BFCL介绍以及本地模型评测大致流程
文章目录
- 1. BFCL介绍
- 2. 主要构成
-
- 2.1 架构图
- 2.2 代码组成
- 2.2 数据类型
- 3. 评测本地模型
-
- 3.1 增加 handler
- 3.2 增加配置
-
- 3.2.1 配置 bfcl/model_handler/handler_map.py
- 3.2.2 配置 bfcl/eval_checker/model_metadata.py
- 3.2.3 (可选)配置 bfcl/constant.py
- 4. 启动评测
1. BFCL介绍
Berkeley Function Call Leaderboard 是一个用于评估和比较不同函数调用性能的排行榜系统。它是由加州大学伯克利分校的研究人员开发的,旨在帮助研究人员和开发者了解不同函数调用实现的性能表现。
当前已经到 v3 版本,bfcl 的官方资料如下:
- 排行榜:https://gorilla.cs.berkeley.edu/leaderboard
- v1版本:https://gorilla.cs.berkeley.edu/blogs/8_berkeley_function_calling_leaderboard.html
- v2版本:https://gorilla.cs.berkeley.edu/blogs/12_bfcl_v2_live.html
- v3版本:https://gorilla.cs.berkeley.edu/blogs/13_bfcl_v3_multi_turn.html
- github:https://github.com/ShishirPatil/gorilla/tree/main/berkeley-function-call-leaderboard
2. 主要构成
2.1 架构图
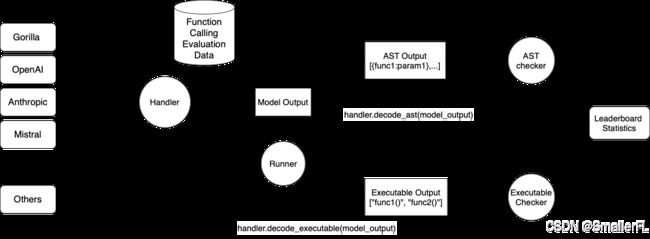
整体而言,BFCL框架可以根据模块划分为以下两块内容:
其中:
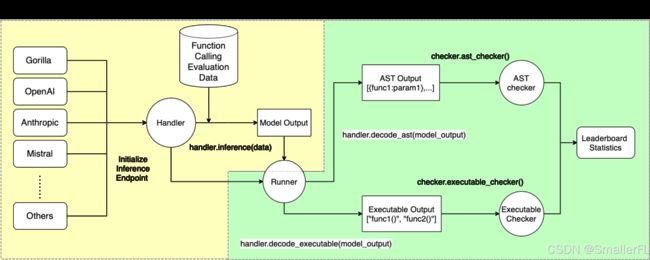
其中:
- 左边黄色框中表示模型根据提供的评测数据集输出推理的结果
- 右边绿色框中表示对模型的推理结果进行评估,计算准确率
2.2 代码组成
berkeley-function-call-leaderboard/
├── bfcl/
│ ├── eval_checker/ # Evaluation modules
│ │ ├── ast_eval/ # AST-based evaluation
│ │ ├── executable_eval/ # Evaluation by execution
│ │ ├── multi_turn_eval/ # Multi-turn evaluation
│ ├── model_handler/ # All model-specific handlers
│ │ ├── oss_model/ # Handlers for locally-hosted models
│ │ │ ├── base_oss_handler.py # Base handler for OSS models
│ │ │ ├── llama_fc.py # Example: LLaMA (FC mode)
│ │ │ ├── deepseek_coder.py # Example: DeepSeek Coder
│ │ │ ├── ...
│ │ ├── proprietary_model/ # Handlers for API-based models
│ │ │ ├── openai.py # Example: OpenAI models
│ │ │ ├── claude.py # Example: Claude models
│ │ │ ├── ...
│ │ ├── parser/ # Parsing utilities for Java/JavaScript
│ │ ├── base_handler.py # Base handler blueprint
│ │ ├── handler_map.py # Maps model names to handler classes
├── data/ # Datasets
├── result/ # Model responses
├── score/ # Evaluation results
├── utils/ # Helper scripts2. 数据类型
2.2 数据类型
- all:包含全部的评测数据集;
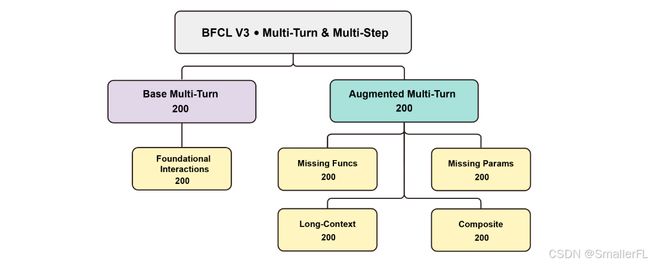
- multi_turn。仅包含多轮对话的评测数据集,v3版本新增;
- single_turn。仅包含单轮对话的评测数据集,v1+v2版本的数据集;
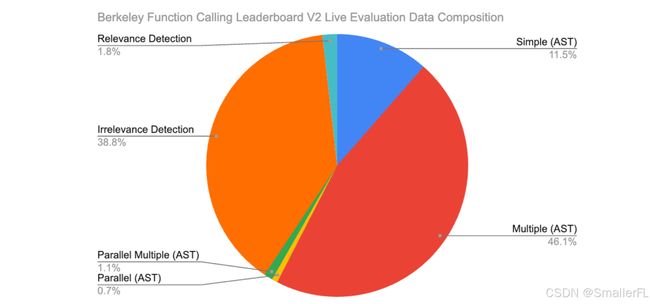
- live。仅包含 live 的评测数据集,live 是指用户提供的、定期更新的,非原官方自带的;
- non_live。除live评测数据集之外的,可以理解为官方提供的;
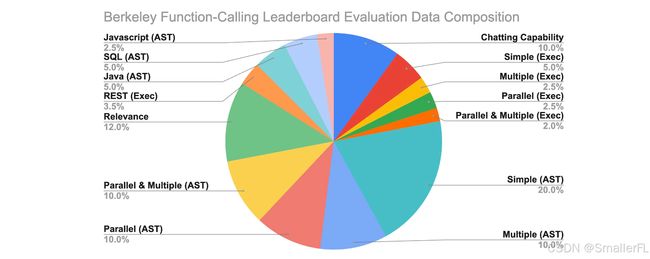
- ast:本地函数调用,包含 live/non_live,评测函数名+函数参数,除去 live 的内容是此前 v1 版本主要的评测内容;
- executable:需要执行出函数结果,包含本地执行+API调用;
- non_python:除去 python 函数,包含 java、javascript等函数的;
- python:只包含 python 函数调用的;
- python_ast:python 中仅包含 ast 类别的
3. 评测本地模型
用 bfcl 评测你的模型,需要先做好以下准备工作:
- 下载 bfcl 代码,https://github.com/ShishirPatil/gorilla/tree/main/berkeley-function-call-leaderboard
- 进入到 berkeley-function-call-leaderboard-v3 目录下,进行下面章节的代码配置工作
- 用 vllm 服务拉起你的模型
3.1 增加 handler
handler 是用于控制具体模型的代码细节的,继承代码中的 Base Handler:bfcl/model_handler/base_handler.py,下面代码是官方已经实现的openai模型的handler代码:
import json
import os
import time
from bfcl.model_handler.base_handler import BaseHandler
from bfcl.model_handler.constant import GORILLA_TO_OPENAPI
from bfcl.model_handler.model_style import ModelStyle
from bfcl.model_handler.utils import (
combine_consecutive_user_prompts,
convert_system_prompt_into_user_prompt,
convert_to_function_call,
convert_to_tool,
default_decode_ast_prompting,
default_decode_execute_prompting,
format_execution_results_prompting,
func_doc_language_specific_pre_processing,
retry_with_backoff,
system_prompt_pre_processing_chat_model,
)
from openai import OpenAI, RateLimitError
class OpenAIHandler(BaseHandler):
def __init__(self, model_name, temperature) -> None:
super().__init__(model_name, temperature)
self.model_style = ModelStyle.OpenAI
self.client = OpenAI(api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"))
def decode_ast(self, result, language="Python"):
if "FC" in self.model_name or self.is_fc_model:
decoded_output = []
for invoked_function in result:
name = list(invoked_function.keys())[0]
params = json.loads(invoked_function[name])
decoded_output.append({name: params})
return decoded_output
else:
return default_decode_ast_prompting(result, language)
def decode_execute(self, result):
if "FC" in self.model_name or self.is_fc_model:
return convert_to_function_call(result)
else:
return default_decode_execute_prompting(result)
@retry_with_backoff(RateLimitError)
def generate_with_backoff(self, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
api_response = self.client.chat.completions.create(**kwargs)
end_time = time.time()
return api_response, end_time - start_time
#### FC methods ####
def _query_FC(self, inference_data: dict):
message: list[dict] = inference_data["message"]
tools = inference_data["tools"]
inference_data["inference_input_log"] = {"message": repr(message), "tools": tools}
if len(tools) > 0:
return self.generate_with_backoff(
messages=message,
model=self.model_name.replace("-FC", ""),
temperature=self.temperature,
tools=tools,
)
else:
return self.generate_with_backoff(
messages=message,
model=self.model_name.replace("-FC", ""),
temperature=self.temperature,
)
def _pre_query_processing_FC(self, inference_data: dict, test_entry: dict) -> dict:
inference_data["message"] = []
return inference_data
def _compile_tools(self, inference_data: dict, test_entry: dict) -> dict:
functions: list = test_entry["function"]
test_category: str = test_entry["id"].rsplit("_", 1)[0]
functions = func_doc_language_specific_pre_processing(functions, test_category)
tools = convert_to_tool(functions, GORILLA_TO_OPENAPI, self.model_style)
inference_data["tools"] = tools
return inference_data
def _parse_query_response_FC(self, api_response: any) -> dict:
try:
model_responses = [
{func_call.function.name: func_call.function.arguments}
for func_call in api_response.choices[0].message.tool_calls
]
tool_call_ids = [
func_call.id for func_call in api_response.choices[0].message.tool_calls
]
except:
model_responses = api_response.choices[0].message.content
tool_call_ids = []
model_responses_message_for_chat_history = api_response.choices[0].message
return {
"model_responses": model_responses,
"model_responses_message_for_chat_history": model_responses_message_for_chat_history,
"tool_call_ids": tool_call_ids,
"input_token": api_response.usage.prompt_tokens,
"output_token": api_response.usage.completion_tokens,
}
def add_first_turn_message_FC(
self, inference_data: dict, first_turn_message: list[dict]
) -> dict:
inference_data["message"].extend(first_turn_message)
return inference_data
def _add_next_turn_user_message_FC(
self, inference_data: dict, user_message: list[dict]
) -> dict:
inference_data["message"].extend(user_message)
return inference_data
def _add_assistant_message_FC(
self, inference_data: dict, model_response_data: dict
) -> dict:
inference_data["message"].append(
model_response_data["model_responses_message_for_chat_history"]
)
return inference_data
def _add_execution_results_FC(
self,
inference_data: dict,
execution_results: list[str],
model_response_data: dict,
) -> dict:
# Add the execution results to the current round result, one at a time
for execution_result, tool_call_id in zip(
execution_results, model_response_data["tool_call_ids"]
):
tool_message = {
"role": "tool",
"content": execution_result,
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
}
inference_data["message"].append(tool_message)
return inference_data
#### Prompting methods ####
def _query_prompting(self, inference_data: dict):
inference_data["inference_input_log"] = {"message": repr(inference_data["message"])}
# These two models have temperature fixed to 1
# Beta limitation: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/reasoning/beta-limitations
if "o1-preview" in self.model_name or "o1-mini" in self.model_name:
return self.generate_with_backoff(
messages=inference_data["message"],
model=self.model_name,
temperature=1,
)
else:
return self.generate_with_backoff(
messages=inference_data["message"],
model=self.model_name,
temperature=self.temperature,
)
def _pre_query_processing_prompting(self, test_entry: dict) -> dict:
functions: list = test_entry["function"]
test_category: str = test_entry["id"].rsplit("_", 1)[0]
functions = func_doc_language_specific_pre_processing(functions, test_category)
test_entry["question"][0] = system_prompt_pre_processing_chat_model(
test_entry["question"][0], functions, test_category
)
# Special handling for o1-preview and o1-mini as they don't support system prompts yet
if "o1-preview" in self.model_name or "o1-mini" in self.model_name:
for round_idx in range(len(test_entry["question"])):
test_entry["question"][round_idx] = convert_system_prompt_into_user_prompt(
test_entry["question"][round_idx]
)
test_entry["question"][round_idx] = combine_consecutive_user_prompts(
test_entry["question"][round_idx]
)
return {"message": []}
def _parse_query_response_prompting(self, api_response: any) -> dict:
return {
"model_responses": api_response.choices[0].message.content,
"model_responses_message_for_chat_history": api_response.choices[0].message,
"input_token": api_response.usage.prompt_tokens,
"output_token": api_response.usage.completion_tokens,
}
def add_first_turn_message_prompting(
self, inference_data: dict, first_turn_message: list[dict]
) -> dict:
inference_data["message"].extend(first_turn_message)
return inference_data
def _add_next_turn_user_message_prompting(
self, inference_data: dict, user_message: list[dict]
) -> dict:
inference_data["message"].extend(user_message)
return inference_data
def _add_assistant_message_prompting(
self, inference_data: dict, model_response_data: dict
) -> dict:
inference_data["message"].append(
model_response_data["model_responses_message_for_chat_history"]
)
return inference_data
def _add_execution_results_prompting(
self, inference_data: dict, execution_results: list[str], model_response_data: dict
) -> dict:
formatted_results_message = format_execution_results_prompting(
inference_data, execution_results, model_response_data
)
inference_data["message"].append(
{"role": "user", "content": formatted_results_message}
)
return inference_data
BFCL 评测模型支持两种模式:
- Function Calling (FC) Mode:可以通过 openai API 访问。模型用 VLLM 的推理服务拉起来的,适用于这种。对应于上面代码中的
#### FC methods ####注解下需要实现的内容。 - Prompting Mode:没有本地函数调用能力的模型依赖于传统的基于 prompt 的交互,我们在 system prompt 部分提供函数定义,而不是专用的工具部分。提示模式也可以作为支持 FC 模式但不能充分利用其函数调用能力的模型的替代方法。对应于上面代码中的
#### Prompting methods ####注解下需要实现的内容。
无论 Function Calling Mode 还是 Prompting Mode,所有的handlers 都需要实现的函数:
decode_ast: 将原始模型输出转换为字典的结构化列表,每个字典代表一个函数调用:
[{"func1": {"param1": "val1", "param2": "val2"}}, {"func2": {"param1": "val1"}}]decode_execute: 将原始模型输出转换为表示可调用函数的字符串列表:
["func1(param1=val1, param2=val2)", "func2(param1=val1)"]
3.2 增加配置
3.2.1 配置 bfcl/model_handler/handler_map.py
在代码文件中 bfcl/model_handler/handler_map.py 把新增的 handler 添加到下面的 map 中:
# 对应 Function Calling (FC) Mode
api_inference_handler_map = {
"gorilla-openfunctions-v2": GorillaHandler,
"o1-preview-2024-09-12": OpenAIHandler,
"o1-mini-2024-09-12": OpenAIHandler,
"gpt-4o-2024-08-06": OpenAIHandler,
...
}
# 对应 Prompting Mode
local_inference_handler_map = {
"google/gemma-2-2b-it": GemmaHandler,
"google/gemma-2-9b-it": GemmaHandler,
"google/gemma-2-27b-it": GemmaHandler,
"meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct": LlamaHandler
...
}
3.2.2 配置 bfcl/eval_checker/model_metadata.py
在代码文件中 bfcl/eval_checker/model_metadata.py 将你的模型信息添加下面的 map 中 :
# 将你的模型信息添加下面的map中
MODEL_METADATA_MAPPING = {
"gorilla-openfunctions-v2": [
"Gorilla-OpenFunctions-v2 (FC)",
"https://gorilla.cs.berkeley.edu/blogs/7_open_functions_v2.html",
"Gorilla LLM",
"Apache 2.0",
],
"o1-preview-2024-09-12": [
"o1-preview-2024-09-12 (Prompt)",
"https://openai.com/index/introducing-openai-o1-preview/",
"OpenAI",
"Proprietary",
],
...
}
3.2.3 (可选)配置 bfcl/constant.py
如果你需要自定义测试的数据集内容,可以添加你需要评测的内容,在代码文件 bfcl/constant.py 中新增评测数据集,例如:
TEST_COLLECTION_MAPPING = {
# 自定义新添的
"youtest": [
...
"simple",
"irrelevance",
"parallel",
"multiple",
"parallel_multiple",
"java",
"javascript",
...
],
...
}
4. 启动评测
注意,以上流程为大致流程,涉及到的具体细节没有完全展开。
- 推理
python openfunctions_evaluation.py \
--model xxx \ # 模型名称
--test-category xxx \ # 评测的类型,默认是all
--temperature xx \ # 推理的参数,温度设置,默认0.001
--num-threads xx \ # 线程数量,默认1
--num-gpus xx \ # 推理的gpu数量,默认1
--gpu-memory-utilization xx # gpu内存使用率,默认0.9
上述结果完成后,在 ./result 目录下会有对应数据集的推理结果
- 打分
python bfcl/eval_checker/eval_runner.py \
--model xxx \
--test-category xxx
上述结果完成后,在 ./score 目录下会有对应数据集的打分结果,并且有 .csv 文件的全部分数汇总。
ps:如果出现 python 本地导包路径报错,在代码开头手动添加包路径:
import sys
sys.path.append("./")
sys.path.append("../")
sys.path.append("../../")
欢迎关注本人,我是喜欢搞事的程序猿; 一起进步,一起学习;
欢迎关注知乎/CSDN:SmallerFL
也欢迎关注我的wx公众号(精选高质量文章):一个比特定乾坤