C++ STL 关联式容器之二 map
Hello!!大家早上中午晚上好!!上一篇写到set的实现底层是对红黑树的套用,今天我们也来实现一下map吧!!
一、为什么要用map?
1.1 当通过一个值找另一个值的时候可以使用map
二、map的实现
2.1map的使用
对于map来说重要掌握oprerator[]的实现,只要会operator[]的实现其他都好说!
#include 2.2 实现
上一篇已经实现了RBTree直接包下头文件拉过来用就行:
已实现的RBT头文件:
#pragma once
#include
//定义一个表示颜色的枚举
enum color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
//定义节点
template //这里改成T,T可以是int string 、 pair...只要传什么就给它实例化出什么类型来
struct RBTreeNode
{
T _data;//数据
color _col;//标记颜色
RBTreeNode* _left;//指向左子树
RBTreeNode* _right;//指向右子树
RBTreeNode* _parent;//指向父节点
RBTreeNode(const T& data)//节点的构造函数
:_data(data),_col(RED),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr)//节点默认设置为红色
{
}
};
//包装迭代器
template
class RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeIterator Self;
typedef RBTreeNode Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator iterator;
public:
RBTreeIterator( Node*node)
{
_node = node;
}
RBTreeIterator(const iterator& it)
{
_node = it._node;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self &operator--()
{
//红黑树迭代器--实现方法:1、当左子树不为空时,找左子树最右节点 2、当左子树为空时,找cur是parent右边的parent就是下一个访问的节点
Node* cur = _node;
if (cur->_left)
{
Node* rightmost = cur->_left;
while (rightmost->_right)
{
rightmost = rightmost->_right;
}
_node = rightmost;
}
else
{
//左为空
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent)
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
{
break;
}
else
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self &operator++()
{
//红黑树迭代器++实现方法:1、当右子树不为空时,找右子树最左节点 2、当右子树为空时,找cur是parent左边的parent就是下一个访问的节点
if (_node->_right)
{//右不为空
Node* leftmost = _node->_right;
while (leftmost->_left)
{
leftmost = leftmost->_left;
}
_node = leftmost;
}
else
{//右为空
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent&&cur==parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const Self&it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
Node* _node;
};
//定义红黑树
//set -> RBTree _t;
// map -> RBTree,mapKeyofT> _t;
template
class RBTree
{
public:
typedef RBTreeNode Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator iterator;
typedef RBTreeIterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return iterator(cur);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return const_iterator(cur);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
KeyofT kot;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(key))
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(key))
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
return cur;
}
return nullptr;
}
pair insert(const T& data)//这里为什么要用pair作返回值? 因为map
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
//如果为空树,插入的结点成为根节点
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点必须黑色
return pair(iterator(_root),true);//插入成功
}
//走到这里说明不为空树,开始找插入位置(保证它是一棵二叉搜索树)
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
KeyofT KOT;// 这里为什么要用KOT ? 因为map
while (cur)
{
if (KOT(cur->_data) > KOT(data))
{
parent = cur;//cur往下走之前记录一下
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if(KOT(cur->_data)_right;
}
else
{
//走到这里说明相等,插入失败
return pair(cur,false);
}
}
//走到这里说明找到插入位置,创建新节点并链接
cur = new Node(data);
cur->_col = RED;
Node* newnode = cur;//保存一下新节点位置
//需要判断一下在parent的左还是右
if (KOT(parent->_data) > KOT(data))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//开始判断parent跟uncle的颜色来决定需不需要调整
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)//parent 不为空且parent的颜色为红说明一定存在两个连着的红色节点
{
Node* grandparent = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grandparent->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandparent->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)//如果uncle存在且颜色为红
{
parent->_col = BLACK; //父跟uncle变黑,grandparentB变红并继续往上调整
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
cur = grandparent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//父为空或者黑,需要旋转+变色
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandparent); // 1
grandparent->_col = RED; // 1
parent->_col = BLACK; // 1
}
else
{
RotateL(parent); // 1
RotateR(grandparent); // 1
grandparent->_col = RED; // 1
cur->_col = BLACK;
}
break;//旋转后就平衡了不需要继续往上走
}
}
else //parent==grandparent->right
{
Node* uncle = parent->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色向上调整
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
cur = grandparent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//uncle为黑或不存在,需要旋转
{
if (cur == parent->_right) // 1
{ // 1
RotateL(grandparent); // 1
grandparent->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandparent);
grandparent->_col = RED; // 1
cur->_col = BLACK; // 1
} // 1
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return pair(newnode,true);
}
void RotateL(Node* parent) // 1
{ // 1
Node* cur = parent->_right; // 1
Node* curleft = cur->_left;
parent->_right = curleft;
if (curleft)
{
curleft->_parent = parent;
}
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
cur->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
ppnode->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = ppnode;//记得要链上
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_left; // 1
Node* curright = cur->_right; // 1
parent->_left = curright; // 1
if (curright)
{
curright->_parent = parent;
}
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
cur->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (ppnode==nullptr)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
ppnode->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = ppnode;//记得要链上
}
}
void inOrder()
{
inOrder(_root);
}
void inOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
inOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " : " << root->_kv.second << endl;
inOrder(root->_right);
}
int Hight()//求树高度
{
return Hight(_root);
}
int Hight(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int lefthight = Hight(root->_left);
int righthight = Hight(root->_right);
return lefthight > righthight ? lefthight + 1 : righthight + 1;
}
bool isBalance()
{
return isBalance(_root);
}
bool isBalance(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
if (root->_col != BLACK)
return false;//如果根节点不为黑
//走到这里说明不是空且根节点为黑色
int fiducial = 0;//求出某一条路径的黑色节点数作为基准值
Node* cur = root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
++fiducial;
cur = cur->_left;
}
return checkColour(root, 0, fiducial);
}
bool checkColour(Node* root, int blacknum, int _fiducial)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (blacknum != _fiducial)
{
return false;
}
else
return true;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
++blacknum;
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent && root->_parent->_col == RED)
return false;
return checkColour(root->_left, blacknum, _fiducial) && checkColour(root->_right, blacknum, _fiducial);
}
private:
Node* _root=nullptr;
}; Map的封装:
#pragma once
#include"RBTree4_13.h"
namespace ldc
{
template
class map
{
struct mapKeyofT
{
const K& operator()(const pair& data)
{
return data.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree, mapKeyofT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree,mapKeyofT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
V&operator[](const K&key)
{
pair ret = insert(make_pair(key,V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
pair insert(const pair& kv)
{
return _t.insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree, mapKeyofT> _t;
};
} 三、测试
3.1 用自己自己实现的
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include
using namespace std;
#include
#include "MYset04_12.h"
#include "MYmap.h"
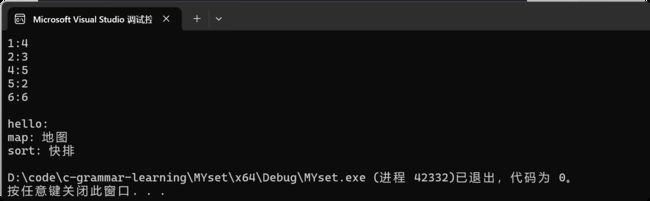
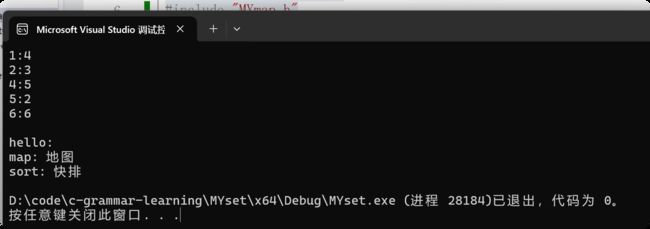
int main()
{
ldc::map mp1;
mp1.insert(make_pair(5, 2));
mp1.insert(make_pair(2, 3));
mp1.insert(make_pair(1, 4));
mp1.insert(make_pair(4, 5));
mp1.insert(make_pair(6, 6));
ldc::map::iterator it1 = mp1.begin();
while (it1 != mp1.end())
{
cout << it1->first <<":" << it1->second <<" ";
++it1;
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
ldc::mapmp2;
mp2.insert(pair("sort","排序"));
mp2["hello"];//插入
mp2["sort"] = "快排";//修改
mp2["map"] = "地图";//插入+修改
ldc::map::iterator it2 = mp2.begin();
while (it2 != mp2.end())
{
cout << it2->first << ": " << it2->second;
++it2;
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
} OK!!以上是map的实现过程,如果对你有所帮助记得点赞收藏+关注哦!!谢谢!!
咱下期见!!(哈希)