QML 中实现程序开机自启动功能
承接Qt/C++软件开发项目,高质量交付,灵活沟通,长期维护支持。需求所寻,技术正适,共创完美,欢迎私信联系!
一、在非QML中设置开机自启动
如果在main函数中直接调用setAutoRun函数,那么不需要将AutoRunManager类注册到QML。可以直接在main函数中创建一个AutoRunManager对象,然后调用其setAutoRun函数。例如:
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling);
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
AutoRunManager autoRunManager;
autoRunManager.setAutoRun(true);
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
engine.load(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml")));
if (engine.rootObjects().isEmpty())
return -1;
return app.exec();
}
二、在QML中设置开机自启动
1、注册对象模式
在Qt中,QML和C++是两个不同的环境,它们有各自的运行时和类型系统。因此,要在QML中使用C++函数,需要通过某种方式将这两个环境连接起来。注册一个可以在QML中访问的对象是实现这种连接的一种方法。
- 创建一个 AutoRunManager 类,实现开启或关闭开机自启动函数setAutoRun
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#define AUTO_RUN_KEY "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run"
class AutoRunManager : public QObject {
Q_OBJECT
public:
Q_INVOKABLE void setAutoRun(bool isStart) {
QString application_name = QGuiApplication::applicationName();
QSettings * settings = new QSettings(AUTO_RUN_KEY, QSettings::NativeFormat);
if (isStart) {
QString application_path = QGuiApplication::applicationFilePath();
settings->setValue(application_name, application_path.replace("/", "\\"));
}
else {
settings->remove(application_name);
}
}
}; - 实现简单的QML界面功能 ,提供开启和关闭按钮
import QtQuick 2.9
import QtQuick.Window 2.2
import com.example 1.0
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12
import QtQuick.Layouts 1.3
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("Hello World")
AutoRunManager {
id: autoRunManager
}
ColumnLayout {
anchors.centerIn: parent
spacing: 20
Button {
text: "Set Auto Run"
onClicked: autoRunManager.setAutoRun(true)
}
Button {
text: "Set Auto Run Stop"
onClicked: autoRunManager.setAutoRun(false)
}
}
}
- 通过qmlRegisterType把AutoRunManager类注册为QML 对象 com.example
#include
#include
#include "AutoRunManager.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
#if defined(Q_OS_WIN)
QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling);
#endif
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
qmlRegisterType("com.example", 1, 0, "AutoRunManager");
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
engine.load(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml")));
if (engine.rootObjects().isEmpty())
return -1;
return app.exec();
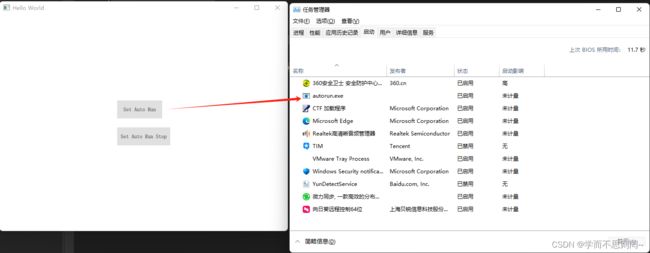
} - 运行程序,点击 Set Auto Run 按钮,任务管理器的启动界面中会新增autorun.exe程序,表示已加入开机自启动;点击 Set Auto Run Stop 按钮,任务管理器的启动界面中会删除autorun.exe程序,表示已退出开机自启动
二、信号和槽模式
如果希望直接在QML中调用C++函数,也可以考虑使用Qt的信号和槽机制。可以在C++中定义一个槽函数,然后在QML中发出一个信号来调用这个槽函数。但是,这种方法需要你在C++和QML之间建立一个信号和槽的连接,这可能会比直接注册一个对象更复杂。
- 创建一个 AutoRunManager 类,实现开启或关闭开机自启动槽函数setAutoRun
#include
#include
#include
#define AUTO_RUN_KEY "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run"
class AutoRunManager : public QObject {
Q_OBJECT
public slots:
void setAutoRun(bool isStart) {
QString application_name = QApplication::applicationName();
QSettings * settings = new QSettings(AUTO_RUN_KEY, QSettings::NativeFormat);
if(isStart) {
QString application_path = QApplication::applicationFilePath();
settings->setValue(application_name, application_path.replace("/", "\\"));
} else {
settings->remove(application_name);
}
}
};
- 通过setContextProperty把AutoRunManager类注册到QML环境中
#include
#include
#include "AutoRunManager.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling);
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
AutoRunManager autoRunManager;
engine.rootContext()->setContextProperty("autoRunManager", &autoRunManager);
engine.load(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml")));
if (engine.rootObjects().isEmpty())
return -1;
return app.exec();
}
- 在QML文件中,就可以直接用已注册得类
AutoRunManager
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
Window {
visible: true
width: 640
height: 480
title: qsTr("Hello World")
ColumnLayout {
anchors.centerIn: parent
spacing: 20
Button {
text: "Set Auto Run"
onClicked: autoRunManager.setAutoRun(true)
}
Button {
text: "Set Auto Run Stop"
onClicked: autoRunManager.setAutoRun(false)
}
}
}
- 运行程序,点击 Set Auto Run 按钮,任务管理器的启动界面中会新增autorun.exe程序,表示已加入开机自启动;点击 Set Auto Run Stop 按钮,任务管理器的启动界面中会删除autorun.exe程序,表示已退出开机自启动
三、注册类型的区别
qmlRegisterType和setContextProperty都是将C++对象暴露给QML,但它们的使用场景和方式有所不同。
- qmlRegisterType是用来注册C++类到QML的类型系统中。这样,就可以在QML中像使用内置类型一样使用C++类。每次在QML中创建一个新的实例时,都会创建一个新的C++对象。例如,可以这样在QML中使用你的类:
import com.example 1.0
AutoRunManager {
id: autoRunManager
}
- setContextProperty则是将一个已经创建的C++对象添加到QML的上下文中。这样,就可以在QML中直接访问这个对象,而不需要创建新的实例。例如,可以这样在QML中使用对象:
Button {
text: "Set Auto Run"
onClicked: autoRunManager.setAutoRun(true)
}
总的来说,如果希望在QML中复用C++类,或者类需要有多个实例,那么应该使用qmlRegisterType。如果类只需要一个实例,或者希望在QML中直接访问一个已经创建的C++对象,那么你应该使用setContextProperty 。