Linux驱动开发IO操作之阻塞与非阻塞
阻塞IO
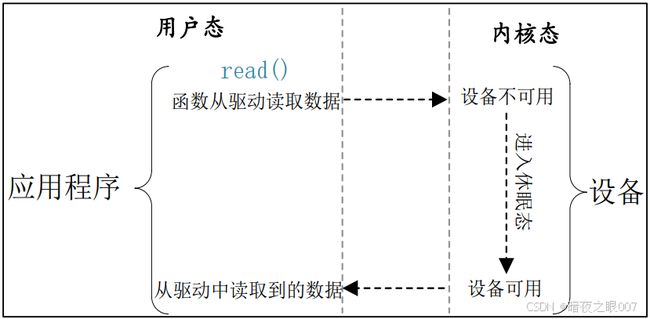
当应用程序通过read读取或write写入设备文件的某些数据时,就会调用驱动程序的read或者write函数,此时可能会遇到没有数据可读或者写满的情况,这时如果驱动程序会进入睡眠,当有数据可读或者可写的时候唤醒再返回,我们称这种操作为阻塞IO。
下图是阻塞式 IO 访问示意图:
阻塞IO相关函数
init_waitqueue_head函数
init_waitqueue_head是Linux内核中用于初始化等待队列头的宏。等待队列是Linux内核中用于同步和唤醒休眠进程的数据结构。等待队列头(wait_queue_head_t)是一个双向循环链表,用于管理所有等待特定事件的进程。等待队列头通过宏init_waitqueue_head进行初始化。其定义如下:
#define init_waitqueue_head(q) \
do { \
static struct lock_class_key __key; \
\
__init_waitqueue_head((q), #q, &__key); \
} while (0)wait_event函数
wait_event函数是Linux内核中用于进程同步的一种机制,主要用于在条件不满足时使进程进入睡眠状态,直到条件满足或被其他进程唤醒。是一种深度睡眠,只有满足条件才能被唤醒。其函数原型如下
#define wait_event(wq, condition) \
do { \
might_sleep(); \
if (condition) \
break; \
__wait_event(wq, condition); \
} while (0)其还有其他系列的变种函数,比如:
wait_event_timeout(wq_head, condition, timeout);
这个函数是增加了超时机制,功能和 wait_event 类似,但是此函数可以添加超时时间,以 jiffies 为单位。此函数有返回值,如果返回 0 的话表示超时时间到,而且 condition 为假。为 1 的话表示condition 为真,也就是条件满足了。
wait_event_interruptible(wq_head, condition);
与 wait_event 函数类似,该函数是一种浅度睡眠,可以被信号唤醒,此函数将进程设置为 TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE,就是可以被信号打断。
wait_event_interruptible_timeout(wq_head,condition, timeout);
与 wait_event_timeout 函数类似,此函数也将进程设置为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE,可以被信号打断。
wake_up函数
该函数是用来唤醒等待中的队列,其函数原型如下:
#define wake_up(x) __wake_up(x, TASK_NORMAL, 1, NULL)
void __wake_up(wait_queue_head_t *q, unsigned int mode,
int nr_exclusive, void *key)
{
unsigned long flags;
spin_lock_irqsave(&q->lock, flags);
__wake_up_common(q, mode, nr_exclusive, 0, key);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&q->lock, flags);
}
该函数的功能是将深度睡眠的的等待队列,也有一些列变种函数
void wake_up_interruptible(struct wait_queue_head *wq_head);
该函数可以唤醒浅度睡眠的队列。
非阻塞IO
在Linux系统中,非阻塞IO(Non-blocking IO)是一种IO操作模式,它与阻塞IO(Blocking IO)相对。在阻塞IO中,当一个进程尝试读取数据但该数据尚未准备好时,该进程会进入等待状态,直到数据准备好并被读取。而非阻塞IO允许进程在数据未就绪时立即返回,而不是阻塞等待。
在Linux中,你可以使用fcntl()系统调用来设置文件描述符为非阻塞模式:
#include
#include
int flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL, 0);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags | O_NONBLOCK); 阻塞IO驱动代码
#include "linux/errno.h"
#include "linux/wait.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define DEV_NAME "block_dev"
#define DEV_CONT 1
typedef struct block_dev{
int major;
int minor;
dev_t dev;
struct cdev cdev;
struct class *cdev_class;
struct device *cdev_device;
/*等待队列头*/
wait_queue_head_t queue_head_read;
wait_queue_head_t queue_head_write;
} Cdev;
static Cdev hello_dev;
/*定义一个内核fifo*/
static DEFINE_KFIFO(fifo, char, 32);
static int cdev_open(struct inode *node, struct file *filp){
filp->private_data = &hello_dev;
return 0;
}
static ssize_t cdev_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset){
int ret;
unsigned int copied;
if(kfifo_is_empty(&fifo)){
if(filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK){
return -EAGAIN;
}else{
printk(KERN_WARNING "\nRead fifo is empty\n");
if(wait_event_interruptible(hello_dev.queue_head_read, !kfifo_is_empty(&fifo)))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
}
ret = kfifo_to_user(&fifo, buf, size, &copied);
if(kfifo_is_empty(&fifo))
wake_up_interruptible(&hello_dev.queue_head_write);
return ret==0 ? copied : ret;
}
static ssize_t cdev_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset){
int ret;
unsigned int copied = 0;
if(kfifo_is_full(&fifo)){
if(filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK){
return -EAGAIN;
}else{
printk(KERN_WARNING "\nWrite fifo is full\n");
if(wait_event_interruptible(hello_dev.queue_head_write, !kfifo_is_full(&fifo)))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
}
ret = kfifo_from_user(&fifo, buf, size, &copied);
if(kfifo_is_full(&fifo))
wake_up_interruptible(&hello_dev.queue_head_read);
return ret==0 ? copied : ret;
}
int cdev_release(struct inode *node, struct file *filp){
return 0;
}
static const struct file_operations cdev_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = &cdev_open,
.read = &cdev_read,
.write = &cdev_write,
.release = &cdev_release
};
/*驱动入口函数*/
static int __init block_io_init(void)
{
int ret;
/*申请设备号*/
hello_dev.major = 0;
if(hello_dev.major){
hello_dev.dev = MKDEV(hello_dev.major, 0);
ret = register_chrdev_region(hello_dev.dev, DEV_CONT , DEV_NAME);
if (ret) {
printk(KERN_ERR "failed to register chrdev region\n");
goto failed_cdev_region;
}
}else{
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&hello_dev.dev, 0, DEV_CONT, DEV_NAME);
if (ret < 0){
printk(KERN_ERR "failed to alloc chrdev region\n");
goto failed_cdev_region;
}
}
/*cdev初始化*/
cdev_init(&hello_dev.cdev, &cdev_ops);
ret = cdev_add(&hello_dev.cdev, hello_dev.dev, DEV_CONT);
if (ret < 0) {
printk(KERN_ERR "err: cdev_add failed\n");
goto err_add;
}
/*在/dev目录自动创建设备节点*/
hello_dev.cdev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, DEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(hello_dev.cdev_class))
goto err_class_create;
hello_dev.cdev_device = device_create(hello_dev.cdev_class, hello_dev.cdev_device, hello_dev.dev, NULL, DEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(hello_dev.cdev_device)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(hello_dev.cdev_device);
goto err_device_create;
}
/*初始化等待队列头*/
init_waitqueue_head(&hello_dev.queue_head_read);
init_waitqueue_head(&hello_dev.queue_head_write);
return 0;
err_device_create:
class_destroy(hello_dev.cdev_class);
err_class_create:
cdev_del(&hello_dev.cdev);
err_add:
unregister_chrdev_region(hello_dev.dev, DEV_CONT);
failed_cdev_region:
return -EFAULT;
}
/*驱动出口函数*/
static void __exit block_io_exit(void)
{
device_destroy(hello_dev.cdev_class, hello_dev.dev);
class_destroy(hello_dev.cdev_class);
cdev_del(&hello_dev.cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(hello_dev.dev, DEV_CONT);
}
/*指定驱动入口函数*/
module_init(block_io_init);
/*指定驱动出口函数*/
module_exit(block_io_exit);
/*标识模块的授权许可*/
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
应用层测试代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define DEVICE_NAME "/dev/block_dev"
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd,ret;
char cmd;
char buf[512];
fd = open(DEVICE_NAME, O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0){
perror("open device");
return -1;
}
while(1){
printf("Next to write or read ?\n");
printf("W is write or R is read\n");
scanf("%c", &cmd);
getchar();
if(cmd == 'W' || cmd == 'w'){
printf("Please enter write data:\n");
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
scanf("%s", buf);
getchar();
//printf("%s\n", buf);
ret = write(fd, buf, strlen(buf)+1);
if(ret < 0){
perror("write device");
close(fd);
}
}else if(cmd == 'R' || cmd == 'r'){
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
ret = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if(ret < 0){
perror("read device");
close(fd);
}
printf("Read: %s\n", buf);
}else{
printf("Cmd is error: %c\n", cmd);
}
putchar('\n');
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
Makefile文件修改
#指定平台
ARCH = arch
#指定交叉编译器
CROSS_COMPILE = arm-linux-gnueabihf
CC = ${CROSS_COMPILE}-gcc
#指定linux源码路径
KERNELDIR := /home/linux_0
CURRENT_PATH := $(shell pwd)
obj-m := wait_event.o
build: kernel_modules
kernel_modules:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) modules
${CC} block_test.c -o block_test
clean:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(CURRENT_PATH) clean
@rm block_test -f
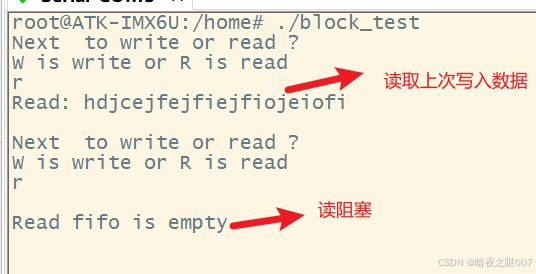
驱动代码验证
将编译的wait_event.ko与block_test拷贝到开发板进行验证: