Windows核心编程学习三:利用专有命名空间实现单一实例
注:源码为学习《Windows核心编程》的一些尝试,非原创。若能有助于一二访客,幸甚。
1.基本框架
/*******************************************************************************
* File: ErrorShow.cpp
* Time: 2013-04-16
* 描述: 修改试验原书同名程序
*******************************************************************************/
#include <Windows.h>
#include <Windowsx.h>
#include <tchar.h>
#include "resource.h"
// Always compiler using Unicode.
#ifndef UNICODE
#define UNICODE
#endif
#define chHANDLE_DLGMSG(hWnd, message, fn) \
case (message): return (SetDlgMsgResult(hWnd, uMsg, \
HANDLE_##message((hWnd), (wParam), (lParam), (fn))))
BOOL Dlg_OnInitDialog(HWND hwnd, HWND hwndFocus, LPARAM lParam)
{
return TRUE;
}
void Dlg_OnCommand(HWND hwnd, int id, HWND hwndCtl, UINT codeNotify)
{
switch (id) {
case IDOK:
case IDCANCEL:
EndDialog(hwnd, id);
break;
}
}
INT_PTR WINAPI Dlg_Proc(HWND hwnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch (uMsg) {
chHANDLE_DLGMSG(hwnd, WM_COMMAND, Dlg_OnCommand);
chHANDLE_DLGMSG(hwnd, WM_INITDIALOG, Dlg_OnInitDialog);
}
return FALSE;
}
int APIENTRY _tWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, LPTSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(hPrevInstance);
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(lpCmdLine);
DialogBox(hInstance, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_SINGLETON), NULL, Dlg_Proc);
return 0;
}

2.使用可变参数
// Main dialog
HWND g_hDlg;
// 添加一个字符串到编辑框
void AddText(PCTSTR pszFormat, ...)
{
/* VA_LIST的用法:
*(1)首先在函数里定义一具VA_LIST型的变量,这个变量是指向参数的指针;
*(2)然后用VA_START宏初始化变量刚定义的VA_LIST变量;
*(3)然后用VA_ARG返回可变的参数,VA_ARG的第二个参数是你要返回的参数的
* 类型(如果函数有多个可变参数的,依次调用VA_ARG获取各个参数);
*(4)最后用VA_END宏结束可变参数的获取。 */
va_list argList;
va_start(argList, pszFormat);
TCHAR sz[20 * 1024];
Edit_GetText(GetDlgItem(g_hDlg, IDC_EDIT_DETAILS), sz, _countof(sz));
_vstprintf_s(_tcschr(sz, TEXT('\0')), _countof(sz) - _tcslen(sz), pszFormat, argList);
Edit_SetText(GetDlgItem(g_hDlg, IDC_EDIT_DETAILS), sz);
va_end(argList);
}
BOOL Dlg_OnInitDialog(HWND hwnd, HWND hwndFocus, LPARAM lParam)
{
g_hDlg = hwnd;
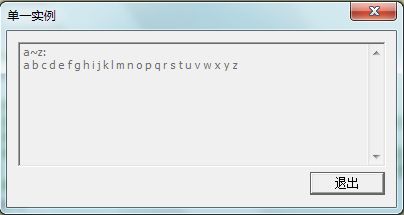
AddText(TEXT("a~z: \r\n"));
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++)
AddText(TEXT("%c "), c);
return TRUE;
}
3.利用专有命名空间实现单实例应用程序
void CheckInstances()
{
// 创建边界描述符
g_hBoundary = CreateBoundaryDescriptor(g_szBoundary, 0);
// 创建一个对应于本地管理员组的安全描述符SID
BYTE localAdminSID[SECURITY_MAX_SID_SIZE];
PSID pLocalAdminSID = &localAdminSID;
DWORD cbSID = sizeof(localAdminSID);
/*
The CreateWellKnownSid function creates a SID for predefined aliases.
BOOL WINAPI CreateWellKnownSid(
__in WELL_KNOWN_SID_TYPE WellKnownSidType,
__in_opt PSID DomainSid,
__out_opt PSID pSid,
__inout DWORD* cbSid
);
Parameters
WellKnownSidType
Member of the WELL_KNOWN_SID_TYPE enumeration that specifies what the SID will identify.
DomainSid
A pointer to a SID that identifies the domain control to use when creating the SID.
Pass NULL to use the local computer.
pSid
A pointer to memory where CreateWellKnownSid will store the new SID.
cbSid
A pointer to a DWORD that contains the number of bytes available at pSid.
The CreateWellKnownSid function stores the number of bytes actually used at this location.
*/
if (!CreateWellKnownSid(WinBuiltinAdministratorsSid, NULL, pLocalAdminSID, &cbSID))
{
AddText(TEXT("添加安全描述符到边界描述符失败: %u\r\n"), GetLastError());
return;
}
// 将本地管理员组的安全描述符与边界描述符关联起来
// 只有管理员身份运行的应用程序能获得该命名空间下的内核对象
if (!AddSIDToBoundaryDescriptor(&g_hBoundary, pLocalAdminSID))
{
AddText(TEXT("添加安全描述符到边界描述符失败: %u\r\n"), GetLastError());
return;
}
// 为本地管理员创建命名空间
SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES sa;
sa.nLength = sizeof(sa);
sa.bInheritHandle = FALSE;
if (!ConvertStringSecurityDescriptorToSecurityDescriptor(TEXT("D:(A;;GA;;;BA)"),
SDDL_REVISION_1, &sa.lpSecurityDescriptor, NULL))
{
AddText(TEXT("安全描述符创建失败: %u\r\n"), GetLastError());
return;
}
g_hNamespace = CreatePrivateNamespace(&sa, g_hBoundary, g_szNamespace);
LocalFree(sa.lpSecurityDescriptor);
// 检查私有命名空间创建是否成功
DWORD dwLastError = GetLastError();
// 创建失败
if (g_hNamespace == NULL)
{
// 如果被拒绝访问,则直接返回
// 这段代码必须在本地管理员账户运行
if (dwLastError == ERROR_ACCESS_DENIED)
{
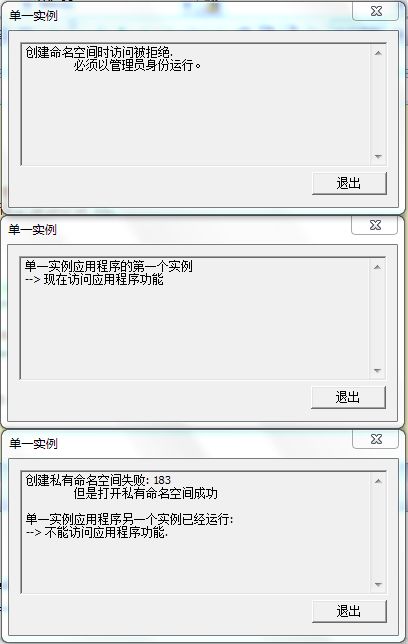
AddText(TEXT("创建命名空间时访问被拒绝.\r\n"));
AddText(TEXT(" 必须以管理员身份运行。\r\n\r\n"));
return;
}
else
{
// 如果在该命名空间另一个实例已经被创建
if (dwLastError == ERROR_ALREADY_EXISTS)
{
AddText(TEXT("创建私有命名空间失败: %u\r\n"), dwLastError);
g_hNamespace = OpenPrivateNamespace(g_hBoundary, g_szNamespace);
if (g_hNamespace == NULL)
{
AddText(TEXT(" 并且打开私有命名空间失败: %u\r\n"), dwLastError);
return;
}
else
{
g_bNamespaceOpened = TRUE;
AddText(TEXT(" 但是打开私有命名空间成功\r\n\r\n"));
}
}
else
{
AddText(TEXT("发生了未知的错误: %u\r\n\r\n"), dwLastError);
return;
}
}
}
// 尝试创建命名互斥量对象
TCHAR szMutexName[64];
StringCchPrintf(szMutexName, _countof(szMutexName), TEXT("%s\\%s"),
g_szNamespace, TEXT("单一实例"));
g_hSingleton = CreateMutex(NULL, FALSE, szMutexName);
if (GetLastError() == ERROR_ALREADY_EXISTS)
{
AddText(TEXT("单一实例应用程序另一个实例已经运行:\r\n"));
AddText(TEXT("--> 不能访问应用程序功能.\r\n"));
}
else
{
AddText(TEXT("单一实例应用程序的第一个实例\r\n"));
AddText(TEXT("--> 现在访问应用程序功能\r\n"));
}
}