java servlet使用velocity引擎
我用的是velocity1.7版本,要在web使用velocity引擎,必须把它的velocity-1.7.jar包放在tomcat(整个tomcat的多个项目可以共用)或者webroot下的web-inf下(只有自己可以用);当然用到servle,就要引入tomcat的servlet-api.jar包,在引入java通用包:rt.jar环境就配置好了
下面写入html(velocity默认的后缀名是vm,我习惯用html):
代码
< html >
< head >
< title > My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page </ title >
</ head >
< body >
#set( $this = "Velocity")
$this is so great!
< br >
#foreach( $name in $list )
$name 真的太奇妙啦! < br />
#end
#set( $condition = true)
#if ($condition)
您选择的是1!
#else
您选择的是0!
#end
< br >
我的主页. < br >
</ body >
</ html >
servlet服务端代码:
doget的方法:
代码
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType( " text/html " );
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
Velocity.init();
VelocityContext context = new VelocityContext();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add( " ArrayList element 1 " );
list.add( " ArrayList element 2 " );
list.add( " ArrayList element 3 " );
list.add( " ArrayList element 4 " );
context.put( " list " , list);
Template template = null ;
String path = null ;
try
{
VelocityEngine velocityEngine = new VelocityEngine();
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 也可以在这里指定绝对路径。当指定相对路径时, 在不同的环境下是有区别的。
// 比如把程序部署到tomcat以后,相对路径相对到哪里是个很恶心的事情。
// String basePath = "";
// 可设置绝对路径
path = this .getClass().getResource( " / " ).toString()
.replaceAll( " ^file:/ " , "" );
path = request.getRealPath( " / " );
// String basePath = "E:/maven/test/velocity/src/main/resources";
// String path =
properties.setProperty(Velocity.FILE_RESOURCE_LOADER_PATH, path);
velocityEngine.init(properties);
template = velocityEngine.getTemplate( " index.html " );
}
catch ( ResourceNotFoundException rnfe )
{
out.println( " Example : error : cannot find template " + path);
}
catch ( ParseErrorException pee )
{
out.println( " Example : Syntax error in template " + " : " + pee );
}
/*
* Now have the template engine process your template using the
* data placed into the context. Think of it as a 'merge'
* of the template and the data to produce the output stream.
*/
// BufferedWriter writer = writer = new BufferedWriter(
// new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
if ( template != null )
template.merge(context, out);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
引入的包名:
 代码
代码
import
java.io.IOException;
import
java.io.PrintWriter;
import
javax.servlet.ServletException;
import
javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import
javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import
javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import
org.apache.velocity.app.Velocity;
import
org.apache.velocity.VelocityContext;
import
org.apache.velocity.Template;
import
org.apache.velocity.exception.ParseErrorException;
import
org.apache.velocity.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import
java.util.ArrayList;
import
java.util.Properties;
import
org.apache.velocity.exception.ParseErrorException;
import
org.apache.velocity.exception.MethodInvocationException;
import
org.apache.velocity.app.VelocityEngine;
请求端:
<
html
>
<
head
>
<
title
>
测试模板
</
title
>
</
head
>
<
body
>
<
a
href
="/servlet/WebServlet?id=aa"
>
测试模板
</
a
>
</
body
>
</
html
>
另存为wellcom.html
添加webroot下面web-inf的web.xml内容:
在web-app标签下添加:
 代码
代码
<
servlet
>
<
servlet-name
>
WebServlet
</
servlet-name
>
<
servlet-class
>
javaweb.WebServlet
</
servlet-class
>
</
servlet
>
<
servlet-mapping
>
<
servlet-name
>
WebServlet
</
servlet-name
>
<
url-pattern
>
/servlet/WebServlet
</
url-pattern
>
</
servlet-mapping
>
<!--
设置开始主页
-->
<
welcome-file-list
>
<
welcome-file
>
wellcom.html
</
welcome-file
>
</
welcome-file-list
>
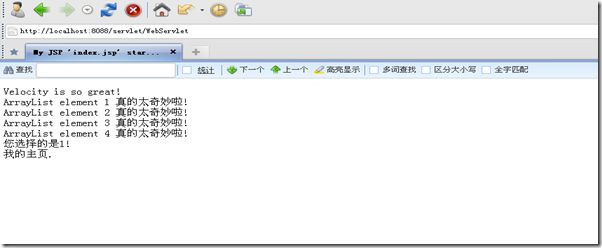
然后打开tomcat,开始运行,结果如下:
这里需要说明一下,welocity引擎会把html页面完全分离,就算你把模板页的后缀修改为jsp,在里面写<%%>服务端语言,输出后,tomcat也不会执行里面的服务器语言,你可以在servlet端添加模板变量,然后由模板语言代替原来的服务端代码
参考velocity api:http://velocity.apache.org/engine/releases/velocity-1.7/apidocs/index.html
这里讲一下里面用到的几个velocity api:
Velocity.init();
velocityEngine.init();
都是初始化引擎,Velocity的官方解释是:Simple Velocity Runtime engine initialization methods.也就是使用的是一个单独的引擎,不能实例化。
velocityEngine:This class provides a separate new-able instance of the Velocity template engine。可以创建多个实例化的引擎,也就是说,一个类里面可以创建多个模板
当然,如果一般网站项目都不会只用到一个项目,所以一般我们还是用velocityEngine的好
VelocityContext 是存放变量的地方,通过初始化:
VelocityContext context = new VelocityContext();
context.put("list", “test”);
可以放置数组,数字,字符串的java类型
Template 类就是通过
template = velocityEngine.getTemplate("index.html"); 获取所用的模板,这里有个地方,如果你的模板不在同一个文件夹了,需要修改
velocityEngine的模板存放文件属性,如:
Properties properties = new Properties();
path = request.getRealPath("/");
properties.setProperty(Velocity.FILE_RESOURCE_LOADER_PATH, path);
velocityEngine.init(properties);
然后通过template.merge(context, out)合成到out流;这里的out是writer的类或子类
然后就可以输出了