LeetCode热题100JS(37/100)第七天|排序链表|合并K个升序链表|LRU缓存|二叉树的中序遍历|二叉树的最大深度|对称二叉树
148. 排序链表
题目链接:148. 排序链表
难度:中等
刷题状态:1刷
新知识:
- `dic.reduceRight((t,c)=>(c.next=t,c),null)` 方法从数组的末尾开始执行
解题过程
思考
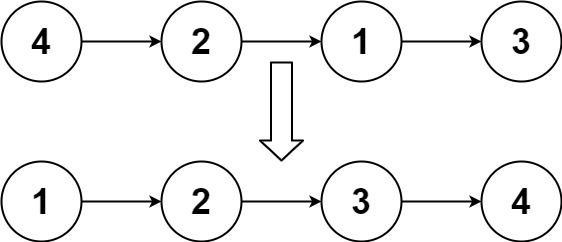
示例 1:
输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
当然可以转成数组排序再生成链表,但我感觉这考点应该不是这个
题解分析
参考题解链接:240. 搜索二维矩阵 II(贪心,清晰图解)
好吧,可以这么写,,而且速度还挺快
详细分析如下
var sortList = function(head) {
let dic=[]
while(head){
//将当前节点压入数组中
dic.push(head)
head=head.next
}
dic.sort((a,b)=>a.val-b.val)
//reduceRight 方法从数组的末尾开始执行,逐步向数组的开头移动。
//reduceRight 的回调函数接受两个参数:累加器 t 和当前值 c。
//t(累加器):在每次迭代中,t 代表已经连接好的链表部分。在第一次迭代时,t 是 null,因为链表的最后一个节点的 next 应该是 null。
//(c.next = t, c) 是一个使用逗号运算符的表达式。
//c.next = t:将当前节点 c 的 next 指针指向累加器 t。这样就将当前节点连接到了已经连接好的链表部分。
//c:逗号运算符会返回其第二个操作数的结果,因此这里返回的是当前节点 c。这个返回值将成为下一次迭代中的累加器 t。
return dic.reduceRight((t,c)=>(c.next=t,c),null)
}手搓答案(无非废话版)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var sortList = function(head) {
let dic=[]
while(head){
dic.push(head)
head=head.next
}
dic.sort((a,b)=>a.val-b.val)
return dic.reduceRight((t,c)=>(c.next=t,c),null)
}总结
done
23. 合并 K 个升序链表
题目链接:23. 合并 K 个升序链表
难度:困难
刷题状态:1刷
新知识:
- `lists.flat()`
- `const flatArray = nestedArray.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => {
return accumulator.concat(currentValue);
}, []);` 拍平数组
解题过程
思考
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6] 解释:链表数组如下: [ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
注意这里是链表数组
还是转换成数组处理好了再生成链表
题解分析
参考题解链接:合并K个排序链表
手搓答案(无非废话版)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode[]} lists
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeKLists = function(lists) {
let dic=[]
for(let l of lists){
while(l){
dic.push(l.val)
l=l.next
}
}
dic.sort((a,b)=>a-b)
let dum=new ListNode(dic[0]),cur=dum
if(!dic.length) return dum.next
for(let i=1;i总结
done
146. LRU 缓存
题目链接:146. LRU 缓存
难度:中等
刷题状态:1刷
新知识:
- `this.cache.keys().next().value;` 这行代码用于获取
Map对象中最旧的键(即第一个插入的键)
解题过程
思考
示例:
输入
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
一看就没刷过,直接看答案
题解分析
参考题解链接:240. 搜索二维矩阵 II(贪心,清晰图解)
详细分析如下
/**
* @param {number} capacity
*/
//LRUCache(int capacity) 以 正整数 作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
var LRUCache = function(capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity; // 初始化缓存的最大容量
this.cache = new Map(); // 使用 Map 对象来存储缓存的键值对
};
/**
* @param {number} key
* @return {number}
*/
//int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。
LRUCache.prototype.get = function(key) {
if (!this.cache.has(key)) {
return -1; // 如果缓存中没有这个key,返回-1
}
// 获取值,并将该键值对移到 Map 的末尾,表示最近使用
const value = this.cache.get(key);
this.cache.delete(key);
this.cache.set(key, value);
return value;
};
/**
* @param {number} key
* @param {number} value
* @return {void}
*/
//void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字 key 已经存在,则变更其数据值 value ;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组 key-value 。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过 capacity ,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
LRUCache.prototype.put = function(key, value) {
if (this.cache.has(key)) {
// 如果键已经存在,删除旧记录
this.cache.delete(key);
} else if (this.cache.size >= this.capacity) {
// 如果缓存已满,删除最旧的记录
//this.cache 是一个 Map 对象。
// keys() 方法返回一个迭代器对象,该迭代器对象按插入顺序包含 Map 对象中所有的键。
// .next():
// next() 方法被调用在迭代器对象上,用于获取迭代器中的下一个值。
// next() 返回一个对象,该对象具有两个属性:value 和 done。
// value 是当前迭代的值(在这个情况下是一个键)。
const oldestKey = this.cache.keys().next().value;
this.cache.delete(oldestKey);
}
// 插入新记录
this.cache.set(key, value);
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new LRUCache(capacity)
* var param_1 = obj.get(key)
* obj.put(key,value)
*/手搓答案(无非废话版)
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @param {number} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
var searchMatrix = function(matrix, target) {
let tag=matrix[0].length-1
for(let i=0;itarget) return false
if(matrix[i][matrix[i].length-1]=0;j--){
if(matrix[i][j]==target) return true
if(matrix[i][j]>target){
tag--
}else{
break
}
}
}
return false
} 总结
难死了,不好理解,多看几遍
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
题目链接:94. 二叉树的中序遍历
难度:简单
刷题状态:1刷
新知识:
解题过程
思考
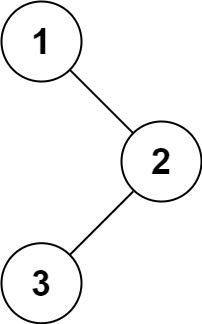
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3] 输出:[1,3,2]
二叉树经典问题,就是我忘了
题解分析
参考题解链接:二叉树的中序遍历
详细分析如下
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
let res=[]
//箭头函数
function inorder(root){
if(!root) return
//体现了中序遍历的“先遍历左子树”的原则。
inorder(root.left)
//体现了中序遍历的“访问根节点”的步骤。
res.push(root.val)
//体现了中序遍历的“再遍历右子树”的原则。
inorder(root.right)
}
inorder(root)
return res
};手搓答案(无非废话版)
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
let res=[]
function inorder(root){
if(!root) return
inorder(root.left)
res.push(root.val)
inorder(root.right)
}
inorder(root)
return res
}总结
拿下
104. 二叉树的最大深度
题目链接:104. 二叉树的最大深度
难度:简单
刷题状态:2刷
新知识:
解题过程
思考
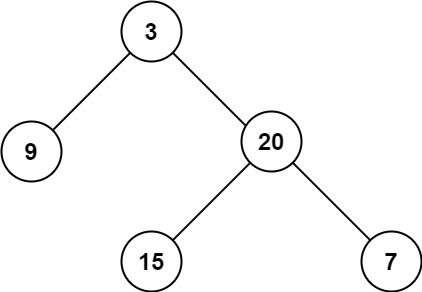
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:3
也是2刷了,放下1刷过程在题解
题解分析
参考题解链接:画解算法:104. 二叉树的最大深度
详细分析如下
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(root){
// console.log('root.left',root.left)
// console.log('root.right',root.right)
let left=maxDepth(root.left)
let right=maxDepth(root.right)
return Math.max(left,right) +1
}else{
return 0
}
};手搓答案(无非废话版)
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function(root) {
let res=0,i=0
function depth(root){
if(!root){
res=Math.max(res,i)
return
}
i++
let tmp=i
depth(root.left)
i=tmp
depth(root.right)
}
depth(root)
return res
};总结
emm,我用的是套路
101. 对称二叉树
题目链接:101. 对称二叉树
难度:简单
刷题状态:2刷
新知识:
解题过程
思考
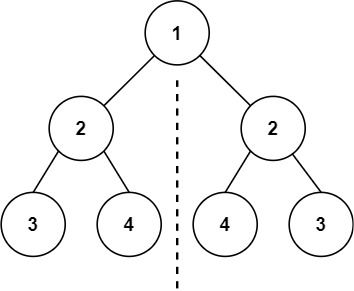
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出:true
也是2刷了,放下1刷过程在题解
没写出来555
题解分析
参考题解链接:对称二叉树
详细分析如下
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
function check(L,R){
if(!L&&!R) return true
if(!L||!R) return false
let ret=L.val==R.val
return ret&&check(L.left,R.right)&&check(L.right,R.left)
}
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
let res=check(root.left,root.right)
return !root||res
};
手搓答案(无非废话版)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
function check(l,r){
if(!l&&!r) return true
if(!l||!r) return false
return l.val==r.val&&check(l.left,r.right)&&check(l.right,r.left)
}
return root?check(root.left,root.right):true
};
总结
emm,我用的是套路