JavaSE——IO流(上)
一、文件
文件是保存数据的地方,文件中的数据最终是由01这样的数字组成的,从文件中读到内存或者从内存中写一些数据到文件中,一行行二进制数据就像河流一样流动。
1.1创建文件
new File(String pathName) 根据路径建立一个File对象
public void create01() {
String pathName = "D:\\news.txt";
File file = new File(pathName);
try{
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}new File(File parent,String child) 根据父目录文件+子路径构建
public void create02(){
File parentFile = new File("D:\\");
String FileName = "news1.txt";
//这里只是Java中的一个对象
File file = new File(parentFile,FileName);
try{
//这里才真正的创建了文件
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}new File(String parent,String child) 根据父目录+子路径构建
public void create03(){
String parentPath = "D:\\";
String FileName = "news2.txt";
File file = new File(parentPath,FileName);
try{
//这里才真正的创建了文件
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}1.2文件相关方法
public void info(){
File file = new File("D:\\news1.txt");
System.out.println("文件名字=" + file.getName());
System.out.println("文件绝对路径=" + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件父级目录=" + file.getParent());
System.out.println("文件大小(字节)=" + file.length());
System.out.println("文件是否存在=" + file.exists());
System.out.println("是不是一个文件=" + file.isFile());
System.out.println("是不是一个目录=" + file.isDirectory());
}1.3 目录的操作和文件删除
文件删除:
public void m1(){
String filePath = "D:\\news1.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
if(file.exists()){
if(file.delete()){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}else{
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
}
else{
System.out.println("该文件不存在");
}
}目录创建:
mkdir方法创建一级目录
mkdirs方法创建多级目录
public void m2(){
String directoryPath = "D:\\demo\\a\\b\\c";
File file = new File(directoryPath);
if(!file.exists()){
//mkdir方法只能创建单级目录
if(file.mkdirs()){
System.out.println("创建成功");
}else{
System.out.println("创建失败");
}
}
else{
System.out.println("该文件已经存在");
}
}在Java中,将目录视作文件进行处理。
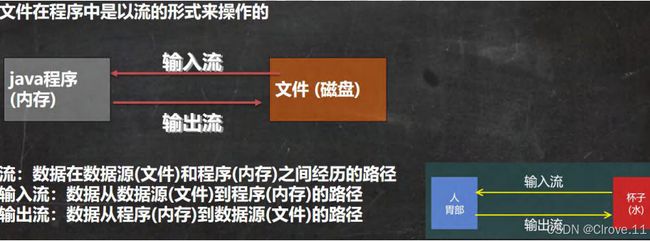
二、IO流原理及流的分类
2.1IO流原理
I/O是Input和Output的缩写,用于处理数据的输入输出,在Java中对于数据的输入输出操作以流(stream)的方式进行。java.io包下提供了各种流类和接口,用于获取不同种类的数据。
2.2流的分类
- 按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流二进制文件,字符流文本文件。
- 按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流。
- 按流的角色不同分为:节点流,处理流/包装流。
Java中的IO流共涉及40多个类,都是从字节输入流InputStream,字符输入流Reader,字节输出流OutputStream,字符输出流Writer这四个抽象基类中派生的。所有子类名称都以其父类作为子类名后缀。
三、FileInputStream
read() 从输入流中读取一个字节。
read(byte[] b) 从输入流中读取最多b.length个字节。public void readFile01(){
String filePath = "D:\\news.txt";
int Data = 0;
FileInputStream fis = null;
try{
fis = new FileInputStream(filePath);
while((Data = fis.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)Data);}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try{
fis.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//通过read(byte[] b)一次读取多个字节
public void readFile02(){
//字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
String filePath = "D:\\news.txt";
int Data = 0;
FileInputStream fis = null;
try{
fis = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流读取最多bytes.length字节的数据到字节数组。
//如果返回-1,表示读取完毕
//如果读取正常,返回实际读取的字节数
while((Data = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,Data));}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try{
fis.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}四、FileOutputStream
write(int) 每次输出一个字节
write(byte[] b, int off, int len)将len字节从位于偏移量off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出public void test() {
//new FileOutStream(filePath) 当前写入内容会覆盖原内容
//new FileOutStream(filePath,true) 当前写入内容时追加到文件后
String filePath = "D:\\news.txt";
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try{
fos = new FileOutputStream(filePath,true);
//写入一个字节
//fos.write('H');
//写入字符串
String str = "hello world";
//getBytes方法可以把字符串->字节数组
//fos.write(str.getBytes());
//write(byte[] b, int off, int len)将len字节从位于偏移量off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流
fos.write(str.getBytes(),0,4);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try{
fos.close();
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}五、FileReader
public void readFile01(){
FileReader fileReader = null;
int data = 0;
try{
fileReader = new FileReader("D:\\news.txt");
while((data = fileReader.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
//一个读入多个字符
@Test
public void readFile02(){
char[] chars = new char[1024];
FileReader fileReader = null;
int data = 0;
try{
fileReader = new FileReader("D:\\news.txt");
while((data = fileReader.read(chars)) != -1){
System.out.print(new String(chars,0,data));
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}六、FileWriter
write(int):写入单个字符
write(char[]):写入指定数组
write(String):写入整个字符串
write(String,off,len):写入字符串的指定部分
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
String filePath = "D:\\news.txt";
char[] chars = {'a','b','c'};
try{
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath);
//write(int):写入单个字符
fileWriter.write('H');
//write(char[]):写入指定数组
fileWriter.write(chars);
write(char[],off,len):写入指定数组的指定部分
fileWriter.write("哔哩哔哩教育",0,3);
//write(String):写入整个字符串
//write(String,off,len):写入字符串的指定部分
}catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//对于FileWriter,一定要关闭流或者flush才能真正把数据写入到文件
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}