C++过程化编程的复习之数组、指针、函数参数的传递
先问你个问题
你觉得下面这种创建数组的方式正确吗?如果正确,数组中的元素是什么呢?
int arr[10] {};
C++11标准以后,这种方法是正确的,可以创建一个储存10个元素的数组,其中每个元素都是0.
有人可能会觉得奇怪,不是应该有个 = 吗?
在C++11标准以后,下面这些初始化语句都是正确的
int emus{7}; // set emus to 7
int rheas = {12}; // set rheas to 12
int rocs = {}; // set rocs to 0
int psychics{}; // set psychics to 0
double earnings[4] {1.2e4, 1.6e4, 1.1e4, 1.7e4}; // okay with C++11
unsigned int counts[10] = {}; // all elements set to 0
float balances[100] {}; // all elements set to 0
大括号({}) 前的等号(=)有没有都可以。不论是int、float、double 等数据类型,还是数组,没有被初始化为某个具体值的都设置为零。
数组
数组的的声明应指出以下三点:
- 存储在每个元素中的值的类型;
- 数组名;
- 数组中的元素数。
声明数组的通用格式为 typeName arrayName[arraySize];
对,数组的元素数目在声明的时候就要确定的指出 。当然,后面会提到可以用new来创建动态的数组。
指针
指针的基本概念
(1) 什么是指针?
- 指针是一个变量,存储的是另一个变量的内存地址。
- 通过指针,可以间接访问和操作内存中的数据。
(2) 指针的声明
- 语法:
数据类型* 指针变量名;数据类型 *指针变量名;数据类型 * 指针变量名;int* p; // 声明一个指向 int 类型变量的指针 - 数据类型:指针指向的变量的类型。
*符号:表示这是一个指针变量。
(3) 指针的初始化
- 指针在使用前必须初始化,否则会指向一个未知的内存地址(野指针)。
- 初始化方式:
int a = 10; int* p = &a; // p 指向变量 a 的地址
(4) 取地址运算符 &
&用于获取变量的内存地址。int a = 10; int* p = &a; // p 存储 a 的地址
(5) 解引用运算符 *
*用于访问指针指向的内存地址中的值。int a = 10; int* p = &a; cout << *p; // 输出 10
指针与数组
- 数组名是一个常量指针,指向数组的第一个元素。
int arr[3] = {1, 2, 3}; int *p = arr; // p 指向 arr[0] cout << *p; // 输出 1 cout << *(p+1); // 输出 2 - 通过指针遍历数组:
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { cout << *(p + i) << " "; // 输出 1 2 3 }
指针即是数组,数组即是指针(数组是常量指针)
但应注意:
-
数组是固定大小的连续内存块,其名称退化为首元素地址的常量指针。
-
指针是变量,可以指向任意内存地址。
-
关键区别:
- 数组名不可重新赋值(如 int arr[5]; arr = new int[10]; 非法)。
- 指针可以重新指向其他内存(如 int* p; p = new int[10]; 合法)。
new操作符
new可以动态分配内存(为变量和数组分配都可以)
int* p = new int(4);
用new创建动态数组
下面是一个例子
cout << "Input an array size: ";
int sizeofArray;
cin >> sizeofArray;
// Allocation
int * arr1 = new int [sizeofArray]; // An array was created dymaically
cout << "Input the elements of the array allcated: ";
for(int i=0; i> arr1[i];
}
cout << "The array created dynamically is printed as followed: " << endl;
for(int i=0; i 务必确保每次 new 操作都有对应的 delete,避免内存泄漏。
不能将delete用于不是由new分配的内存的释放。
函数参数的传递
函数参数的传递有值传递和引用传递
下面是一个课堂案例
#include
using namespace std;
// 函数原型声明
void swapValues1(int a, int b); // 函数原型
void swapValues2(int* a, int* b); // 函数原型
void swapValues3(int& a, int& b); // 函数原型
void printArray1(int* arr, int len);
void printArray2(int** arr, int row, int col);
void allocateArray1(int** arr1, int len); // 分配一维数组内存
void reclaimArray1(int** arr1);
void allocateArray2(int*& arr1, int len); // 分配二维数组内存
int main() {
int a, b;
cout << "Input two integers: ";
cin >> a >> b;
cout << "Before function calling******************swapValues(int a, int b)" << endl;
cout << "a=" << a << " " << "b=" << b << endl;
// 函数调用
swapValues1(a, b);
cout << "After function calling******************swapValues(int a, int b)" << endl;
cout << "a=" << a << " " << "b=" << b << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "Before function calling******************swapValues2(int *a, int *b)" << endl;
cout << "a=" << a << " " << "b=" << b << endl;
// 函数调用
swapValues2(&a, &b);
cout << "After function calling******************swapValues2(int *a, int *b)" << endl;
cout << "a=" << a << " " << "b=" << b << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "Before function calling******************swapValues3(int & a, int & b)" << endl;
cout << "a=" << a << " " << "b=" << b << endl;
// 函数调用
swapValues3(a, b);
cout << "After function calling******************swapValues3(int & a, int & b)" << endl;
cout << "a=" << a << " " << "b=" << b << endl;
cout << endl;
int array1[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
printArray1(array1, 5);
int row, col;
cout << "Input the row and col of the two demensional array: ";
cin >> row >> col;
int** arr2; // 动态分配二维数组
// 分配内存
arr2 = new int* [row];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
arr2[i] = new int[col];
}
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
arr2[i][j] = i + j + 1; // arr2[i][j]
}
}
printArray2(arr2, row, col);
// 回收内存
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
delete[] arr2[i];
}
delete[] arr2;
arr2 = NULL;
int* list1 = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
list1[i] = i + 1;
}
printArray1(list1, 5);
allocateArray1(&list1, 10);
reclaimArray1(&list1);
return 0;
}
void swapValues1(int a, int b) {
int x = a;
a = b;
b = x;
}
void swapValues2(int* a, int* b) {
int x = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = x;
}
void swapValues3(int& a, int& b) {
int x = a;
a = b;
b = x;
}
void printArray1(int* arr, int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void printArray2(int** arr, int row, int col) {
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << " "; // arr[i][j]
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void allocateArray1(int** arr1, int len) {
*arr1 = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
(*arr1)[i] = i + 1;
}
printArray1(*arr1, len);
}
void reclaimArray1(int** arr1) {
delete[] * arr1;
*arr1 = NULL;
}
void allocateArray2(int*& arr1, int len) {
arr1 = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
arr1[i] = i + 1;
}
}
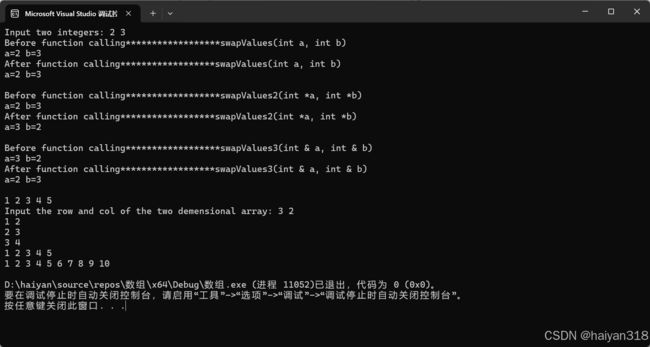
代码说明:
- swapValues1:使用值传递,不会改变原始变量的值。
- swapValues2:使用指针传递,可以改变原始变量的值。
- swapValues3:使用引用传递,可以改变原始变量的值。
- printArray1:打印一维数组。
- printArray2:打印二维数组。
- allocateArray1:分配一维数组内存。
- reclaimArray1:回收一维数组内存。
- allocateArray2:分配二维数组内存。