javascript中的继承方法
从Javascript面向对象编程(二):构造函数的继承这里,可以看到详细的说明。
我只是将其中的例子做成html文件,便于调试罢了。
1. 构造函数绑定
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function Animal(){
this.species = "动物";
}
Animal.prototype.species2 = "动物2"
function Cat(name,color){
Animal.apply(this, arguments);
this.name=name;
this.color=color;
}
Cat.prototype.type = "猫科动物";
Cat.prototype.eat = function(){alert("吃老鼠")};
var cat1 = new Cat("大毛","黄色");
var cat2 = new Cat("二毛","黑色");
alert(cat1.species); // 大毛
alert(cat1.species2); // 黄色
</script>
</head>
<body>
Test
</body>
</html>
但是这种方法只适合本地变量的继承,并且Animal和Cat之间也没有关系。
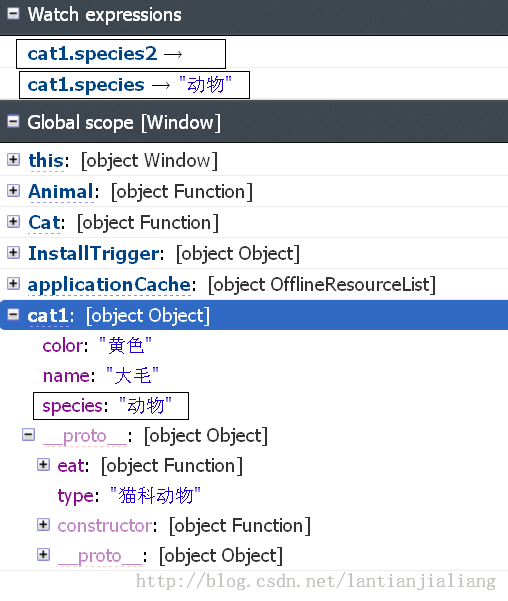
看截图,可以看到从cat1并不能访问Animal.prototype.species2。
2。 prototype模式
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function Animal(){
this.species = "动物";
}
function Cat(name,color){
this.name=name;
this.color=color;
}
Cat.prototype = new Animal();
Cat.prototype.constructor = Cat;
Cat.prototype.type = "猫科动物";
Cat.prototype.eat = function(){alert("吃老鼠")};
var cat1 = new Cat("大毛","黄色");
var cat2 = new Cat("二毛","黑色");
alert(cat1.name); // 大毛
alert(cat1.color); // 黄色
</script>
</head>
<body>
Test
</body>
</html>
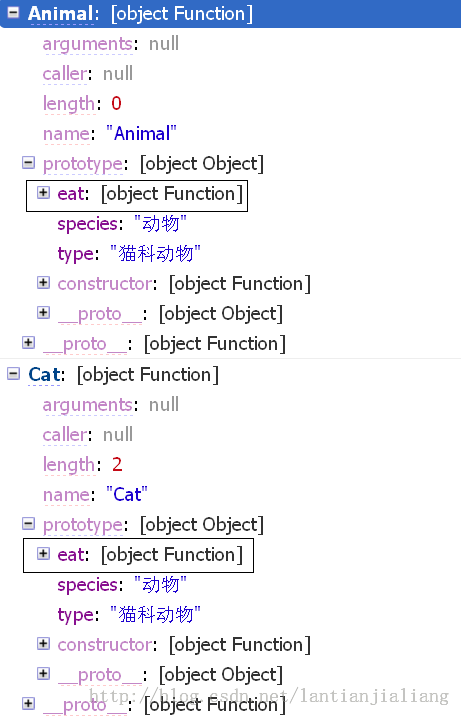
从截图可以看出,prototype还是没有改变javascript内部的继承关系,见直角方框;
圆角方框中的内容就是通过改变prototype,来实现继承。
3. 直接继承prototype
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function Animal(){ }
Animal.prototype.species = "动物";
function Cat(name,color){
this.name=name;
this.color=color;
}
Cat.prototype = Animal.prototype;
Cat.prototype.constructor = Cat;
Cat.prototype.type = "猫科动物";
Cat.prototype.eat = function(){alert("吃老鼠")};
var cat1 = new Cat("大毛","黄色");
var cat2 = new Cat("二毛","黑色");
alert(cat1.name); // 大毛
alert(cat1.color); // 黄色
</script>
</head>
<body>
Test
</body>
</html>
从下面的截图上可以看出,修改Cat.prototype会同时修改Animal.prototype。
4. 利用空对象作为中介
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function extend(Child, Parent) {
var F = function(){};
F.prototype = Parent.prototype;
Child.prototype = new F();
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
Child.uber = Parent.prototype;
}
function Animal(){ }
Animal.prototype.species = "动物";
Animal.prototype.birthPlaces = ['北京','上海','香港'];
function Cat(name,color){
this.name=name;
this.color=color;
}
extend(Cat,Animal);
Cat.prototype.type = "猫科动物";
Cat.prototype.eat = function(){alert("吃老鼠")};
var cat1 = new Cat("大毛","黄色");
cat1.birthPlaces.push('厦门');
var cat2 = new Cat("二毛","黑色");
alert(cat1.name); // 大毛
alert(cat1.color); // 黄色
</script>
</head>
<body>
Test
</body>
</html>
但是这种方法,还是存在子类修改父类的方法。
cat1.birthPlaces.push('厦门');
会直接导致Animal中的birthPlaces变量变化,这时就会牵扯到浅拷贝和深拷贝了。

一句话,上面的方法,都是在模拟继承,但是都不是正的继承。
javascript中现在还不支持继承,只能能下一个版本。