freeMarker入门示例
1.创建Web项目freeMarkerDemo。
2.添加jar包---freemarker-2.3.9.jar。
3.在WebContent目录下新建templates文件夹,用于放置模板文件ftl。
4.在templates目录下新建hello.ftl。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello ${user}!</h1>
</body>
</html>
5.在src目录下创建Hello.java文件。
package example;
import freemarker.template.Configuration;
import freemarker.template.Template;
import freemarker.template.TemplateException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Hello extends HttpServlet {
private Configuration cfg;
public void init(){
cfg = new Configuration();
//设置FreeMarker的模版文件位置---此处的templates就是上面建的那个文件夹
cfg.setServletContextForTemplateLoading(getServletContext(),"templates");
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException,IOException{
//数据模型
Map root = new HashMap();
root.put("user", "xin");
//模版文件
Template temp =cfg.getTemplate("hello.ftl");
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=" + temp.getEncoding());
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
//模版+数据模型=输出
try{
temp.process(root,out);
}catch(TemplateException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request,response);
}
}
6.配置web.xml文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>freeMarkerDemo</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Hello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>example.Hello</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
7.新建引导页面index.html。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
点击下面链接看看效果:
<hr>
<a href="hello.do">调用Hello模板</a>
</body>
</html>
8.把项目部署到tomcate服务器,即可运行。
项目工作流程:首先看到index页面,发现程序跳转到hello.do;然后通过web.xml找到执行主体example.Hello,即Hello.java;执行该程序将数据user输出到模板文件hello.ftl中。
作为入门,我们来快速了解三个最为常见的指令---if,list,include
1.if指令
使用if指令可以有条件地跳过模板的一部分。
用法:<#if condition>…</#if>
使用<#else>标签可以指定当条件为假时程序执行的内容。
用法:<#if condition>…<#else>…</#if>
例子,修改hello.ftl
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
hello ${user}!
<#if user=="xin">
,my best friend!!!
<#else>
,happy new year!!!
</#if>
</h1>
</body>
</html>
2.list指令
当需要用列表来遍历集合的内容时,list指令是非常好用的。
list指令的一般格式为:
<#list sequence as loopVariable>repeatThis</#list>
repeatThis部分将会在给定的sequence遍历时在每项中重复,从第一项开始,一个接着一个。在所有的重复中,loopVariable将持有当前项的值。这个循环变量仅在于<#list …>和</#list>标签之间。
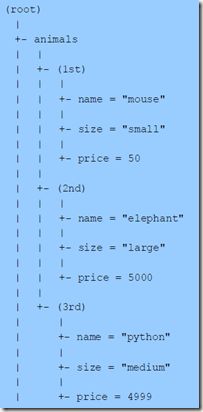
例子,假设有一组animals数据,如下:
java语句为:
List<Animal> animals = new ArrayList<Animal>();
Animal mouse = new Animal("mouse","small",50);
Animal elephant = new Animal("elephant","large",5000);
Animal python = new Animal("python","medium",4999);
animals.add(mouse);
animals.add(elephant);
animals.add(python);
Map<String, List<Animal>> root = new HashMap<String, List<Animal>>();
root.put("animals", animals);
其中Animal是自定义的一个实体类。
修改hello.ftl,以list的方式遍历animals列出所有的animal
<#list animals as being>
<h1>${being.name}---${being.size}---${being.price}</h1>
</#list>
3.include指令
使用include指令,可以在当前的模板中插入其他文件的内容。
用法:<#include “/a.html”>
在templates目录下新建文件a.html,内容为:
<hr> <h3>Hello World~~~</h3>
当需要用到这个文件时,可以使用include指令来实现插入。
修改hello.ftl
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello ${user}!</h1>
<#include "/a.html">
</body>
</html>
运行后将会在页面中显示出a.html中的内容。
上面的图显示的是一组以sequence序列存储的数据。
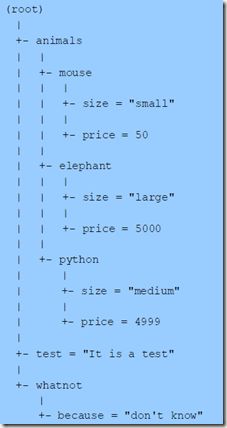
下面给出一组以hash表的形式存储的数据:
java语句为:
Map mouse = new HashMap();
mouse.put("size", "small");
mouse.put("price", 50);
Animal elephant = new Animal("large",5000);
Animal python = new Animal("medium",4999);
Map animals = new HashMap();
animals.put("mouse", mouse);
animals.put("elephant", elephant);
animals.put("python", python);
Map<String, Object> root = new HashMap<String, Object>();
root.put("animals", animals);
root.put("test", "It is a test");
Map whatnot = new HashMap();
whatnot.put("because", "don't know");
root.put("whatnot", whatnot);