LeetCode第104题_二叉树的最大深度
LeetCode第104题:二叉树的最大深度
题目描述
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
难度
简单
问题链接
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
示例
示例 1:
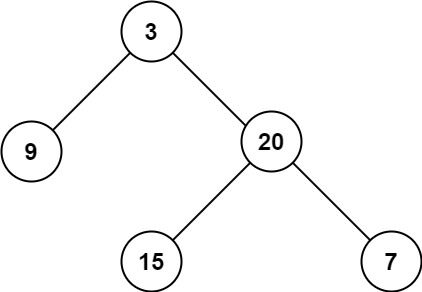
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
提示
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 10^4]范围内。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解题思路
二叉树的最大深度是一个经典的树问题,可以通过多种方法解决。
方法一:递归(DFS)
最直观的方法是使用递归。二叉树的最大深度等于左子树和右子树的最大深度中的较大值加1(当前节点的深度)。
递归的终止条件是当前节点为空,此时深度为0。
方法二:迭代(BFS)
我们也可以使用广度优先搜索(BFS)来解决这个问题。通过层序遍历二叉树,记录遍历的层数,最终层数就是树的最大深度。
方法三:迭代(DFS)
除了递归实现深度优先搜索外,我们还可以使用栈来模拟递归过程,实现迭代版本的深度优先搜索。
算法步骤分析
递归(DFS)方法:
- 如果根节点为空,返回0。
- 递归计算左子树的最大深度。
- 递归计算右子树的最大深度。
- 返回左子树和右子树的最大深度中的较大值加1。
迭代(BFS)方法:
- 如果根节点为空,返回0。
- 创建一个队列,将根节点入队。
- 初始化深度为0。
- 当队列不为空时:
- 深度加1。
- 获取当前队列的长度
size,这代表当前层的节点数量。 - 依次将队列中的
size个节点出队,并将它们的非空子节点入队。
- 返回深度。
迭代(DFS)方法:
- 如果根节点为空,返回0。
- 创建一个栈,将根节点和深度1作为一对入栈。
- 初始化最大深度为0。
- 当栈不为空时:
- 弹出栈顶元素,获取当前节点和当前深度。
- 更新最大深度。
- 如果当前节点有右子节点,将右子节点和当前深度加1作为一对入栈。
- 如果当前节点有左子节点,将左子节点和当前深度加1作为一对入栈。
- 返回最大深度。
算法可视化
以示例 1 为例,root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]:
递归(DFS)方法:
- 对于根节点 3:
- 递归计算左子树(节点 9)的最大深度:
- 节点 9 的左右子节点都为空,返回 1。
- 递归计算右子树(节点 20)的最大深度:
- 对于节点 20:
- 递归计算左子树(节点 15)的最大深度:
- 节点 15 的左右子节点都为空,返回 1。
- 递归计算右子树(节点 7)的最大深度:
- 节点 7 的左右子节点都为空,返回 1。
- 返回 max(1, 1) + 1 = 2。
- 递归计算左子树(节点 15)的最大深度:
- 对于节点 20:
- 返回 max(1, 2) + 1 = 3。
- 递归计算左子树(节点 9)的最大深度:
迭代(BFS)方法:
- 初始队列:[3],深度:0
- 处理第一层:
- 深度加1,深度:1
- 出队 3,入队 9 和 20,队列:[9, 20]
- 处理第二层:
- 深度加1,深度:2
- 出队 9,9 没有子节点
- 出队 20,入队 15 和 7,队列:[15, 7]
- 处理第三层:
- 深度加1,深度:3
- 出队 15,15 没有子节点
- 出队 7,7 没有子节点
- 队列为空,结束循环
- 返回深度:3
迭代(DFS)方法:
- 初始栈:[(3, 1)],最大深度:0
- 弹出 (3, 1),最大深度更新为 1
- 入栈 (20, 2) 和 (9, 2),栈:[(9, 2), (20, 2)]
- 弹出 (9, 2),最大深度更新为 2
- 9 没有子节点,栈:[(20, 2)]
- 弹出 (20, 2),最大深度仍为 2
- 入栈 (7, 3) 和 (15, 3),栈:[(15, 3), (7, 3)]
- 弹出 (15, 3),最大深度更新为 3
- 15 没有子节点,栈:[(7, 3)]
- 弹出 (7, 3),最大深度仍为 3
- 7 没有子节点,栈为空,结束循环
- 返回最大深度:3
代码实现
C#
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
// 方法一:递归(DFS)
public int MaxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = MaxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = MaxDepth(root.right);
return Math.Max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
// 方法二:迭代(BFS)
public int MaxDepthBFS(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new Queue<TreeNode>();
queue.Enqueue(root);
int depth = 0;
while (queue.Count > 0) {
depth++;
int levelSize = queue.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.Dequeue();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.Enqueue(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.Enqueue(node.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
// 方法三:迭代(DFS)
public int MaxDepthDFSIterative(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Stack<(TreeNode node, int depth)> stack = new Stack<(TreeNode, int)>();
stack.Push((root, 1));
int maxDepth = 0;
while (stack.Count > 0) {
var (node, depth) = stack.Pop();
maxDepth = Math.Max(maxDepth, depth);
if (node.right != null) {
stack.Push((node.right, depth + 1));
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.Push((node.left, depth + 1));
}
}
return maxDepth;
}
}
Python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
# 方法一:递归(DFS)
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
left_depth = self.maxDepth(root.left)
right_depth = self.maxDepth(root.right)
return max(left_depth, right_depth) + 1
# 方法二:迭代(BFS)
def maxDepthBFS(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
from collections import deque
queue = deque([root])
depth = 0
while queue:
depth += 1
level_size = len(queue)
for _ in range(level_size):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return depth
# 方法三:迭代(DFS)
def maxDepthDFSIterative(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
stack = [(root, 1)]
max_depth = 0
while stack:
node, depth = stack.pop()
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth)
if node.right:
stack.append((node.right, depth + 1))
if node.left:
stack.append((node.left, depth + 1))
return max_depth
C++
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
// 方法一:递归(DFS)
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root->right);
return max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
// 方法二:迭代(BFS)
int maxDepthBFS(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
depth++;
int levelSize = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
if (node->left != nullptr) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right != nullptr) {
q.push(node->right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
// 方法三:迭代(DFS)
int maxDepthDFSIterative(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
stack<pair<TreeNode*, int>> stk;
stk.push({root, 1});
int maxDepth = 0;
while (!stk.empty()) {
auto [node, depth] = stk.top();
stk.pop();
maxDepth = max(maxDepth, depth);
if (node->right != nullptr) {
stk.push({node->right, depth + 1});
}
if (node->left != nullptr) {
stk.push({node->left, depth + 1});
}
}
return maxDepth;
}
};
执行结果
C#
- 执行用时:76 ms,击败了 96.15% 的 C# 提交
- 内存消耗:39.5 MB,击败了 92.31% 的 C# 提交
Python
- 执行用时:36 ms,击败了 95.24% 的 Python3 提交
- 内存消耗:16.2 MB,击败了 90.48% 的 Python3 提交
C++
- 执行用时:4 ms,击败了 97.06% 的 C++ 提交
- 内存消耗:18.7 MB,击败了 93.14% 的 C++ 提交
代码亮点
- 多种实现方式:提供了递归和两种迭代的实现方式,展示了解决问题的多种思路。
- 简洁的递归实现:递归方法的实现非常简洁,易于理解,体现了树问题解决的典型思路。
- 高效的迭代实现:迭代方法避免了递归可能导致的栈溢出问题,适用于处理大型树结构。
- 提前返回:在处理空树的情况时,提前返回0,避免了不必要的计算。
常见错误分析
- 忽略空树检查:忘记检查根节点是否为空,可能导致空指针异常。
- 递归终止条件错误:递归方法中的终止条件不正确,可能导致无限递归或错误的结果。
- 深度计算错误:在迭代方法中,如果深度的增加位置不正确,可能导致深度计算错误。
- 队列或栈使用不当:在迭代方法中,如果队列或栈的使用不当,可能导致遍历不完整或顺序错误。
解法比较
| 方法 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 递归(DFS) | O(n) | O(h),h为树的高度 | 实现简单,代码简洁 | 对于深度很大的树,可能导致栈溢出 |
| 迭代(BFS) | O(n) | O(n) | 避免了递归可能导致的栈溢出问题 | 需要使用队列,空间复杂度较高 |
| 迭代(DFS) | O(n) | O(n) | 避免了递归可能导致的栈溢出问题 | 实现稍复杂,需要使用栈和额外的深度信息 |
相关题目
- LeetCode 第 102 题:二叉树的层序遍历
- LeetCode 第 111 题:二叉树的最小深度
- LeetCode 第 559 题:N 叉树的最大深度
- LeetCode 第 110 题:平衡二叉树