的方法setIndicator(),以及设置Tab内容的方法setContent()。利用这两个方法,我们便可以将我们在xml布局文件中定义好的Tab内容加载到对应的TabHost控件中了。具体实现方法如下:
1 /* 2 * Function : onCreate() 3 * Author : 博客园-依旧淡然 4 */ 5 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 6 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 7 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 8 9 mTabHost = getTabHost(); //获取TabHost对象 10 11 //添加“主页”Tab到TabHost控件中 12 mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("home") 13 .setIndicator("主页", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.home))//设置Tab标签和图标 14 .setContent(R.id.homeimage)); //设置Tab内容 15 16 //添加“时间”Tab到TabHost控件中 17 mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("time") 18 .setIndicator("时间", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.time)) 19 .setContent(R.id.time)); 20 21 //添加“联系人”Tab到TabHost控件中 22 mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("persons") 23 .setIndicator("联系人", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.persons)) 24 .setContent(R.id.personlist)); 25 26 //添加“搜索”Tab到TabHost控件中 27 mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("searcher") 28 .setIndicator("搜索", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.search)) 29 .setContent(R.id.searcher)); 30 31 mTabHost.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.background); //设置TabHost控件的背景图片 32 mTabHost.setCurrentTab(0); //设置当前显示第一个Tab 33 mTabHost.setOnTabChangedListener(this); //设置TabHost控件的事件监听
通过以上代码,我们向TabHost控件中添加了四个Tab对象,并设置了各自的Tab标签和图标以及Tab内容。此外,我们还为TabHost控件设置了背景图片以及默认显示第一个Tab。
4.事件监听
对TabHost控件进行事件监听,需要实现OnTabChangeListener接口中的OnTabChanged()方法。
相关资料:
多页显示Tag的使用
http://blog.csdn.net/flowingflying/article/details/6304289
Android应用底部导航栏(选项卡)实例
http://blog.csdn.net/cjjky/article/details/7209056